Butylacetate
General
Type : Acetate || Alkyl ester
Chemical_Nomenclature : butyl acetate
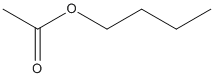
Canonical SMILES : CCCCOC(=O)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C6H12O2\/c1-3-4-5-8-6(2)7\/h3-5H2,1-2H3
InChIKey : DKPFZGUDAPQIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Butyl acetate, N-Butyl acetate, Acetic acid, butyl ester, 1-Butyl acetate, Butyl ethanoate
Target
Families : ACHE, Canar_LipB
References (13)
| Title : Combined effects of ultrasound and immobilization protocol on butyl acetate synthesis catalyzed by CALB - Alves_2014_Molecules_19_9562 |
| Author(s) : Alves JS , Garcia-Galan C , Schein MF , Silva AM , Barbosa O , Ayub MA , Fernandez-Lafuente R , Rodrigues RC |
| Ref : Molecules , 19 :9562 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Alves_2014_Molecules_19_9562 |
| ESTHER : Alves_2014_Molecules_19_9562 |
| PubMedSearch : Alves_2014_Molecules_19_9562 |
| PubMedID: 25004067 |
| Title : Ultrasound-assisted butyl acetate synthesis catalyzed by Novozym 435: enhanced activity and operational stability - Martins_2013_Ultrason.Sonochem_20_1155 |
| Author(s) : Martins AB , Schein MF , Friedrich JL , Fernandez-Lafuente R , Ayub MA , Rodrigues RC |
| Ref : Ultrason Sonochem , 20 :1155 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Martins_2013_Ultrason.Sonochem_20_1155 |
| ESTHER : Martins_2013_Ultrason.Sonochem_20_1155 |
| PubMedSearch : Martins_2013_Ultrason.Sonochem_20_1155 |
| PubMedID: 23453821 |
| Title : A thermoactive uropygial esterase from chicken: purification, characterisation and synthesis of flavour esters - Fendri_2012_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_50_1238 |
| Author(s) : Fendri A , Louati H , Sellami M , Gargouri H , Smichi N , Zarai Z , Aissa I , Miled N , Gargouri Y |
| Ref : Int J Biol Macromol , 50 :1238 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Fendri_2012_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_50_1238 |
| ESTHER : Fendri_2012_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_50_1238 |
| PubMedSearch : Fendri_2012_Int.J.Biol.Macromol_50_1238 |
| PubMedID: 22531158 |
| Title : Immobilization of lipase B from Candida antarctica on porous styrene-divinylbenzene beads improves butyl acetate synthesis - Graebin_2012_Biotechnol.Prog_28_406 |
| Author(s) : Graebin NG , Martins AB , Lorenzoni AS , Garcia-Galan C , Fernandez-Lafuente R , Ayub MA , Rodrigues RC |
| Ref : Biotechnol Prog , 28 :406 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Graebin_2012_Biotechnol.Prog_28_406 |
| ESTHER : Graebin_2012_Biotechnol.Prog_28_406 |
| PubMedSearch : Graebin_2012_Biotechnol.Prog_28_406 |
| PubMedID: 22271615 |
| Title : Co-expression of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase and its cognate foldase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa CS-2 and the application of the immobilized recombinant lipase - Peng_2011_Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol_165_926 |
| Author(s) : Peng R , Lin J , Wei D |
| Ref : Appl Biochem Biotechnol , 165 :926 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Peng_2011_Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol_165_926 |
| ESTHER : Peng_2011_Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol_165_926 |
| PubMedSearch : Peng_2011_Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol_165_926 |
| PubMedID: 21720839 |
| Title : Production of butyl acetate ester by lipase from novel strain of Rhizopus oryzae - Ben Salah_2007_J.Biosci.Bioeng_103_368 |
| Author(s) : Ben Salah R , Ghamghui H , Miled N , Mejdoub H , Gargouri Y |
| Ref : J Biosci Bioeng , 103 :368 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Ben Salah_2007_J.Biosci.Bioeng_103_368 |
| ESTHER : Ben Salah_2007_J.Biosci.Bioeng_103_368 |
| PubMedSearch : Ben Salah_2007_J.Biosci.Bioeng_103_368 |
| PubMedID: 17502279 |
| Title : Criteria to design green enzymatic processes in ionic liquid\/supercritical carbon dioxide systems - Lozano_2004_Biotechnol.Prog_20_661 |
| Author(s) : Lozano P , De Diego T , Gmouh S , Vaultier M , Iborra JL |
| Ref : Biotechnol Prog , 20 :661 , 2004 |
| Abstract : Lozano_2004_Biotechnol.Prog_20_661 |
| ESTHER : Lozano_2004_Biotechnol.Prog_20_661 |
| PubMedSearch : Lozano_2004_Biotechnol.Prog_20_661 |
| PubMedID: 15176866 |
| Title : A continuous membrane bioreactor for ester synthesis in organic media: I. Operational characterization and stability - Carvalho_2001_Biotechnol.Bioeng_72_127 |
| Author(s) : Carvalho CM , Aires-Barros MR , Cabral JM |
| Ref : Biotechnol Bioeng , 72 :127 , 2001 |
| Abstract : Carvalho_2001_Biotechnol.Bioeng_72_127 |
| ESTHER : Carvalho_2001_Biotechnol.Bioeng_72_127 |
| PubMedSearch : Carvalho_2001_Biotechnol.Bioeng_72_127 |
| PubMedID: 11114650 |
| Title : General occurrence of binding to acetylcholinesterase-substrate complex in noncompetitive inhibition and in inhibition by substrate - Cohen_1991_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1076_112 |
| Author(s) : Cohen SG , Chishti SB , Bell DA , Howard SI , Salih E , Cohen JB |
| Ref : Biochimica & Biophysica Acta , 1076 :112 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Cohen_1991_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1076_112 |
| ESTHER : Cohen_1991_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1076_112 |
| PubMedSearch : Cohen_1991_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1076_112 |
| PubMedID: 1986784 |
| Title : Carboxylesterases in the respiratory tracts of rabbits, rats and Syrian hamsters - Dahl_1987_Toxicol.Lett_36_129 |
| Author(s) : Dahl AR , Miller SC , Petridou-Fischer J |
| Ref : Toxicol Lett , 36 :129 , 1987 |
| Abstract : Dahl_1987_Toxicol.Lett_36_129 |
| ESTHER : Dahl_1987_Toxicol.Lett_36_129 |
| PubMedSearch : Dahl_1987_Toxicol.Lett_36_129 |
| PubMedID: 3576643 |
| Title : 1-Bromopinacolone, an active site-directed covalent inhibitor for acetylcholinesterase - Cohen_1982_J.Biol.Chem_257_14087 |
| Author(s) : Cohen SG , Lieberman DL , Hasan FB , Cohen JB |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 257 :14087 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Cohen_1982_J.Biol.Chem_257_14087 |
| ESTHER : Cohen_1982_J.Biol.Chem_257_14087 |
| PubMedSearch : Cohen_1982_J.Biol.Chem_257_14087 |
| PubMedID: 7142196 |
| Title : Structure-activity relationships in acetylcholinesterase reactions. Hydrolysis of non-ionic acetic esters - Jarv_1976_Eur.J.Biochem_67_315 |
| Author(s) : Jarv J , Kesvatera T , Aaviksaar A |
| Ref : European Journal of Biochemistry , 67 :315 , 1976 |
| Abstract : Jarv_1976_Eur.J.Biochem_67_315 |
| ESTHER : Jarv_1976_Eur.J.Biochem_67_315 |
| PubMedSearch : Jarv_1976_Eur.J.Biochem_67_315 |
| PubMedID: 964245 |