DDAB
General
Type : Fluorescent Probe || Benzoate
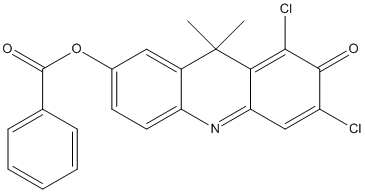
Chemical_Nomenclature : 6,8-dichloro-9,9-dimethyl-7-oxo-7,9-dihydroacridin-2-yl benzoate
Canonical SMILES : N2=C1C(=C(C(C(=C1)Cl)=O)Cl)C(C3=CC(=CC=C23)OC(C4=CC=CC=C4)=O)(C)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C22H15Cl2NO3\/c1-22(2)14-10-13(28-21(27)12-6-4-3-5-7-12)8-9-16(14)25-17-11-15(23)20(26)19(24)18(17)22\/h3-11H,1-2H3
InChIKey : SAIKAFGMHFZGKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) :
MW : 412.27
Formula : C22H15Cl2NO3
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
Families : Carb_B_Chordata
References (8)
| Title : Prognostic and Immunological Roles of CES2 in Breast Cancer and Potential Application of CES2-Targeted Fluorescent Probe DDAB in Breast Surgery - Qu_2023_Int.J.Gen.Med_16_1567 |
| Author(s) : Qu W , Yao Y , Liu Y , Jo H , Zhang Q , Zhao H |
| Ref : Int J Gen Med , 16 :1567 , 2023 |
| Abstract : Qu_2023_Int.J.Gen.Med_16_1567 |
| ESTHER : Qu_2023_Int.J.Gen.Med_16_1567 |
| PubMedSearch : Qu_2023_Int.J.Gen.Med_16_1567 |
| PubMedID: 37139258 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CES2 |
| Title : Investigation of the inhibitory effect of protostanes on human carboxylesterase 2 and their interaction: Inhibition kinetics and molecular stimulations - Lv_2021_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_167_1262 |
| Author(s) : Lv X , Bai R , Yan JK , Huang HL , Huo XK , Tian XG , Zhao XY , Zhang BJ , Zhao WY , Sun CP |
| Ref : Int J Biol Macromol , 167 :1262 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Lv_2021_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_167_1262 |
| ESTHER : Lv_2021_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_167_1262 |
| PubMedSearch : Lv_2021_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_167_1262 |
| PubMedID: 33189757 |
| Title : Demethylbellidifolin isolated from Swertia bimaculate against human carboxylesterase 2: Kinetics and interaction mechanism merged with docking simulations - Liu_2019_Bioorg.Chem_90_103101 |
| Author(s) : Liu TT , Huo XK , Tian XG , Liang JH , Yi J , Zhang XY , Zhang S , Feng L , Ning J , Zhang BJ , Sun CP , Ma XC |
| Ref : Bioorg Chem , 90 :103101 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Liu_2019_Bioorg.Chem_90_103101 |
| ESTHER : Liu_2019_Bioorg.Chem_90_103101 |
| PubMedSearch : Liu_2019_Bioorg.Chem_90_103101 |
| PubMedID: 31291611 |
| Title : A natural inhibitor from Alisma orientale against human carboxylesterase 2: Kinetics, circular dichroism spectroscopic analysis, and docking simulation - Yi_2019_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_133_184 |
| Author(s) : Yi J , Bai R , An Y , Liu TT , Liang JH , Tian XG , Huo XK , Feng L , Ning J , Sun CP , Ma XC , Zhang HL |
| Ref : Int J Biol Macromol , 133 :184 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Yi_2019_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_133_184 |
| ESTHER : Yi_2019_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_133_184 |
| PubMedSearch : Yi_2019_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_133_184 |
| PubMedID: 30991064 |
| Title : Comparative metabolism of DDAO benzoate in liver microsomes from various species - Ma_2017_Toxicol.In.Vitro_44_280 |
| Author(s) : Ma HY , Yang JD , Hou J , Zou LW , Jin Q , Hao DC , Ning J , Ge GB , Yang L |
| Ref : Toxicol In Vitro , 44 :280 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Ma_2017_Toxicol.In.Vitro_44_280 |
| ESTHER : Ma_2017_Toxicol.In.Vitro_44_280 |
| PubMedSearch : Ma_2017_Toxicol.In.Vitro_44_280 |
| PubMedID: 28647665 |
| Title : Structure-Activity Relationships of Pentacyclic Triterpenoids as Potent and Selective Inhibitors against Human Carboxylesterase 1 - Zou_2017_Front.Pharmacol_8_435 |
| Author(s) : Zou LW , Dou TY , Wang P , Lei W , Weng ZM , Hou J , Wang DD , Fan YM , Zhang WD , Ge GB , Yang L |
| Ref : Front Pharmacol , 8 :435 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Zou_2017_Front.Pharmacol_8_435 |
| ESTHER : Zou_2017_Front.Pharmacol_8_435 |
| PubMedSearch : Zou_2017_Front.Pharmacol_8_435 |
| PubMedID: 28713276 |
| Title : Assessment of the inhibitory effects of pyrethroids against human carboxylesterases - Lei_2017_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_321_48 |
| Author(s) : Lei W , Wang DD , Dou TY , Hou J , Feng L , Yin H , Luo Q , Sun J , Ge GB , Yang L |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 321 :48 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Lei_2017_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_321_48 |
| ESTHER : Lei_2017_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_321_48 |
| PubMedSearch : Lei_2017_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_321_48 |
| PubMedID: 28242322 |
| Title : A highly selective near-infrared fluorescent probe for carboxylesterase 2 and its bioimaging applications in living cells and animals - Jin_2016_Biosens.Bioelectron_83_193 |
| Author(s) : Jin Q , Feng L , Wang DD , Wu JJ , Hou J , Dai ZR , Sun SG , Wang JY , Ge GB , Cui JN , Yang L |
| Ref : Biosensors & Bioelectronics , 83 :193 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Jin_2016_Biosens.Bioelectron_83_193 |
| ESTHER : Jin_2016_Biosens.Bioelectron_83_193 |
| PubMedSearch : Jin_2016_Biosens.Bioelectron_83_193 |
| PubMedID: 27129028 |