Chlorpyrifos-oxon
General
Type : Insecticide || Organophosphate
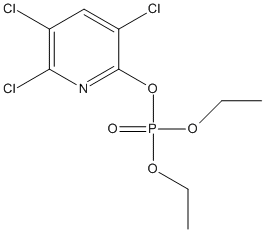
Chemical_Nomenclature : diethyl (3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl) phosphate
Canonical SMILES :
InChI :
InChIKey :
Other name(s) : 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl diethyl phosphate, 2,3,5-trichloro-6-diethoxyphosphoryloxy-pyridine, Dursbanoxon, Fospirate-ethyl, Chlorpyrifos oxon, Phospyrat ethyl, Chloropyrifos oxon, Dursban O-analog, Dursban oxygen analog, Chloropyrifos oxygen analog, CCRIS 7774
Target
References (2)
| Title : A novel chlorpyrifos hydrolase CPD from Paracoccus sp. TRP: Molecular cloning, characterization and catalytic mechanism - Fan_2018_Electron.J.Biotechnol_31_10 |
| Author(s) : Fan S , Li K , Yan Y , Wang J , Qiao C , Yang T , Jia Y , Zhao B |
| Ref : Electronic Journal of Biotechnology , 31 :10 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Fan_2018_Electron.J.Biotechnol_31_10 |
| ESTHER : Fan_2018_Electron.J.Biotechnol_31_10 |
| PubMedSearch : Fan_2018_Electron.J.Biotechnol_31_10 |
| PubMedID: |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: 9rhob-a0a1x7ll67 |
| Title : A brain detoxifying enzyme for organophosphorus nerve poisons - Nomura_2005_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_102_6195 |
| Author(s) : Nomura DK , Leung D , Chiang KP , Quistad GB , Cravatt BF , Casida JE |
| Ref : Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A , 102 :6195 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Nomura_2005_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_102_6195 |
| ESTHER : Nomura_2005_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_102_6195 |
| PubMedSearch : Nomura_2005_Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A_102_6195 |
| PubMedID: 15840715 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-NCEH1 , mouse-Q8BLF1 |