DAM
General
Type : Oxime, Uncharged Oxime
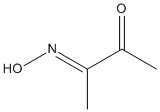
Chemical_Nomenclature : (3E)-3-hydroxyiminobutan-2-one
Canonical SMILES : CC(=NO)C(=O)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C4H7NO2\/c1-3(5-7)4(2)6\/h7H,1-2H3\/b5-3+
InChIKey : FSEUPUDHEBLWJY-HWKANZROSA-N
Other name(s) : Diacetylmonoxime, 2-oximino-3-butanone, diacetylmonooxime, 2,3-Butanedione-2-monoxime, 2,3-butanedione monoxime, Biacetyl monoxime
MW : 101.10
Formula : C4H7NO2
CAS_number : 57-71-6
CID PubChem :
InChIKey UniChem :
Iuphar :
Wikipedia :
Target
Structure : No structure
Families : No family
References
No reference