CNDE
General
Type : Cyanide
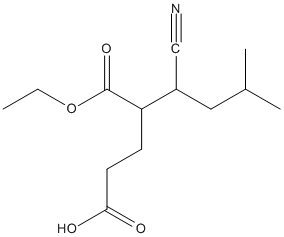
Chemical_Nomenclature : 5-cyano-4-ethoxycarbonyl-7-methyloctanoic acid
Canonical SMILES : CCOC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)C(CC(C)C)C#N
InChI : InChI=1S\/C13H21NO4\/c1-4-18-13(17)11(5-6-12(15)16)10(8-14)7-9(2)3\/h9-11H,4-7H2,1-3H3,(H,15,16)
InChIKey : MBZSCAJFNRHIKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N || MBZSCAJFNRHIKS-DTIOYNMSSA-N || MBZSCAJFNRHIKS-VUWPPUDQSA-N
Other name(s) : SCHEMBL2223205, 2-carboxyethyl-3-cyano-5-methylhexanoic acid, ethyl ester, Rac-2-carboxyethyl-3-cyano-5-methylhexanoic acid ethyl ester, (+\/-)-2-carboxyethyl-3-cyano-5-methyl hexanoic acid ethyl ester, 2-(2-Carboxyethyl)-3-cyano-5-methylhexanoic acid 1-ethyl ester
MW : 255.31
Formula : C13H21NO4
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
Families : Lipase_3
References (4)
| Title : Engineering of Talaromyces thermophilus lipase by altering its crevice-like binding site for highly efficient biocatalytic synthesis of chiral intermediate of Pregablin - Ding_2018_Bioorg.Chem_77_330 |
| Author(s) : Ding X , Zheng RC , Tang XL , Zheng YG |
| Ref : Bioorg Chem , 77 :330 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Ding_2018_Bioorg.Chem_77_330 |
| ESTHER : Ding_2018_Bioorg.Chem_77_330 |
| PubMedSearch : Ding_2018_Bioorg.Chem_77_330 |
| PubMedID: 29421709 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: talth-f6lqk7 |
| Title : Engineering of Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase Lip: creation of novel biocatalyst for efficient biosynthesis of chiral intermediate of Pregabalin - Li_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_2473 |
| Author(s) : Li XJ , Zheng RC , Ma HY , Zheng YG |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 98 :2473 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Li_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_2473 |
| ESTHER : Li_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_2473 |
| PubMedSearch : Li_2014_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_98_2473 |
| PubMedID: 23917635 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: thela-m4tp71 |
| Title : Biocatalytic synthesis of chiral intermediate of pregabalin with high substrate loading by a newly isolated Morgarella morganii ZJB-09203 - Zheng_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_4839 |
| Author(s) : Zheng RC , Wang TZ , Fu DJ , Li AP , Li XJ , Zheng YG |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 97 :4839 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Zheng_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_4839 |
| ESTHER : Zheng_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_4839 |
| PubMedSearch : Zheng_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_4839 |
| PubMedID: 23504060 |