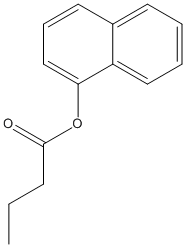
1-Naphtylbutyrate
General
Type : Butyrate || Naphtyl ester || Aromatic ester (two rings) || Naphthalen
Chemical_Nomenclature : naphthalen-1-yl butanoate
Canonical SMILES : CCCC(=O)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21
InChI : InChI=1S\/C14H14O2\/c1-2-6-14(15)16-13-10-5-8-11-7-3-4-9-12(11)13\/h3-5,7-10H,2,6H2,1H3
InChIKey : XIVJNRXPRQKFRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 1-Naphthyl butyrate, Naphthalen-1-yl butyrate, Butanoic acid, 1-naphthalenyl ester, 1-Butyroxynaphthalene, Alpha-Naphthyl butyrate, 1-Naphthol, butyrate, A-Naphthyl butyrate, Alpha-NB, C4-naphthyl ester
Target
References (6)
| Title : Identification and characterization of an acetyl xylan esterase from Aspergillus oryzae - Kato_2021_J.Biosci.Bioeng__ |
| Author(s) : Kato T , Shiono Y , Koseki T |
| Ref : J Biosci Bioeng , : , 2021 |
| Abstract : Kato_2021_J.Biosci.Bioeng__ |
| ESTHER : Kato_2021_J.Biosci.Bioeng__ |
| PubMedSearch : Kato_2021_J.Biosci.Bioeng__ |
| PubMedID: 34376338 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: aspfu-faec , aspor-faec |
| Title : Characterization of a novel lipolytic enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae - Koseki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_5351 |
| Author(s) : Koseki T , Asai S , Saito N , Mori M , Sakaguchi Y , Ikeda K , Shiono Y |
| Ref : Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology , 97 :5351 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Koseki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_5351 |
| ESTHER : Koseki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_5351 |
| PubMedSearch : Koseki_2013_Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol_97_5351 |
| PubMedID: 23001008 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: aspor-q2uf27 |
| Title : An inserted alpha\/beta subdomain shapes the catalytic pocket of Lactobacillus johnsonii cinnamoyl esterase - Lai_2011_PLoS.One_6_e23269 |
| Author(s) : Lai KK , Stogios PJ , Vu C , Xu X , Cui H , Molloy S , Savchenko A , Yakunin A , Gonzalez CF |
| Ref : PLoS ONE , 6 :e23269 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Lai_2011_PLoS.One_6_e23269 |
| ESTHER : Lai_2011_PLoS.One_6_e23269 |
| PubMedSearch : Lai_2011_PLoS.One_6_e23269 |
| PubMedID: 21876742 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: lacjo-q74hk5 |
| Title : Isolation, characterization, and heterologous expression of a carboxylesterase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 - Pesaresi_2005_Curr.Microbiol_50_102 |
| Author(s) : Pesaresi A , Devescovi G , Lamba D , Venturi V , Degrassi G |
| Ref : Curr Microbiol , 50 :102 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Pesaresi_2005_Curr.Microbiol_50_102 |
| ESTHER : Pesaresi_2005_Curr.Microbiol_50_102 |
| PubMedSearch : Pesaresi_2005_Curr.Microbiol_50_102 |
| PubMedID: 15717224 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: pseae-PA3859 |
| Title : Cloning and analysis of CUT1, a cutinase gene from Magnaporthe grisea - Sweigard_1992_Mol.Gen.Genet_232_174 |
| Author(s) : Sweigard JA , Chumley FG , Valent B |
| Ref : Molecular & General Genetics , 232 :174 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Sweigard_1992_Mol.Gen.Genet_232_174 |
| ESTHER : Sweigard_1992_Mol.Gen.Genet_232_174 |
| PubMedSearch : Sweigard_1992_Mol.Gen.Genet_232_174 |
| PubMedID: 1557023 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: maggr-cutas |