4-methylumbelliferyl-palmitate
General
Type : Coumarin || Palmitate || Hexadecanoate
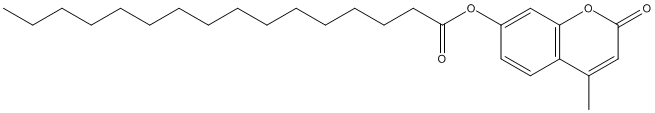
Chemical_Nomenclature : (4-methyl-2-oxochromen-7-yl) hexadecanoate
Canonical SMILES : CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC1=CC2=C(C=C1)C(=CC(=O)O2)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C26H38O4\/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-25(27)29-22-17-18-23-21(2)19-26(28)30-24(23)20-22\/h17-20H,3-16H2,1-2H3
InChIKey : QKQVFFACWLFRRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 4-Methylumbelliferyl palmitate, 4-Methylumbelliferone palmitate, 4-Methylumbelliferone-palmitate, palmitoyl-4MU, 17695-48-6, Palmitic acid 4-methylumbelliferyl ester, 4-methyl-2-oxo-2h-chromen-7-yl palmitate, 4-METHYL-2-OXOCHROMEN-7-YL HEXADECANOATE, 4-MU-Pal
MW : 414.57
Formula : C26H38O4
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem :
Iuphar :
Target
References (2)
| Title : High-resolution crystal structure of plant carboxylesterase AeCXE1, from Actinidia eriantha, and its complex with a high-affinity inhibitor paraoxon - Ileperuma_2007_Biochemistry_46_1851 |
| Author(s) : Ileperuma NR , Marshall SD , Squire CJ , Baker HM , Oakeshott JG , Russell RJ , Plummer KM , Newcomb RD , Baker EN |
| Ref : Biochemistry , 46 :1851 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Ileperuma_2007_Biochemistry_46_1851 |
| ESTHER : Ileperuma_2007_Biochemistry_46_1851 |
| PubMedSearch : Ileperuma_2007_Biochemistry_46_1851 |
| PubMedID: 17256879 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: actde-CXE1 |
| Title : Geotrichum candidum NRRL Y-553 lipase: purification, characterization and fatty acid specificity - Baillargeon_1991_Lipids_26_831 |
| Author(s) : Baillargeon MW , McCarthy SG |
| Ref : Lipids , 26 :831 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Baillargeon_1991_Lipids_26_831 |
| ESTHER : Baillargeon_1991_Lipids_26_831 |
| PubMedSearch : Baillargeon_1991_Lipids_26_831 |
| PubMedID: 1795605 |