delta-Valerolactone
General
Type : Lactone
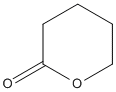
Chemical_Nomenclature : oxan-2-one
Canonical SMILES : C1CCOC(=O)C1
InChI : InChI=1S\/C5H8O2\/c6-5-3-1-2-4-7-5\/h1-4H2
InChIKey : OZJPLYNZGCXSJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, 5-Valerolactone, Oxan-2-one, 2H-Pyran-2-one, tetrahydro-
Target
Families : Epoxide_hydrolase, 6_AlphaBeta_hydrolase
References (6)
| Title : Isolation and characterization of 9-lipoxygenase and epoxide hydrolase 2 genes: Insight into lactone biosynthesis in mango fruit (Mangifera indica L.) - Deshpande_2017_Phytochemistry_138_65 |
| Author(s) : Deshpande AB , Chidley HG , Oak PS , Pujari KH , Giri AP , Gupta VS |
| Ref : Phytochemistry , 138 :65 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Deshpande_2017_Phytochemistry_138_65 |
| ESTHER : Deshpande_2017_Phytochemistry_138_65 |
| PubMedSearch : Deshpande_2017_Phytochemistry_138_65 |
| PubMedID: 28291596 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: manin-a0a1u9zcc2 |
| Title : Characterization of LipN (Rv2970c) of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis H37Rv and its Probable Role in Xenobiotic Degradation - Jadeja_2016_J.Cell.Biochem_117_390 |
| Author(s) : Jadeja D , Dogra N , Arya S , Singh G , Kaur J |
| Ref : Journal of Cellular Biochemistry , 117 :390 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Jadeja_2016_J.Cell.Biochem_117_390 |
| ESTHER : Jadeja_2016_J.Cell.Biochem_117_390 |
| PubMedSearch : Jadeja_2016_J.Cell.Biochem_117_390 |
| PubMedID: 26212120 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: myctu-Rv2970c |
| Title : Pseudomonas putida esterase contains a GGG(A)X-motif confering activity for the kinetic resolution of tertiary alcohols - Rehdorf_2012_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_93_1119 |
| Author(s) : Rehdorf J , Behrens GA , Nguyen GS , Kourist R , Bornscheuer UT |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 93 :1119 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Rehdorf_2012_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_93_1119 |
| ESTHER : Rehdorf_2012_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_93_1119 |
| PubMedSearch : Rehdorf_2012_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_93_1119 |
| PubMedID: 21779846 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9psed-a0a077fe85 |
| Title : MmPPOX inhibits Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipolytic enzymes belonging to the hormone-sensitive lipase family and alters mycobacterial growth - Delorme_2012_PLoS.One_7_e46493 |
| Author(s) : Delorme V , Diomande SV , Dedieu L , Cavalier JF , Carriere F , Kremer L , Leclaire J , Fotiadu F , Canaan S |
| Ref : PLoS ONE , 7 :e46493 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Delorme_2012_PLoS.One_7_e46493 |
| ESTHER : Delorme_2012_PLoS.One_7_e46493 |
| PubMedSearch : Delorme_2012_PLoS.One_7_e46493 |
| PubMedID: 23029536 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: myctu-Rv2970c |
| Title : Biocatalytic Synthesis of Poly(delta-Valerolactone) Using a Thermophilic Esterase from Archaeoglobus fulgidus as Catalyst - Cao_2012_Int.J.Mol.Sci_13_12232 |
| Author(s) : Cao H , Han H , Li G , Yang J , Zhang L , Yang Y , Fang X , Li Q |
| Ref : Int J Mol Sci , 13 :12232 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Cao_2012_Int.J.Mol.Sci_13_12232 |
| ESTHER : Cao_2012_Int.J.Mol.Sci_13_12232 |
| PubMedSearch : Cao_2012_Int.J.Mol.Sci_13_12232 |
| PubMedID: 23202895 |
| Title : Screening, nucleotide sequence, and biochemical characterization of an esterase from Pseudomonas fluorescens with high activity towards lactones - Khalameyzer_1999_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_65_477 |
| Author(s) : Khalameyzer V , Fischer I , Bornscheuer UT , Altenbuchner J |
| Ref : Applied Environmental Microbiology , 65 :477 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Khalameyzer_1999_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_65_477 |
| ESTHER : Khalameyzer_1999_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_65_477 |
| PubMedSearch : Khalameyzer_1999_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_65_477 |
| PubMedID: 9925571 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psefl-estF1 |