Lindane
General
Type : Insecticide || Organochlorine
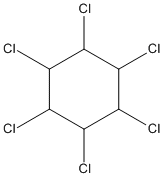
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane
Canonical SMILES : C1(C(C(C(C(C1Cl)Cl)Cl)Cl)Cl)Cl
InChI : InChI=1S\/C6H6Cl6\/c7-1-2(8)4(10)6(12)5(11)3(1)9\/h1-6H
InChIKey : JLYXXMFPNIAWKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : beta-HCH, gamma-HCH, gamma-BHC, Hexachlorane, Hexachlorocyclohexane, 1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexachlorocyclohexane, alpha-HCH, Benzene hexachloride, CHEMBL389022, CHEMBL1200921, CHEMBL1714528, CHEMBL1874247, CHEMBL2272381, SCHEMBL25895, SCHEMBL25896, SCHEMBL75689, CHEBI:24536, CHEBI:28428, CHEBI:32888, CHEBI:39095, CHEBI:39096
MW : 290.81
Formula : C6H6Cl6
CAS_number : 319-85-7 || 608-73-1 || 58-89-9
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
References (41)
| Title : Protocol for in-vitro purification and refolding of hexachlorocyclohexane degrading enzyme haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from inclusion bodies - Kaur_2021_Enzyme.Microb.Technol_146_109760 |
| Author(s) : Kaur J , Singh A , Panda AK , Lal R |
| Ref : Enzyme Microb Technol , 146 :109760 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Kaur_2021_Enzyme.Microb.Technol_146_109760 |
| ESTHER : Kaur_2021_Enzyme.Microb.Technol_146_109760 |
| PubMedSearch : Kaur_2021_Enzyme.Microb.Technol_146_109760 |
| PubMedID: 33812559 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Bacterial diversity and real-time PCR based assessment of linA and linB gene distribution at hexachlorocyclohexane contaminated sites - Lal_2015_J.Basic.Microbiol_55_363 |
| Author(s) : Lal D , Jindal S , Kumari H , Jit S , Nigam A , Sharma P , Kumari K , Lal R |
| Ref : J Basic Microbiol , 55 :363 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Lal_2015_J.Basic.Microbiol_55_363 |
| ESTHER : Lal_2015_J.Basic.Microbiol_55_363 |
| PubMedSearch : Lal_2015_J.Basic.Microbiol_55_363 |
| PubMedID: 24002962 |
| Title : Insights into Ongoing Evolution of the Hexachlorocyclohexane Catabolic Pathway from Comparative Genomics of Ten Sphingomonadaceae Strains - Pearce_2015_G3.(Bethesda)_5_1081 |
| Author(s) : Pearce SL , Oakeshott JG , Pandey G |
| Ref : G3 (Bethesda) , 5 :1081 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Pearce_2015_G3.(Bethesda)_5_1081 |
| ESTHER : Pearce_2015_G3.(Bethesda)_5_1081 |
| PubMedSearch : Pearce_2015_G3.(Bethesda)_5_1081 |
| PubMedID: 25850427 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-a0a0j7y7k8 , 9sphn-a0a0j7xep7 , 9sphn-a0a0j8aaf5 |
| Title : Functional screening of enzymes and bacteria for the dechlorination of hexachlorocyclohexane by a high-throughput colorimetric assay - Sharma_2014_Biodegradation_25_179 |
| Author(s) : Sharma P , Jindal S , Bala K , Kumari K , Niharika N , Kaur J , Pandey G , Pandey R , Russell RJ , Oakeshott JG , Lal R |
| Ref : Biodegradation , 25 :179 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Sharma_2014_Biodegradation_25_179 |
| ESTHER : Sharma_2014_Biodegradation_25_179 |
| PubMedSearch : Sharma_2014_Biodegradation_25_179 |
| PubMedID: 23740574 |
| Title : A computational study of the dechlorination of beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (beta-HCH) catalyzed by the haloalkane dehalogenase LinB - Manna_2014_Arch.Biochem.Biophys_562_43 |
| Author(s) : Manna RN , Dybala-Defratyka A |
| Ref : Archives of Biochemistry & Biophysics , 562 :43 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Manna_2014_Arch.Biochem.Biophys_562_43 |
| ESTHER : Manna_2014_Arch.Biochem.Biophys_562_43 |
| PubMedSearch : Manna_2014_Arch.Biochem.Biophys_562_43 |
| PubMedID: 25102308 |
| Title : Stepwise enhancement of catalytic performance of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB towards beta-hexachlorocyclohexane - Moriuchi_2014_AMB.Express_4_72 |
| Author(s) : Moriuchi R , Tanaka H , Nikawadori Y , Ishitsuka M , Ito M , Ohtsubo Y , Tsuda M , Damborsky J , Prokop Z , Nagata Y |
| Ref : AMB Express , 4 :72 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Moriuchi_2014_AMB.Express_4_72 |
| ESTHER : Moriuchi_2014_AMB.Express_4_72 |
| PubMedSearch : Moriuchi_2014_AMB.Express_4_72 |
| PubMedID: 25401073 |
| Title : Kinetic and Sequence-Structure-Function Analysis of LinB Enzyme Variants with beta- and delta-Hexachlorocyclohexane - Pandey_2014_PLoS.One_9_e103632 |
| Author(s) : Pandey R , Lucent D , Kumari K , Sharma P , Lal R , Oakeshott JG , Pandey G |
| Ref : PLoS ONE , 9 :e103632 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Pandey_2014_PLoS.One_9_e103632 |
| ESTHER : Pandey_2014_PLoS.One_9_e103632 |
| PubMedSearch : Pandey_2014_PLoS.One_9_e103632 |
| PubMedID: 25076214 |
| Title : Complete Genome Sequence of Pseudomonas sp. Strain TKP, Isolated from a gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane-Degrading Mixed Culture - Ohtsubo_2014_Genome.Announc_2_e01241 |
| Author(s) : Ohtsubo Y , Kishida K , Sato T , Tabata M , Kawasumi T , Ogura Y , Hayashi T , Tsuda M , Nagata Y |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 2 : , 2014 |
| Abstract : Ohtsubo_2014_Genome.Announc_2_e01241 |
| ESTHER : Ohtsubo_2014_Genome.Announc_2_e01241 |
| PubMedSearch : Ohtsubo_2014_Genome.Announc_2_e01241 |
| PubMedID: 24482516 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psefl-e2xn15 , psefs-c3k632 , psefs-laaa , psefs-c3k813 , psefl-e2xkc8 , 9psed-v9qxq1 , 9psed-v9qr47 |
| Title : Complete Genome Sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTB-1, Isolated from a Microbial Community Enriched by the Technical Formulation of Hexachlorocyclohexane - Ohtsubo_2014_Genome.Announc_2_e01130 |
| Author(s) : Ohtsubo Y , Sato T , Kishida K , Tabata M , Ogura Y , Hayashi T , Tsuda M , Nagata Y |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 2 : , 2014 |
| Abstract : Ohtsubo_2014_Genome.Announc_2_e01130 |
| ESTHER : Ohtsubo_2014_Genome.Announc_2_e01130 |
| PubMedSearch : Ohtsubo_2014_Genome.Announc_2_e01130 |
| PubMedID: 24459257 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: pseae-PA3695 , pseae-PA5080 , pseae-q9i252 |
| Title : Draft Genome Sequence of Sphingobium sp. Strain HDIPO4, an Avid Degrader of Hexachlorocyclohexane - Mukherjee_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00749 |
| Author(s) : Mukherjee U , Kumar R , Mahato NK , Khurana JP , Lal R |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 1 : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Mukherjee_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00749 |
| ESTHER : Mukherjee_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00749 |
| PubMedSearch : Mukherjee_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00749 |
| PubMedID: 24051321 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphju-d4z7y1 , sphju-d4z363 , sphpi-linb |
| Title : Genome Sequence of Novosphingobium lindaniclasticum LE124T, Isolated from a Hexachlorocyclohexane Dumpsite - Saxena_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00715 |
| Author(s) : Saxena A , Nayyar N , Sangwan N , Kumari R , Khurana JP , Lal R |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 1 : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Saxena_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00715 |
| ESTHER : Saxena_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00715 |
| PubMedSearch : Saxena_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00715 |
| PubMedID: 24029761 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-t0hqb1 , 9sphn-t0hmn5 , 9sphn-t0iya6 , 9sphn-t0gy64 , 9sphn-t0hhu1 , 9sphn-t0i5p8 , 9sphn-t0hp61 |
| Title : Draft Genome Sequence of Sphingobium chinhatense Strain IP26T, Isolated from a Hexachlorocyclohexane Dumpsite - Niharika_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00680 |
| Author(s) : Niharika N , Sangwan N , Ahmad S , Singh P , Khurana JP , Lal R |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 1 : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Niharika_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00680 |
| ESTHER : Niharika_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00680 |
| PubMedSearch : Niharika_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00680 |
| PubMedID: 23990581 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphju-d4z7y1 , sphju-d4z363 |
| Title : Complete Genome Sequence of the gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane-Degrading Bacterium Sphingomonas sp. Strain MM-1 - Tabata_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00247 |
| Author(s) : Tabata M , Ohtsubo Y , Ohhata S , Tsuda M , Nagata Y |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 1 : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Tabata_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00247 |
| ESTHER : Tabata_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00247 |
| PubMedSearch : Tabata_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00247 |
| PubMedID: 23682148 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-m4s0a2 , 9sphn-m4sjq0 , 9sphn-m4s4n0 , 9sphn-m4rwk9 , 9sphn-m4s1q7 |
| Title : Draft Genome Sequence of Sphingobium ummariense Strain RL-3, a Hexachlorocyclohexane-Degrading Bacterium - Kohli_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00956 |
| Author(s) : Kohli P , Dua A , Sangwan N , Oldach P , Khurana JP , Lal R |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 1 : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Kohli_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00956 |
| ESTHER : Kohli_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00956 |
| PubMedSearch : Kohli_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00956 |
| PubMedID: 24233594 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb , 9sphn-t0kby4 , 9sphn-t0kfu7 , sphpi-a0a197bwy5 , 9sphn-t0jaw2 |
| Title : Draft Genome Sequence of Sphingobium lactosutens Strain DS20T, Isolated from a Hexachlorocyclohexane Dumpsite - Kumar_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00753 |
| Author(s) : Kumar R , Dwivedi V , Negi V , Khurana JP , Lal R |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 1 : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Kumar_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00753 |
| ESTHER : Kumar_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00753 |
| PubMedSearch : Kumar_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00753 |
| PubMedID: 24051323 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-q1n750 , 9sphn-t0hf11 , 9sphn-t0him9 , 9sphn-t0i493 |
| Title : Draft Genome Sequence of a Hexachlorocyclohexane-Degrading Bacterium, Sphingobium baderi Strain LL03T - Kaur_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00751 |
| Author(s) : Kaur J , Verma H , Tripathi C , Khurana JP , Lal R |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 1 : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Kaur_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00751 |
| ESTHER : Kaur_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00751 |
| PubMedSearch : Kaur_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00751 |
| PubMedID: 24051322 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-t0g9p6 , 9sphn-t0g1r2 |
| Title : Draft Genome Sequence of Sphingobium quisquiliarum Strain P25T, a Novel Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-Degrading Bacterium Isolated from an HCH Dumpsite - Kumar_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00717 |
| Author(s) : Kumar Singh A , Sangwan N , Sharma A , Gupta V , Khurana JP , Lal R |
| Ref : Genome Announc , 1 : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Kumar_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00717 |
| ESTHER : Kumar_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00717 |
| PubMedSearch : Kumar_2013_Genome.Announc_1_e00717 |
| PubMedID: 24029763 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9sphn-t0gfp3 , 9sphn-t0gjp1 , 9sphn-t0iek2 |
| Title : Enzymes involved in the biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane: a mini review - Camacho-Perez_2012_J.Environ.Manage_95 Suppl_S306 |
| Author(s) : Camacho-Perez B , Rios-Leal E , Rinderknecht-Seijas N , Poggi-Varaldo HM |
| Ref : J Environ Manage , 95 Suppl :S306 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Camacho-Perez_2012_J.Environ.Manage_95 Suppl_S306 |
| ESTHER : Camacho-Perez_2012_J.Environ.Manage_95 Suppl_S306 |
| PubMedSearch : Camacho-Perez_2012_J.Environ.Manage_95 Suppl_S306 |
| PubMedID: 21992990 |
| Title : Genome sequence of Sphingobium indicum B90A, a hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium - Anand_2012_J.Bacteriol_194_4471 |
| Author(s) : Anand S , Sangwan N , Lata P , Kaur J , Dua A , Singh AK , Verma M , Khurana JP , Khurana P , Mathur S , Lal R |
| Ref : Journal of Bacteriology , 194 :4471 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Anand_2012_J.Bacteriol_194_4471 |
| ESTHER : Anand_2012_J.Bacteriol_194_4471 |
| PubMedSearch : Anand_2012_J.Bacteriol_194_4471 |
| PubMedID: 22843598 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphju-d4z363 , sphpi-linb |
| Title : The lin genes for gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in Sphingomonas sp. MM-1 proved to be dispersed across multiple plasmids - Tabata_2011_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_75_466 |
| Author(s) : Tabata M , Endo R , Ito M , Ohtsubo Y , Kumar A , Tsuda M , Nagata Y |
| Ref : Biosci Biotechnol Biochem , 75 :466 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Tabata_2011_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_75_466 |
| ESTHER : Tabata_2011_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_75_466 |
| PubMedSearch : Tabata_2011_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_75_466 |
| PubMedID: 21389627 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Complete genome sequence of the representative gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium Sphingobium japonicum UT26 - Nagata_2010_J.Bacteriol_192_5852 |
| Author(s) : Nagata Y , Ohtsubo Y , Endo R , Ichikawa N , Ankai A , Oguchi A , Fukui S , Fujita N , Tsuda M |
| Ref : Journal of Bacteriology , 192 :5852 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Nagata_2010_J.Bacteriol_192_5852 |
| ESTHER : Nagata_2010_J.Bacteriol_192_5852 |
| PubMedSearch : Nagata_2010_J.Bacteriol_192_5852 |
| PubMedID: 20817768 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psepa-q6vpf3 , sphju-d4z1p3 , sphju-d4z3u6 , sphpi-linb , sphju-d4yyy8 |
| Title : Genetic diversity of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading sphingomonads isolated from a single experimental field - Yamamoto_2009_Lett.Appl.Microbiol_49_472 |
| Author(s) : Yamamoto S , Otsuka S , Murakami Y , Nishiyama M , Senoo K |
| Ref : Lett Appl Microbiol , 49 :472 , 2009 |
| Abstract : Yamamoto_2009_Lett.Appl.Microbiol_49_472 |
| ESTHER : Yamamoto_2009_Lett.Appl.Microbiol_49_472 |
| PubMedSearch : Yamamoto_2009_Lett.Appl.Microbiol_49_472 |
| PubMedID: 19674290 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Insertion sequence-based cassette PCR: cultivation-independent isolation of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading genes from soil DNA - Fuchu_2008_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_79_627 |
| Author(s) : Fuchu G , Ohtsubo Y , Ito M , Miyazaki R , Ono A , Nagata Y , Tsuda M |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 79 :627 , 2008 |
| Abstract : Fuchu_2008_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_79_627 |
| ESTHER : Fuchu_2008_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_79_627 |
| PubMedSearch : Fuchu_2008_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_79_627 |
| PubMedID: 18425509 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psepa-q6vpf3 , sphpi-linb |
| Title : Isolation of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas sp. by dehalogenase assay and characterization of genes involved in gamma-HCH degradation - Manickam_2008_J.Appl.Microbiol_104_952 |
| Author(s) : Manickam N , Reddy MK , Saini HS , Shanker R |
| Ref : J Appl Microbiol , 104 :952 , 2008 |
| Abstract : Manickam_2008_J.Appl.Microbiol_104_952 |
| ESTHER : Manickam_2008_J.Appl.Microbiol_104_952 |
| PubMedSearch : Manickam_2008_J.Appl.Microbiol_104_952 |
| PubMedID: 18042212 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Selective loss of lin genes from hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa ITRC-5 under different growth conditions - Singh_2007_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_76_895 |
| Author(s) : Singh AK , Chaudhary P , Macwan AS , Diwedi UN , Kumar A |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 76 :895 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Singh_2007_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_76_895 |
| ESTHER : Singh_2007_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_76_895 |
| PubMedSearch : Singh_2007_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_76_895 |
| PubMedID: 17602219 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Degradation of beta-hexachlorocyclohexane by haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-utilizing bacterium Sphingobium sp. MI1205 - Ito_2007_Arch.Microbiol_188_313 |
| Author(s) : Ito M , Prokop Z , Klvana M , Otsubo Y , Tsuda M , Damborsky J , Nagata Y |
| Ref : Arch Microbiol , 188 :313 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Ito_2007_Arch.Microbiol_188_313 |
| ESTHER : Ito_2007_Arch.Microbiol_188_313 |
| PubMedSearch : Ito_2007_Arch.Microbiol_188_313 |
| PubMedID: 17516046 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : A novel pathway for the biodegradation of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane by a Xanthomonas sp. strain ICH12 - Manickam_2007_J.Appl.Microbiol_102_1468 |
| Author(s) : Manickam N , Misra R , Mayilraj S |
| Ref : J Appl Microbiol , 102 :1468 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Manickam_2007_J.Appl.Microbiol_102_1468 |
| ESTHER : Manickam_2007_J.Appl.Microbiol_102_1468 |
| PubMedSearch : Manickam_2007_J.Appl.Microbiol_102_1468 |
| PubMedID: 17578411 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Analysis of the role of LinA and LinB in biodegradation of delta-hexachlorocyclohexane - Wu_2007_Environ.Microbiol_9_2331 |
| Author(s) : Wu J , Hong Q , Sun Y , Hong Y , Yan Q , Li S |
| Ref : Environ Microbiol , 9 :2331 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Wu_2007_Environ.Microbiol_9_2331 |
| ESTHER : Wu_2007_Environ.Microbiol_9_2331 |
| PubMedSearch : Wu_2007_Environ.Microbiol_9_2331 |
| PubMedID: 17686029 |
| Title : Complete nucleotide sequence of an exogenously isolated plasmid, pLB1, involved in gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation - Miyazaki_2006_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_72_6923 |
| Author(s) : Miyazaki R , Sato Y , Ito M , Ohtsubo Y , Nagata Y , Tsuda M |
| Ref : Applied Environmental Microbiology , 72 :6923 , 2006 |
| Abstract : Miyazaki_2006_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_72_6923 |
| ESTHER : Miyazaki_2006_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_72_6923 |
| PubMedSearch : Miyazaki_2006_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_72_6923 |
| PubMedID: 16963556 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Degradation of beta-Hexachlorocyclohexane by Haloalkane Dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 - Nagata_2005_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_71_2183 |
| Author(s) : Nagata Y , Prokop Z , Sato Y , Jerabek P , Kumar A , Ohtsubo Y , Tsuda M , Damborsky J |
| Ref : Applied Environmental Microbiology , 71 :2183 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Nagata_2005_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_71_2183 |
| ESTHER : Nagata_2005_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_71_2183 |
| PubMedSearch : Nagata_2005_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_71_2183 |
| PubMedID: 15812056 |
| Title : Identification and characterization of genes involved in the downstream degradation pathway of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 - Endo_2005_J.Bacteriol_187_847 |
| Author(s) : Endo R , Kamakura M , Miyauchi K , Fukuda M , Ohtsubo Y , Tsuda M , Nagata Y |
| Ref : Journal of Bacteriology , 187 :847 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Endo_2005_J.Bacteriol_187_847 |
| ESTHER : Endo_2005_J.Bacteriol_187_847 |
| PubMedSearch : Endo_2005_J.Bacteriol_187_847 |
| PubMedID: 15659662 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psepa-q6vqy9 |
| Title : Organization of lin genes and IS6100 among different strains of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas paucimobilis: evidence for horizontal gene transfer - Dogra_2004_J.Bacteriol_186_2225 |
| Author(s) : Dogra C , Raina V , Pal R , Suar M , Lal S , Gartemann KH , Holliger C , van der Meer JR , Lal R |
| Ref : Journal of Bacteriology , 186 :2225 , 2004 |
| Abstract : Dogra_2004_J.Bacteriol_186_2225 |
| ESTHER : Dogra_2004_J.Bacteriol_186_2225 |
| PubMedSearch : Dogra_2004_J.Bacteriol_186_2225 |
| PubMedID: 15060023 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: psepa-q6vpf3 , psepa-q6vpf4 , psepa-q6vqy9 , sphpi-linb |
| Title : Cloning and characterization of lin genes responsible for the degradation of Hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain B90 - Kumari_2002_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_68_6021 |
| Author(s) : Kumari R , Subudhi S , Suar M , Dhingra G , Raina V , Dogra C , Lal S , van der Meer JR , Holliger C , Lal R |
| Ref : Applied Environmental Microbiology , 68 :6021 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Kumari_2002_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_68_6021 |
| ESTHER : Kumari_2002_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_68_6021 |
| PubMedSearch : Kumari_2002_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_68_6021 |
| PubMedID: 12450824 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Construction and characterization of histidine-tagged haloalkane dehalogenase (LinB) of a new substrate class from a gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 - Nagata_1999_Protein.Expr.Purif_17_299 |
| Author(s) : Nagata Y , Hynkova K , Damborsky J , Takagi M |
| Ref : Protein Expr Purif , 17 :299 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Nagata_1999_Protein.Expr.Purif_17_299 |
| ESTHER : Nagata_1999_Protein.Expr.Purif_17_299 |
| PubMedSearch : Nagata_1999_Protein.Expr.Purif_17_299 |
| PubMedID: 10545279 |
| Title : Two different types of dehalogenases, LinA and LinB, involved in gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 are localized in the periplasmic space without molecular processing - Nagata_1999_J.Bacteriol_181_5409 |
| Author(s) : Nagata Y , Futamura A , Miyauchi K , Takagi M |
| Ref : Journal of Bacteriology , 181 :5409 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Nagata_1999_J.Bacteriol_181_5409 |
| ESTHER : Nagata_1999_J.Bacteriol_181_5409 |
| PubMedSearch : Nagata_1999_J.Bacteriol_181_5409 |
| PubMedID: 10464214 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Hexachlorocyclohexane-induced behavioural and neurochemical changes in rat - Sahoo_1999_J.Appl.Toxicol_19_13 |
| Author(s) : Sahoo A , Samanta L , Das A , Patra SK , Chainy GB |
| Ref : Journal of Applied Toxicology , 19 :13 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Sahoo_1999_J.Appl.Toxicol_19_13 |
| ESTHER : Sahoo_1999_J.Appl.Toxicol_19_13 |
| PubMedSearch : Sahoo_1999_J.Appl.Toxicol_19_13 |
| PubMedID: 9989472 |
| Title : Purification and characterization of a haloalkane dehalogenase of a new substrate class from a gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 - Nagata_1997_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_63_3707 |
| Author(s) : Nagata Y , Miyauchi K , Damborsky J , Manova K , Ansorgova A , Takagi M |
| Ref : Applied Environmental Microbiology , 63 :3707 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Nagata_1997_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_63_3707 |
| ESTHER : Nagata_1997_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_63_3707 |
| PubMedSearch : Nagata_1997_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_63_3707 |
| PubMedID: 9293022 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Isolation and characterization of a novel gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium - Thomas_1996_J.Bacteriol_178_6049 |
| Author(s) : Thomas JC , Berger F , Jacquier M , Bernillon D , Baud-Grasset F , Truffaut N , Normand P , Vogel TM , Simonet P |
| Ref : Journal of Bacteriology , 178 :6049 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Thomas_1996_J.Bacteriol_178_6049 |
| ESTHER : Thomas_1996_J.Bacteriol_178_6049 |
| PubMedSearch : Thomas_1996_J.Bacteriol_178_6049 |
| PubMedID: 8830705 |
| Title : Dermal toxicity of hexachlorocyclohexane and pirimiphos-methyl in female rats - Raizada_1994_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_36_128 |
| Author(s) : Raizada RB , Srivastava MK , Kaushal RA , Singh RP , Gupta KP , Dikshith TS |
| Ref : Vet Hum Toxicol , 36 :128 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Raizada_1994_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_36_128 |
| ESTHER : Raizada_1994_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_36_128 |
| PubMedSearch : Raizada_1994_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_36_128 |
| PubMedID: 7515208 |
| Title : Cloning and sequencing of a dehalogenase gene encoding an enzyme with hydrolase activity involved in the degradation of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane in Pseudomonas paucimobilis - Nagata_1993_J.Bacteriol_175_6403 |
| Author(s) : Nagata Y , Nariya T , Ohtomo R , Fukuda M , Yano K , Takagi M |
| Ref : Journal of Bacteriology , 175 :6403 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Nagata_1993_J.Bacteriol_175_6403 |
| ESTHER : Nagata_1993_J.Bacteriol_175_6403 |
| PubMedSearch : Nagata_1993_J.Bacteriol_175_6403 |
| PubMedID: 7691794 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphpi-linb |
| Title : Effect of the pesticides phosalone and lindane on the activity of some dipeptidases and disaccharidases in rat intestinal mucosa - Nedkova-Bratanova_1979_Enzyme_24_281 |
| Author(s) : Nedkova-Bratanova N , Ivanov E , Savov G , Michailova Z , Krusteva A , Petrova S |
| Ref : Enzyme , 24 :281 , 1979 |
| Abstract : Nedkova-Bratanova_1979_Enzyme_24_281 |
| ESTHER : Nedkova-Bratanova_1979_Enzyme_24_281 |
| PubMedSearch : Nedkova-Bratanova_1979_Enzyme_24_281 |
| PubMedID: 92405 |