HOPDA-3-Cl
General
Type : Ketone
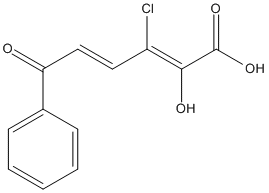
Chemical_Nomenclature : (2Z,4E)-3-chloro-2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoic acid
Canonical SMILES : C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)C=CC(=C(C(=O)O)O)Cl
InChI : InChI=1S\/C12H9ClO4\/c13-9(11(15)12(16)17)6-7-10(14)8-4-2-1-3-5-8\/h1-7,15H,(H,16,17)\/b7-6+,11-9-
InChIKey : IBJDCVXDXGFGIO-FKTQTOOFSA-N
Other name(s) : (2z,4e)-3-Chloro-2-Hydroxy-6-Oxo-6-Phenylhexa-2,4-Dienoic Acid, C1E, DB07516
MW : 252.65
Formula : C12H9ClO4
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
Families : Carbon-carbon_bond_hydrolase
References (2)
| Title : The Lid Domain of the MCP Hydrolase DxnB2 Contributes to the Reactivity toward Recalcitrant PCB Metabolites - Ruzzini_2013_Biochemistry_52_5685 |
| Author(s) : Ruzzini AC , Bhowmik S , Yam KC , Ghosh S , Bolin JT , Eltis LD |
| Ref : Biochemistry , 52 :5685 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Ruzzini_2013_Biochemistry_52_5685 |
| ESTHER : Ruzzini_2013_Biochemistry_52_5685 |
| PubMedSearch : Ruzzini_2013_Biochemistry_52_5685 |
| PubMedID: 23879719 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: sphww-a5j2a5 |
| Title : The molecular basis for inhibition of BphD, a C-C bond hydrolase involved in polychlorinated biphenyls degradation: large 3-substituents prevent tautomerization - Bhowmik_2007_J.Biol.Chem_282_36377 |
| Author(s) : Bhowmik S , Horsman GP , Bolin JT , Eltis LD |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 282 :36377 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Bhowmik_2007_J.Biol.Chem_282_36377 |
| ESTHER : Bhowmik_2007_J.Biol.Chem_282_36377 |
| PubMedSearch : Bhowmik_2007_J.Biol.Chem_282_36377 |
| PubMedID: 17932031 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: burxl-bphD |