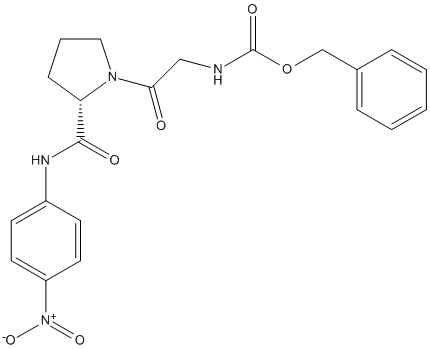
Z-Gly-Pro-pNA
General
Type : Benzyloxycarbonyl || Peptide || Pyrrolidine || Carboxamide || p-nitroaniline || pNP || Chromogen
Chemical_Nomenclature : benzyl N-[2-[(2S)-2-[(4-nitrophenyl)carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-2-oxoethyl]carbamate
Canonical SMILES : C1CC(N(C1)C(=O)CNC(=O)OCC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)[N+](=O)[O-]
InChI : InChI=1S\/C21H22N4O6\/c26-19(13-22-21(28)31-14-15-5-2-1-3-6-15)24-12-4-7-18(24)20(27)23-16-8-10-17(11-9-16)25(29)30\/h1-3,5-6,8-11,18H,4,7,12-14H2,(H,22,28)(H,23,27)\/t18-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : UTXSFKPOIVELPQ-SFHVURJKSA-N
Other name(s) : Z-Gly-Pro-4-nitroanilide, N-Cbz-Glycyl-proline 4-nitroanilide, Cbz-Gly-Pro-pNA
Target
Families : S9N_PPCE_Peptidase_S9
References (8)
| Title : The structure and molecular dynamics of prolyl oligopeptidase from Microbulbifer arenaceous provide insights into catalytic and regulatory mechanisms - Huang_2022_Acta.Crystallogr.D.Struct.Biol_78_735 |
| Author(s) : Huang, P , Lv A , Yan Q , Jiang Z , Yang S. |
| Ref : Acta Crystallographica D Biol Crystallogr , 78 :735 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Huang_2022_Acta.Crystallogr.D.Struct.Biol_78_735 |
| ESTHER : Huang_2022_Acta.Crystallogr.D.Struct.Biol_78_735 |
| PubMedSearch : Huang_2022_Acta.Crystallogr.D.Struct.Biol_78_735 |
| PubMedID: 35647921 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9gamm-MaPOP |
| Title : Alkaloids from Narcissus poeticus cv. Pink Parasol of various structural types and their biological activity - Safratova_2018_Arch.Pharm.Res_41_208 |
| Author(s) : Safratova M , Hostalkova A , Hulcova D , Breiterova K , Hrabcova V , Machado M , Fontinha D , Prudencio M , Kunes J , Chlebek J , Jun D , Hrabinova M , Novakova L , Havelek R , Seifrtova M , Opletal L , Cahlikova L |
| Ref : Arch Pharm Res , 41 :208 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Safratova_2018_Arch.Pharm.Res_41_208 |
| ESTHER : Safratova_2018_Arch.Pharm.Res_41_208 |
| PubMedSearch : Safratova_2018_Arch.Pharm.Res_41_208 |
| PubMedID: 29243039 |
| Title : Alkaloids from Peumus boldus and their acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase and prolyl oligopeptidase inhibition activity - Host'alkova_2015_Nat.Prod.Commun_10_577 |
| Author(s) : Host'alkova A , Opletal L , Kunes J , Novak Z , Hrabinova M , Chlebek J , Cegan L , Cahlikova L |
| Ref : Nat Prod Commun , 10 :577 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Host'alkova_2015_Nat.Prod.Commun_10_577 |
| ESTHER : Host'alkova_2015_Nat.Prod.Commun_10_577 |
| PubMedSearch : Host'alkova_2015_Nat.Prod.Commun_10_577 |
| PubMedID: 25973480 |
| Title : Cloning, Expression, Sequence Analysis and Homology Modeling of the Prolyl Endoprotease from Eurygaster integriceps Puton - Yandamuri_2014_Insects_5_762 |
| Author(s) : Yandamuri RC , Gautam R , Darkoh C , Dareddy V , El-Bouhssini M , Clack BA |
| Ref : Insects , 5 :762 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Yandamuri_2014_Insects_5_762 |
| ESTHER : Yandamuri_2014_Insects_5_762 |
| PubMedSearch : Yandamuri_2014_Insects_5_762 |
| PubMedID: 26462938 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9hemi-e1u339 |
| Title : Alkaloids from Chlidanthus fragrans and their acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase and prolyl oligopeptidase activities - Cahlikova_2013_Nat.Prod.Commun_8_1541 |
| Author(s) : Cahlikova L , Hrabinova M , Kulhankova A , Benesova N , Chlebek J , Jun D , Novak Z , Macakova K , Kunes J , Kuca K , Opletal L |
| Ref : Nat Prod Commun , 8 :1541 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Cahlikova_2013_Nat.Prod.Commun_8_1541 |
| ESTHER : Cahlikova_2013_Nat.Prod.Commun_8_1541 |
| PubMedSearch : Cahlikova_2013_Nat.Prod.Commun_8_1541 |
| PubMedID: 24427936 |
| Title : Processing of the phalloidin proprotein by prolyl oligopeptidase from the mushroom Conocybe albipes - Luo_2009_J.Biol.Chem_284_18070 |
| Author(s) : Luo H , Hallen-Adams HE , Walton JD |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 284 :18070 , 2009 |
| Abstract : Luo_2009_J.Biol.Chem_284_18070 |
| ESTHER : Luo_2009_J.Biol.Chem_284_18070 |
| PubMedSearch : Luo_2009_J.Biol.Chem_284_18070 |
| PubMedID: 19389704 |
| Title : Extracellular prolyl endoprotease from Aspergillus niger and its use in the debittering of protein hydrolysates - Edens_2005_J.Agric.Food.Chem_53_7950 |
| Author(s) : Edens L , Dekker P , van der Hoeven R , Deen F , de Roos A , Floris R |
| Ref : Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry , 53 :7950 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Edens_2005_J.Agric.Food.Chem_53_7950 |
| ESTHER : Edens_2005_J.Agric.Food.Chem_53_7950 |
| PubMedSearch : Edens_2005_J.Agric.Food.Chem_53_7950 |
| PubMedID: 16190655 |
| Title : Overexpression and characterization of a prolyl endopeptidase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus - Harwood_1997_J.Bacteriol_179_3613 |
| Author(s) : Harwood VJ , Denson JD , Robinson-Bidle KA , Schreier HJ |
| Ref : Journal of Bacteriology , 179 :3613 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Harwood_1997_J.Bacteriol_179_3613 |
| ESTHER : Harwood_1997_J.Bacteriol_179_3613 |
| PubMedSearch : Harwood_1997_J.Bacteriol_179_3613 |
| PubMedID: 9171407 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: pyrfu-Q51714 |