Aclacinomycin
General
Type : Antibiotic
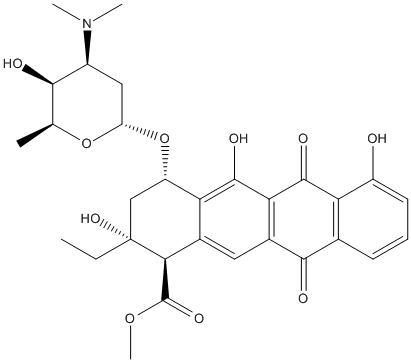
Chemical_Nomenclature : methyl (1R,2R,4S)-4-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-(dimethylamino)-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-2-ethyl-2,5,7-trihydroxy-6,11-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-tetracene-1-carboxylate
Canonical SMILES : CCC1(CC(C2=C(C1C(=O)OC)C=C3C(=C2O)C(=O)C4=C(C3=O)C=CC=C4O)OC5CC(C(C(O5)C)O)N(C)C)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C30H35NO10\/c1-6-30(38)12-19(41-20-11-17(31(3)4)25(33)13(2)40-20)22-15(24(30)29(37)39-5)10-16-23(28(22)36)27(35)21-14(26(16)34)8-7-9-18(21)32\/h7-10,13,17,19-20,24-25,32-33,36,38H,6,11-12H2,1-5H3\/t13-,17-,19-,20-,24-,25+,30+\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : LJZPVWKMAYDYAS-QKKPTTNWSA-N
Other name(s) : Aklavin, Aclacinomycin T, Doxypyrromycin, 1-Deoxypyrromycin, Rhodosaminyl-aklavinone
Target
Families : Aclacinomycin-methylesterase_RdmC
References (2)
| Title : Crystal structure of aclacinomycin methylesterase with bound product analogues: implications for anthracycline recognition and mechanism - Jansson_2003_J.Biol.Chem_278_39006 |
| Author(s) : Jansson A , Niemi J , Mantsala P , Schneider G |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 278 :39006 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Jansson_2003_J.Biol.Chem_278_39006 |
| ESTHER : Jansson_2003_J.Biol.Chem_278_39006 |
| PubMedSearch : Jansson_2003_J.Biol.Chem_278_39006 |
| PubMedID: 12878604 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: ecoli-rdmC , strpu-rdmC |
| Title : Modifications of aclacinomycin T by aclacinomycin methyl esterase (RdmC) and aclacinomycin-10-hydroxylase (RdmB) from Streptomyces purpurascens - Wang_2000_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1480_191 |
| Author(s) : Wang Y , Niemi J , Airas K , Ylihonko K , Hakala J , Mantsala P |
| Ref : Biochimica & Biophysica Acta , 1480 :191 , 2000 |
| Abstract : Wang_2000_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1480_191 |
| ESTHER : Wang_2000_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1480_191 |
| PubMedSearch : Wang_2000_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1480_191 |
| PubMedID: 11004563 |