HLo-7
General
Type : Hagedorn Oxime, Oxime, Bispyridinium
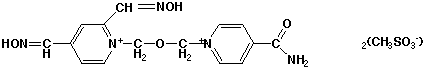
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1-(((4-(aminocarbonyl)pyridinio)methoxy)methyl 2,4-bis((hydroxyimino)methyl pyridinium dimethanesulfonate CAS 145613-73-6, [(E)-[1-[(4-carbamoylpyridin-1-ium-1-yl)methoxymethyl]-2-[(E)-hydroxyiminomethyl]pyridin-4-ylidene]methyl]-oxoazanium\;diiodide
Canonical SMILES : C1=CN(C(=CC1=C[NH+]=O)C=NO)COC[N+]2=CC=C(C=C2)C(=O)N.[I-].[I-]
InChI : InChI=1S\/C15H15N5O4.2HI\/c16-15(21)13-2-4-19(5-3-13)10-24-11-20-6-1-12(8-17-22)7-14(20)9-18-23\;\;\/h1-9H,10-11H2,(H2-,16,21,22,23)\;2*1H
InChIKey : ABYVDBPOASKQRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Hloe 7, HLo 7, HLo7, UNII-E1MMP1J6IK, Pyridinium, 1-(((4-(aminocarbonyl)pyridinio)methoxy)methyl)-2,4-bis((hydroxyimino)methyl)-, diodide
MW : 585.13
Formula : C15H17I2N5O4
CAS_number : 120103-35-7
CID PubChem :
InChIKey UniChem :
Iuphar :
Wikipedia :
References
No reference