Resorufin-butyrate
General
Type : Butyrate || Phenoxazin || Derivative of Resorufin || Fluorescent Probe
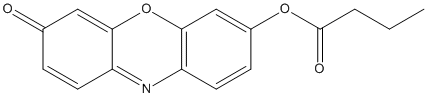
Chemical_Nomenclature : (7-oxophenoxazin-3-yl) butanoate
Canonical SMILES : CCCC(=O)OC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C3C=CC(=O)C=C3O2
InChI : InChI=1S\/C16H13NO4\/c1-2-3-16(19)20-11-5-7-13-15(9-11)21-14-8-10(18)4-6-12(14)17-13\/h4-9H,2-3H2,1H3
InChIKey : RGJTZDRUTUWWTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Resorufin butyrate, butyl resorufin, AC1NMEKF, SCHEMBL12189748, 83637_FLUKA
Target
References (5)
| Title : Monoacylglycerol Lipase Inhibition in Human and Rodent Systems Supports Clinical Evaluation of Endocannabinoid Modulators - Clapper_2018_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_367_494 |
| Author(s) : Clapper JR , Henry CL , Niphakis MJ , Knize AM , Coppola AR , Simon GM , Ngo N , Herbst RA , Herbst DM , Reed AW , Cisar JS , Weber OD , Viader A , Alexander JP , Cunningham ML , Jones TK , Fraser IP , Grice CA , Ezekowitz RAB , O'Neill GP , Blankman JL |
| Ref : Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics , 367 :494 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Clapper_2018_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_367_494 |
| ESTHER : Clapper_2018_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_367_494 |
| PubMedSearch : Clapper_2018_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_367_494 |
| PubMedID: 30305428 |
| Title : Carboxylesterase converts Amplex red to resorufin: Implications for mitochondrial H2O2 release assays - Miwa_2016_Free.Radic.Biol.Med_90_173 |
| Author(s) : Miwa S , Treumann A , Bell A , Vistoli G , Nelson G , Hay S , von Zglinicki T |
| Ref : Free Radic Biol Med , 90 :173 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Miwa_2016_Free.Radic.Biol.Med_90_173 |
| ESTHER : Miwa_2016_Free.Radic.Biol.Med_90_173 |
| PubMedSearch : Miwa_2016_Free.Radic.Biol.Med_90_173 |
| PubMedID: 26577176 |
| Title : Inactivation of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85 complex by covalent, allosteric inhibitors - Favrot_2014_J.Biol.Chem_289_25031 |
| Author(s) : Favrot L , Lajiness DH , Ronning DR |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 289 :25031 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Favrot_2014_J.Biol.Chem_289_25031 |
| ESTHER : Favrot_2014_J.Biol.Chem_289_25031 |
| PubMedSearch : Favrot_2014_J.Biol.Chem_289_25031 |
| PubMedID: 25028518 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: myctu-a85c |
| Title : Directed evolution of an esterase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Random mutagenesis by error-prone PCR or a mutator strain and identification of mutants showing enhanced enantioselectivity by a resorufin-based fluorescence assay - Henke_1999_Biol.Chem_380_1029 |
| Author(s) : Henke E , Bornscheuer UT |
| Ref : Biol Chem , 380 :1029 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Henke_1999_Biol.Chem_380_1029 |
| ESTHER : Henke_1999_Biol.Chem_380_1029 |
| PubMedSearch : Henke_1999_Biol.Chem_380_1029 |
| PubMedID: 10494857 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psefl-este |
| Title : Resorufin butyrate and indoxyl acetate as fluorogenic substrates for cholinesterase - |
| Author(s) : Guilbault GG , Kramer DN |
| Ref : Analytical Chemistry , 37 :120 , 1965 |
| PubMedID: |