N-Formylmaleamic-acid
General
Type :
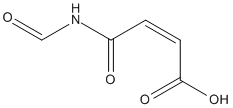
Chemical_Nomenclature : (Z)-4-formamido-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid
Canonical SMILES : C(=CC(=O)O)C(=O)NC=O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C5H5NO4\/c7-3-6-4(8)1-2-5(9)10\/h1-3H,(H,9,10)(H,6,7,8)\/b2-1-
InChIKey : HSKSAKBZUITULZ-UPHRSURJSA-N
Other name(s) : N-formylmaleamic acid, (2Z)-4-formamido-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid, (Z)-4-formamido-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid, CHEBI:59930, LMFA08020194, ZINC100084064
MW : 143.09
Formula : C5H5NO4
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
Families : NFM-deformylase
References (2)
| Title : Structural insights into the specific recognition of N-heterocycle biodenitrogenation-derived substrates by microbial amide hydrolases - Wu_2014_Mol.Microbiol_91_1009 |
| Author(s) : Wu G , Chen D , Tang H , Ren Y , Chen Q , Lv Y , Zhang Z , Zhao YL , Yao Y , Xu P |
| Ref : Molecular Microbiology , 91 :1009 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Wu_2014_Mol.Microbiol_91_1009 |
| ESTHER : Wu_2014_Mol.Microbiol_91_1009 |
| PubMedSearch : Wu_2014_Mol.Microbiol_91_1009 |
| PubMedID: 24397579 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psep6-f8g0m2 |
| Title : Deciphering the genetic determinants for aerobic nicotinic acid degradation: the nic cluster from Pseudomonas putida KT2440 - Jimenez_2008_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_105_11329 |
| Author(s) : Jimenez JI , Canales A , Jimenez-Barbero J , Ginalski K , Rychlewski L , Garcia JL , Diaz E |
| Ref : Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A , 105 :11329 , 2008 |
| Abstract : Jimenez_2008_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_105_11329 |
| ESTHER : Jimenez_2008_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_105_11329 |
| PubMedSearch : Jimenez_2008_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_105_11329 |
| PubMedID: 18678916 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psepu-PP3943 |