SP-134
General
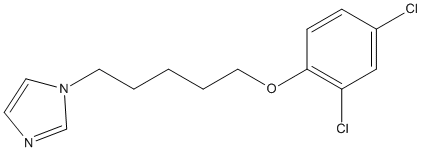
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1-[5-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)pentyl]-1H-imidazole, 1-[5-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)pentyl]imidazole
Canonical SMILES : C1=CC(=C(C=C1Cl)Cl)OCCCCCN2C=CN=C2
InChI : InChI=1S\/C14H16Cl2N2O\/c15-12-4-5-14(13(16)10-12)19-9-3-1-2-7-18-8-6-17-11-18\/h4-6,8,10-11H,1-3,7,9H2
InChIKey : RCLGZIGOWPMCRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : SP134, ZINC02898719, AC1ME8S5, Ambcb5532749, SCHEMBL15894130, MolPort-002-154-435, ZINC2898719
MW : 299.20 || 299.19
Formula : C14H16Cl2N2O
CAS_number :
CID PubChem :
InChIKey UniChem :
Iuphar :
Wikipedia :
Target
Structure : 5DTJ
Families : No family
References
No reference