Fluoroacetate
General
Type : Haloacetate || Acetate
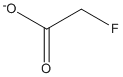
Chemical_Nomenclature : 2-fluoroacetate
Canonical SMILES : C(C(=O)[O-])F
InChI : InChI=1S\/C2H3FO2\/c3-1-2(4)5\/h1H2,(H,4,5)\/p-1
InChIKey : QEWYKACRFQMRMB-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Other name(s) : FCH2CO2 anion, 2-fluoroacetate, Cymoric acid, Alpha-fluoroacetic acid, Monofluoroacetate, MFA
Target
Families : Haloacetate_dehalogenase
References (5)
| Title : Time-resolved crystallography reveals allosteric communication aligned with molecular breathing - Mehrabi_2019_Science_365_1167 |
| Author(s) : Mehrabi P , Schulz EC , Dsouza R , Muller-Werkmeister HM , Tellkamp F , Miller RJD , Pai EF |
| Ref : Science , 365 :1167 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Mehrabi_2019_Science_365_1167 |
| ESTHER : Mehrabi_2019_Science_365_1167 |
| PubMedSearch : Mehrabi_2019_Science_365_1167 |
| PubMedID: 31515393 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: rhopa-q6nam1 |
| Title : Substrate-Based Allosteric Regulation of a Homodimeric Enzyme - Mehrabi_2019_J.Am.Chem.Soc_141_11540 |
| Author(s) : Mehrabi P , Di Pietrantonio C , Kim TH , Sljoka A , Taverner K , Ing C , Kruglyak N , Pomes R , Pai EF , Prosser RS |
| Ref : Journal of the American Chemical Society , 141 :11540 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Mehrabi_2019_J.Am.Chem.Soc_141_11540 |
| ESTHER : Mehrabi_2019_J.Am.Chem.Soc_141_11540 |
| PubMedSearch : Mehrabi_2019_J.Am.Chem.Soc_141_11540 |
| PubMedID: 31188575 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: rhopa-q6nam1 |
| Title : The hit-and-return system enables efficient time-resolved serial synchrotron crystallography - Schulz_2018_Nat.Methods_15_901 |
| Author(s) : Schulz EC , Mehrabi P , Muller-Werkmeister HM , Tellkamp F , Jha A , Stuart W , Persch E , De Gasparo R , Diederich F , Pai EF , Miller RJD |
| Ref : Nat Methods , 15 :901 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Schulz_2018_Nat.Methods_15_901 |
| ESTHER : Schulz_2018_Nat.Methods_15_901 |
| PubMedSearch : Schulz_2018_Nat.Methods_15_901 |
| PubMedID: 30377366 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: rhopa-q6nam1 |
| Title : The role of dimer asymmetry and protomer dynamics in enzyme catalysis - Kim_2017_Science_355_ |
| Author(s) : Kim TH , Mehrabi P , Ren Z , Sljoka A , Ing C , Bezginov A , Ye L , Pomes R , Prosser RS , Pai EF |
| Ref : Science , 355 : , 2017 |
| Abstract : Kim_2017_Science_355_ |
| ESTHER : Kim_2017_Science_355_ |
| PubMedSearch : Kim_2017_Science_355_ |
| PubMedID: 28104837 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: rhopa-q6nam1 |
| Title : The AEROPATH project targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa: crystallographic studies for assessment of potential targets in early-stage drug discovery. - Moynie_2013_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_69_25 |
| Author(s) : Moynie L , Schnell R , McMahon SA , Sandalova T , Boulkerou WA , Schmidberger JW , Alphey M , Cukier C , Duthie F , Kopec J , Liu H , Jacewicz A , Hunter WN , Naismith JH , Schneider G |
| Ref : Acta Crystallographica Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun , 69 :25 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Moynie_2013_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_69_25 |
| ESTHER : Moynie_2013_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_69_25 |
| PubMedSearch : Moynie_2013_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_69_25 |
| PubMedID: 23295481 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: pseae-PA2086 |