Cocaine
General
Type : Natural || Drug || Alkaloid || Benzoate || Azabicyclo
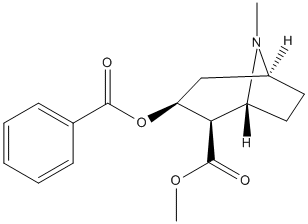
Chemical_Nomenclature : methyl (1S,3S,4R,5R)-3-benzoyloxy-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-4-carboxylate
Canonical SMILES : CN1C2CCC1C(C(C2)OC(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)OC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C17H21NO4\/c1-18-12-8-9-13(18)15(17(20)21-2)14(10-12)22-16(19)11-6-4-3-5-7-11\/h3-7,12-15H,8-10H2,1-2H3\/t12-,13+,14-,15+\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : ZPUCINDJVBIVPJ-LJISPDSOSA-N
Other name(s) : 2beta-carbomethoxy-3beta-benzoyloxytropane hydrochloride, (-)-Cocaine, 3-beta-Hydroxy-, Methyl Ester, Benzoate, Methylbenzoylepgonine, Cocaine Free Base, Benzoylmethylecgonine, Crack, L-Cocain, beta-Cocain, D-cocaine, Cocain, Kokain
Target
Families : BCHE, Carb_B_Chordata, Cocaine_esterase
References (29)
| Title : Catalytic Hydrolysis Mechanism of Cocaine by Human Carboxylesterase 1: An Orthoester Intermediate Slows Down the Reaction - Yan_2019_Molecules_24_ |
| Author(s) : Yan M , Zhang Z , Liu Z , Zhang C , Zhang J , Fan S , Yang Z |
| Ref : Molecules , 24 : , 2019 |
| Abstract : Yan_2019_Molecules_24_ |
| ESTHER : Yan_2019_Molecules_24_ |
| PubMedSearch : Yan_2019_Molecules_24_ |
| PubMedID: 31717501 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CES1 |
| Title : Catalytic Reaction Mechanism for Drug Metabolism in Human Carboxylesterase-1: Cocaine Hydrolysis Pathway - Yao_2018_Mol.Pharm_15_3871 |
| Author(s) : Yao J , Chen X , Zheng F , Zhan CG |
| Ref : Mol Pharm , 15 :3871 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Yao_2018_Mol.Pharm_15_3871 |
| ESTHER : Yao_2018_Mol.Pharm_15_3871 |
| PubMedSearch : Yao_2018_Mol.Pharm_15_3871 |
| PubMedID: 30095924 |
| Title : Reward and Toxicity of Cocaine Metabolites Generated by Cocaine Hydrolase - Murthy_2015_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_35_819 |
| Author(s) : Murthy V , Geng L , Gao Y , Zhang B , Miller JD , Reyes S , Brimijoin S |
| Ref : Cellular Molecular Neurobiology , 35 :819 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Murthy_2015_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_35_819 |
| ESTHER : Murthy_2015_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_35_819 |
| PubMedSearch : Murthy_2015_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_35_819 |
| PubMedID: 25814464 |
| Title : Kinetic characterization of a cocaine hydrolase engineered from mouse butyrylcholinesterase - Chen_2015_Biochem.J_466_243 |
| Author(s) : Chen X , Huang X , Geng L , Xue L , Hou S , Zheng X , Brimijoin S , Zheng F , Zhan CG |
| Ref : Biochemical Journal , 466 :243 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Chen_2015_Biochem.J_466_243 |
| ESTHER : Chen_2015_Biochem.J_466_243 |
| PubMedSearch : Chen_2015_Biochem.J_466_243 |
| PubMedID: 25486543 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-BCHE |
| Title : Rational design, preparation, and characterization of a therapeutic enzyme mutant with improved stability and function for cocaine detoxification - Fang_2014_ACS.Chem.Biol_9_1764 |
| Author(s) : Fang L , Chow KM , Hou S , Xue L , Chen X , Rodgers DW , Zheng F , Zhan CG |
| Ref : ACS Chemical Biology , 9 :1764 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Fang_2014_ACS.Chem.Biol_9_1764 |
| ESTHER : Fang_2014_ACS.Chem.Biol_9_1764 |
| PubMedSearch : Fang_2014_ACS.Chem.Biol_9_1764 |
| PubMedID: 24919140 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: rhosm-cocE |
| Title : Preclinical studies on neurobehavioral and neuromuscular effects of cocaine hydrolase gene therapy in mice - Murthy_2014_J.Mol.Neurosci_53_409 |
| Author(s) : Murthy V , Gao Y , Geng L , LeBrasseur NK , White TA , Brimijoin S |
| Ref : Journal of Molecular Neuroscience , 53 :409 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Murthy_2014_J.Mol.Neurosci_53_409 |
| ESTHER : Murthy_2014_J.Mol.Neurosci_53_409 |
| PubMedSearch : Murthy_2014_J.Mol.Neurosci_53_409 |
| PubMedID: 24085526 |
| Title : The future potential for cocaine vaccines - Orson_2014_Expert.Opin.Biol.Ther_14_1271 |
| Author(s) : Orson FM , Wang R , Brimijoin S , Kinsey BM , Singh RA , Ramakrishnan M , Wang HY , Kosten TR |
| Ref : Expert Opin Biol Ther , 14 :1271 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Orson_2014_Expert.Opin.Biol.Ther_14_1271 |
| ESTHER : Orson_2014_Expert.Opin.Biol.Ther_14_1271 |
| PubMedSearch : Orson_2014_Expert.Opin.Biol.Ther_14_1271 |
| PubMedID: 24835496 |
| Title : A highly efficient cocaine-detoxifying enzyme obtained by computational design - Zheng_2014_Nat.Commun_5_3457 |
| Author(s) : Zheng F , Xue L , Hou S , Liu J , Zhan M , Yang W , Zhan CG |
| Ref : Nat Commun , 5 :3457 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Zheng_2014_Nat.Commun_5_3457 |
| ESTHER : Zheng_2014_Nat.Commun_5_3457 |
| PubMedSearch : Zheng_2014_Nat.Commun_5_3457 |
| PubMedID: 24643289 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-BCHE |
| Title : Amino-acid mutations to extend the biological half-life of a therapeutically valuable mutant of human butyrylcholinesterase - Fang_2014_Chem.Biol.Interact_214C_18 |
| Author(s) : Fang L , Hou S , Xue L , Zheng F , Zhan CG |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 214C :18 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Fang_2014_Chem.Biol.Interact_214C_18 |
| ESTHER : Fang_2014_Chem.Biol.Interact_214C_18 |
| PubMedSearch : Fang_2014_Chem.Biol.Interact_214C_18 |
| PubMedID: 24582612 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-BCHE |
| Title : Plants as a source of butyrylcholinesterase variants designed for enhanced cocaine hydrolase activity - Larrimore_2013_Chem.Biol.Interact_203_217 |
| Author(s) : Larrimore KE , Barcus M , Kannan L , Gao Y , Zhan CG , Brimijoin S , Mor TS |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 203 :217 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Larrimore_2013_Chem.Biol.Interact_203_217 |
| ESTHER : Larrimore_2013_Chem.Biol.Interact_203_217 |
| PubMedSearch : Larrimore_2013_Chem.Biol.Interact_203_217 |
| PubMedID: 23000451 |
| Title : Catalytic activities of a cocaine hydrolase engineered from human butyrylcholinesterase against (+)- and (-)-cocaine - Xue_2013_Chem.Biol.Interact_203_57 |
| Author(s) : Xue L , Hou S , Yang W , Fang L , Zheng F , Zhan CG |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 203 :57 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Xue_2013_Chem.Biol.Interact_203_57 |
| ESTHER : Xue_2013_Chem.Biol.Interact_203_57 |
| PubMedSearch : Xue_2013_Chem.Biol.Interact_203_57 |
| PubMedID: 22917637 |
| Title : Biochemical and molecular analysis of carboxylesterase-mediated hydrolysis of cocaine and heroin - Hatfield_2010_Br.J.Pharmacol_160_1916 |
| Author(s) : Hatfield MJ , Tsurkan LG , Hyatt JL , Yu X , Edwards CC , Hicks LD , Wadkins RM , Potter PM |
| Ref : British Journal of Pharmacology , 160 :1916 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Hatfield_2010_Br.J.Pharmacol_160_1916 |
| ESTHER : Hatfield_2010_Br.J.Pharmacol_160_1916 |
| PubMedSearch : Hatfield_2010_Br.J.Pharmacol_160_1916 |
| PubMedID: 20649590 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CES1 |
| Title : Cocaine metabolism accelerated by a re-engineered human butyrylcholinesterase - Sun_2002_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_302_710 |
| Author(s) : Sun H , Shen ML , Pang YP , Lockridge O , Brimijoin S |
| Ref : Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics , 302 :710 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Sun_2002_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_302_710 |
| ESTHER : Sun_2002_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_302_710 |
| PubMedSearch : Sun_2002_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_302_710 |
| PubMedID: 12130735 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-BCHE |
| Title : Re-engineering butyrylcholinesterase as a cocaine hydrolase - Sun_2002_Mol.Pharmacol_62_220 |
| Author(s) : Sun H , Pang YP , Lockridge O , Brimijoin S |
| Ref : Molecular Pharmacology , 62 :220 , 2002 |
| Abstract : Sun_2002_Mol.Pharmacol_62_220 |
| ESTHER : Sun_2002_Mol.Pharmacol_62_220 |
| PubMedSearch : Sun_2002_Mol.Pharmacol_62_220 |
| PubMedID: 12130672 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-BCHE |
| Title : Predicted Michaelis-Menten complexes of cocaine-butyrylcholinesterase. Engineering effective butyrylcholinesterase mutants for cocaine detoxication. - Sun_2001_J.Biol.Chem_276_9330 |
| Author(s) : Sun H , El Yazal J , Lockridge O , Schopfer LM , Brimijoin S , Pang YP |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 276 :9330 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Sun_2001_J.Biol.Chem_276_9330 |
| ESTHER : Sun_2001_J.Biol.Chem_276_9330 |
| PubMedSearch : Sun_2001_J.Biol.Chem_276_9330 |
| PubMedID: 11104759 |
| Title : Role of cholinergic receptors and cholinesterase activity in hemodynamic responses to cocaine in conscious rats - Knuepfer_1999_Am.J.Physiol_276_R103 |
| Author(s) : Knuepfer MM , Gan Q |
| Ref : American Journal of Physiology , 276 :R103 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Knuepfer_1999_Am.J.Physiol_276_R103 |
| ESTHER : Knuepfer_1999_Am.J.Physiol_276_R103 |
| PubMedSearch : Knuepfer_1999_Am.J.Physiol_276_R103 |
| PubMedID: 9887183 |
| Title : An improved cocaine hydrolase: the A328Y mutant of human butyrylcholinesterase is 4-fold more efficient - Xie_1999_Mol.Pharmacol_55_83 |
| Author(s) : Xie W , Altamirano CV , Bartels CF , Speirs RJ , Cashman JR , Lockridge O |
| Ref : Molecular Pharmacology , 55 :83 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Xie_1999_Mol.Pharmacol_55_83 |
| ESTHER : Xie_1999_Mol.Pharmacol_55_83 |
| PubMedSearch : Xie_1999_Mol.Pharmacol_55_83 |
| PubMedID: 9882701 |
| Title : The influence of plasma butyrylcholinesterase concentration on the in vitro hydrolysis of cocaine in human plasma - Browne_1998_Biopharm.Drug.Dispos_19_309 |
| Author(s) : Browne SP , Slaughter EA , Couch RA , Rudnic EM , McLean AM |
| Ref : Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition , 19 :309 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Browne_1998_Biopharm.Drug.Dispos_19_309 |
| ESTHER : Browne_1998_Biopharm.Drug.Dispos_19_309 |
| PubMedSearch : Browne_1998_Biopharm.Drug.Dispos_19_309 |
| PubMedID: 9673783 |
| Title : Cocaine benzoyl thioester: synthesis, kinetics of base hydrolysis, and application to the assay of cocaine esterases - Cashman_1998_Chem.Res.Toxicol_11_895 |
| Author(s) : Cashman JR , Berkman CE , Underiner G , Kolly CA , Hunter AD |
| Ref : Chemical Research in Toxicology , 11 :895 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Cashman_1998_Chem.Res.Toxicol_11_895 |
| ESTHER : Cashman_1998_Chem.Res.Toxicol_11_895 |
| PubMedSearch : Cashman_1998_Chem.Res.Toxicol_11_895 |
| PubMedID: 9705751 |
| Title : Normal and atypical butyrylcholinesterases in placental development, function, and malfunction - Sternfeld_1997_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_17_315 |
| Author(s) : Sternfeld M , Rachmilewitz J , Loewenstein-Lichtenstein Y , Andres C , Timberg R , Ben-Ari S , Glick C , Soreq H , Zakut H |
| Ref : Cellular Molecular Neurobiology , 17 :315 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Sternfeld_1997_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_17_315 |
| ESTHER : Sternfeld_1997_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_17_315 |
| PubMedSearch : Sternfeld_1997_Cell.Mol.Neurobiol_17_315 |
| PubMedID: 9187488 |
| Title : Enhancing cocaine metabolism with butyrylcholinesterase as a treatment strategy - Gorelick_1997_Drug.Alcohol.Depend_48_159 |
| Author(s) : Gorelick DA |
| Ref : Drug Alcohol Depend , 48 :159 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Gorelick_1997_Drug.Alcohol.Depend_48_159 |
| ESTHER : Gorelick_1997_Drug.Alcohol.Depend_48_159 |
| PubMedSearch : Gorelick_1997_Drug.Alcohol.Depend_48_159 |
| PubMedID: 9449014 |
| Title : Cocaine detoxification by human plasma butyrylcholinesterase - Lynch_1997_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_145_363 |
| Author(s) : Lynch TJ , Mattes CE , Singh A , Bradley RM , Brady RO , Dretchen KL |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 145 :363 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Lynch_1997_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_145_363 |
| ESTHER : Lynch_1997_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_145_363 |
| PubMedSearch : Lynch_1997_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_145_363 |
| PubMedID: 9266810 |
| Title : Therapeutic use of butyrylcholinesterase for cocaine intoxication - Mattes_1997_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_145_372 |
| Author(s) : Mattes CE , Lynch TJ , Singh A , Bradley RM , Kellaris PA , Brady RO , Dretchen KL |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 145 :372 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Mattes_1997_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_145_372 |
| ESTHER : Mattes_1997_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_145_372 |
| PubMedSearch : Mattes_1997_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_145_372 |
| PubMedID: 9266811 |
| Title : Overlapping drug interaction sites of human butyrylcholinesterase dissected by site-directed mutagenesis - Loewenstein-Lichtenstein_1996_Mol.Pharmacol_50_1423 |
| Author(s) : Loewenstein-Lichtenstein Y , Glick D , Gluzman N , Sternfeld M , Zakut H , Soreq H |
| Ref : Molecular Pharmacology , 50 :1423 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Loewenstein-Lichtenstein_1996_Mol.Pharmacol_50_1423 |
| ESTHER : Loewenstein-Lichtenstein_1996_Mol.Pharmacol_50_1423 |
| PubMedSearch : Loewenstein-Lichtenstein_1996_Mol.Pharmacol_50_1423 |
| PubMedID: 8967962 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-BCHE |
| Title : Acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity in the human term placenta: implications for fetal cocaine exposure - Simone_1994_J.Lab.Clin.Med_123_400 |
| Author(s) : Simone C , Derewlany LO , Oskamp M , Johnson D , Knie B , Koren G |
| Ref : Journal of Laboratory & Clinical Medicine , 123 :400 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Simone_1994_J.Lab.Clin.Med_123_400 |
| ESTHER : Simone_1994_J.Lab.Clin.Med_123_400 |
| PubMedSearch : Simone_1994_J.Lab.Clin.Med_123_400 |
| PubMedID: 8133152 |
| Title : Differential toxicity of cocaine and its isomers, (+)-cocaine and (-)-psi-cocaine, is associated with stereoselective hydrolysis by hepatic carboxylesterases in cultured rat hepatocytes - Melchert_1992_Chem.Biol.Interact_84_243 |
| Author(s) : Melchert RB , Goldlin C , Zweifel U , Welder AA , Boelsterli UA |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 84 :243 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Melchert_1992_Chem.Biol.Interact_84_243 |
| ESTHER : Melchert_1992_Chem.Biol.Interact_84_243 |
| PubMedSearch : Melchert_1992_Chem.Biol.Interact_84_243 |
| PubMedID: 1423743 |
| Title : Activities of the enantiomers of cocaine and some related compounds as substrates and inhibitors of plasma butyrylcholinesterase - Gatley_1991_Biochem.Pharmacol_41_1249 |
| Author(s) : Gatley SJ |
| Ref : Biochemical Pharmacology , 41 :1249 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Gatley_1991_Biochem.Pharmacol_41_1249 |
| ESTHER : Gatley_1991_Biochem.Pharmacol_41_1249 |
| PubMedSearch : Gatley_1991_Biochem.Pharmacol_41_1249 |
| PubMedID: 2009099 |
| Title : Genetic variants of human serum cholinesterase influence metabolism of the muscle relaxant succinylcholine. - Lockridge_1990_Pharmacol.Ther_47_35 |
| Author(s) : Lockridge O |
| Ref : Pharmacol Ther , 47 :35 , 1990 |
| Abstract : Lockridge_1990_Pharmacol.Ther_47_35 |
| ESTHER : Lockridge_1990_Pharmacol.Ther_47_35 |
| PubMedSearch : Lockridge_1990_Pharmacol.Ther_47_35 |
| PubMedID: 2195556 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-BCHE |
| Title : Metabolism of cocaine in man - Inaba_1978_Clin.Pharmacol.Ther_23_547 |
| Author(s) : Inaba T , Stewart DJ , Kalow W |
| Ref : Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics , 23 :547 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Inaba_1978_Clin.Pharmacol.Ther_23_547 |
| ESTHER : Inaba_1978_Clin.Pharmacol.Ther_23_547 |
| PubMedSearch : Inaba_1978_Clin.Pharmacol.Ther_23_547 |
| PubMedID: 639429 |