Epoxyoleic-acid
General
Type : Epoxide || Fatty acid
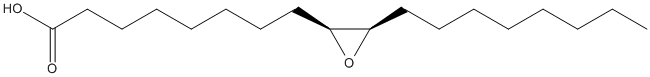
Chemical_Nomenclature : 8-[(2S,3R)-3-octyloxiran-2-yl]octanoic acid
Canonical SMILES : CCCCCCCCC1C(O1)CCCCCCCC(=O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C18H34O3\/c1-2-3-4-5-7-10-13-16-17(21-16)14-11-8-6-9-12-15-18(19)20\/h16-17H,2-15H2,1H3,(H,19,20)\/t16-,17+\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : IMYZYCNQZDBZBQ-SJORKVTESA-N
Other name(s) : Epoxyoleic acid, Cis-DL-9,10-Epoxystearic acid, Octadecanoic acid, 9,10-epoxy-, cis-, Rac cis-9,10-Epoxystearic Acid, 9S,10R-epoxy-stearic acid, Oxiraneoctanoic acid, 3-octyl-, cis-, 9,10-cis-epoxystearic acid
Target
Families : Epoxide_hydrolase
References (3)
| Title : Impact of the epoxide hydrolase EphD on the metabolism of mycolic acids in mycobacteria - Madacki_2018_J.Biol.Chem_293_5172 |
| Author(s) : Madacki J , Laval F , Grzegorzewicz A , Lemassu A , Zahorszka M , Arand M , McNeil M , Daffe M , Jackson M , Laneelle MA , Kordulakova J |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 293 :5172 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Madacki_2018_J.Biol.Chem_293_5172 |
| ESTHER : Madacki_2018_J.Biol.Chem_293_5172 |
| PubMedSearch : Madacki_2018_J.Biol.Chem_293_5172 |
| PubMedID: 29472294 |
| Title : Arabidopsis thaliana EPOXIDE HYDROLASE1 (AtEH1) is a cytosolic epoxide hydrolase involved in the synthesis of poly-hydroxylated cutin monomers - Pineau_2017_New.Phytol_215_173 |
| Author(s) : Pineau E , Xu L , Renault H , Trolet A , Navrot N , Ullmann P , Legeret B , Verdier G , Beisson F , Pinot F |
| Ref : New Phytol , 215 :173 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Pineau_2017_New.Phytol_215_173 |
| ESTHER : Pineau_2017_New.Phytol_215_173 |
| PubMedSearch : Pineau_2017_New.Phytol_215_173 |
| PubMedID: 28497532 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: arath-At2g26740 , arath-At2g26750 , arath-dl4016c.1 , arath-At3g05600 , arath-At3g51000 , arath-T14P8.15 |
| Title : Stereochemical features of the hydrolysis of 9,10-epoxystearic acid catalysed by plant and mammalian epoxide hydrolases - Summerer_2002_Biochem.J_366_471 |
| Author(s) : Summerer S , Hanano A , Utsumi S , Arand M , Schuber F , Blee E |
| Ref : Biochemical Journal , 366 :471 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Summerer_2002_Biochem.J_366_471 |
| ESTHER : Summerer_2002_Biochem.J_366_471 |
| PubMedSearch : Summerer_2002_Biochem.J_366_471 |
| PubMedID: 12020347 |