1-Naphtyldodecanoate
General
Type : Water-insoluble medium and long chain ester || Dodecanoate || Naphtyl ester || Aromatic ester (two rings) || Laurate || Naphthalen
Chemical_Nomenclature : naphthalen-1-yl dodecanoate
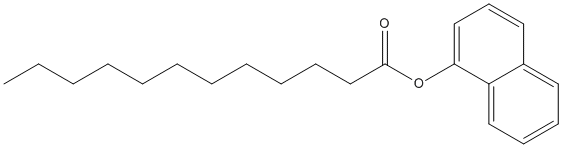
Canonical SMILES : CCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21
InChI : InChI=1S\/C22H30O2\/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-18-22(23)24-21-17-13-15-19-14-11-12-16-20(19)21\/h11-17H,2-10,18H2,1H3
InChIKey : CJSQRFDKBOSEJH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : C12-naphthyl ester, Naphthalen-1-yl Dodecanoate, alpha-NAPHTHYL LAURATE, 1-Naphthyl laurate, naphthyl dodecanoate, SCHEMBL4259480, ZINC2508003
Target
Families : Tannase, LYsophospholipase_carboxylesterase
References (3)
| Title : Characterization of a novel lipolytic enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae - Koseki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_5351 |
| Author(s) : Koseki T , Asai S , Saito N , Mori M , Sakaguchi Y , Ikeda K , Shiono Y |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 97 :5351 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Koseki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_5351 |
| ESTHER : Koseki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_5351 |
| PubMedSearch : Koseki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_5351 |
| PubMedID: 23001008 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: aspor-q2uf27 |
| Title : Functional-based screening methods for lipases, esterases, and phospholipases in metagenomic libraries - Reyes-Duarte_2012_Methods.Mol.Biol_861_101 |
| Author(s) : Reyes-Duarte D , Ferrer M , Garcia-Arellano H |
| Ref : Methods Mol Biol , 861 :101 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Reyes-Duarte_2012_Methods.Mol.Biol_861_101 |
| ESTHER : Reyes-Duarte_2012_Methods.Mol.Biol_861_101 |
| PubMedSearch : Reyes-Duarte_2012_Methods.Mol.Biol_861_101 |
| PubMedID: 22426714 |
| Title : Isolation, characterization, and heterologous expression of a carboxylesterase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 - Pesaresi_2005_Curr.Microbiol_50_102 |
| Author(s) : Pesaresi A , Devescovi G , Lamba D , Venturi V , Degrassi G |
| Ref : Curr Microbiol , 50 :102 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Pesaresi_2005_Curr.Microbiol_50_102 |
| ESTHER : Pesaresi_2005_Curr.Microbiol_50_102 |
| PubMedSearch : Pesaresi_2005_Curr.Microbiol_50_102 |
| PubMedID: 15717224 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: pseae-PA3859 |