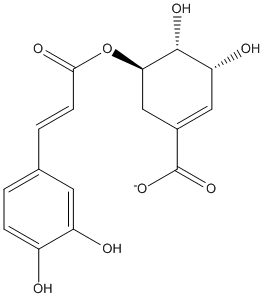
Caffeoylshikimate
General
Type : Natural
Chemical_Nomenclature : (3R,4R,5R)-5-[(E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy-3,4-dihydroxycyclohexene-1-carboxylate
Canonical SMILES : C1C(C(C(C=C1C(=O)[O-])O)O)OC(=O)C=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C16H16O8\/c17-10-3-1-8(5-11(10)18)2-4-14(20)24-13-7-9(16(22)23)6-12(19)15(13)21\/h1-6,12-13,15,17-19,21H,7H2,(H,22,23)\/p-1\/b4-2+\/t12-,13-,15-\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : QMPHZIPNNJOWQI-GDDAOPKQSA-M
Other name(s) : 5-O-[(E)-caffeoyl]-shikimate, 5-O-caffeoylshikimate, 5-[(E)-caffeoyl]shikimate(1-), 5-caffeoylshikimate, caffeoylshikimic acid, CHEBI:91005
MW : 335.28
Formula : C16H15O8-
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
Families : Monoglyceridelipase_lysophospholip
References (4)
| Title : Altered profile of floral volatiles and lignin content by down-regulation of Caffeoyl Shikimate Esterase in Petunia - Kim_2023_BMC.Plant.Biol_23_210 |
| Author(s) : Kim JY , Cho KH , Keene SA , Colquhoun TA |
| Ref : BMC Plant Biol , 23 :210 , 2023 |
| Abstract : Kim_2023_BMC.Plant.Biol_23_210 |
| ESTHER : Kim_2023_BMC.Plant.Biol_23_210 |
| PubMedSearch : Kim_2023_BMC.Plant.Biol_23_210 |
| PubMedID: 37085749 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: pethy-CSE |
| Title : PbCSE1 promotes lignification during stone cell development in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) fruit - Xu_2021_Sci.Rep_11_9450 |
| Author(s) : Xu J , Tao X , Xie Z , Gong X , Qi K , Zhang S , Shiratake K , Tao S |
| Ref : Sci Rep , 11 :9450 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Xu_2021_Sci.Rep_11_9450 |
| ESTHER : Xu_2021_Sci.Rep_11_9450 |
| PubMedSearch : Xu_2021_Sci.Rep_11_9450 |
| PubMedID: 33941813 |
| Title : Silencing CAFFEOYL SHIKIMATE ESTERASE Affects Lignification and Improves Saccharification in Poplar - Saleme_2017_Plant.Physiol_175_1040 |
| Author(s) : Saleme MLS , Cesarino I , Vargas L , Kim H , Vanholme R , Goeminne G , Van Acker R , Fonseca FCA , Pallidis A , Voorend W , Junior JN , Padmakshan D , Van Doorsselaere J , Ralph J , Boerjan W |
| Ref : Plant Physiol , 175 :1040 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Saleme_2017_Plant.Physiol_175_1040 |
| ESTHER : Saleme_2017_Plant.Physiol_175_1040 |
| PubMedSearch : Saleme_2017_Plant.Physiol_175_1040 |
| PubMedID: 28878037 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: poptr-b9gwn9 |
| Title : Caffeoyl shikimate esterase (CSE) is an enzyme in the lignin biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis - Vanholme_2013_Science_341_1103 |
| Author(s) : Vanholme R , Cesarino I , Rataj K , Xiao Y , Sundin L , Goeminne G , Kim H , Cross J , Morreel K , Araujo P , Welsh L , Haustraete J , McClellan C , Vanholme B , Ralph J , Simpson GG , Halpin C , Boerjan W |
| Ref : Science , 341 :1103 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Vanholme_2013_Science_341_1103 |
| ESTHER : Vanholme_2013_Science_341_1103 |
| PubMedSearch : Vanholme_2013_Science_341_1103 |
| PubMedID: 23950498 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: arath-F14G24.3 |