WWL113
Carboxylesterase Ces3 and Ces1f inhibitor (IC50 values are ~100 nM). Also inhibits ABHD6. Promotes lipid storage in adipocytes. Reduces weight gain in diet-induced obese mice and enhances glucose tolerance in diabetic mice. Orally active. The ability of WWL113 to induce UCP1 expression in brown adipocytes does not appear to be mediated by Ces3/1f inhibition, for a structurally distinct Ces3 inhibitor (WWL229) failed to have the same effect on UCP1 expression, whereas the urea version of WWL113 (WWL113U), which does not inhibit Ces3, retained the ability to induce UCP1
General
Type : Carbamate,Benzoate
Chemical_Nomenclature : ethyl 4-[4-[methyl-[(3-pyridin-4-ylphenyl)methyl]carbamoyl]oxyphenyl]benzoate
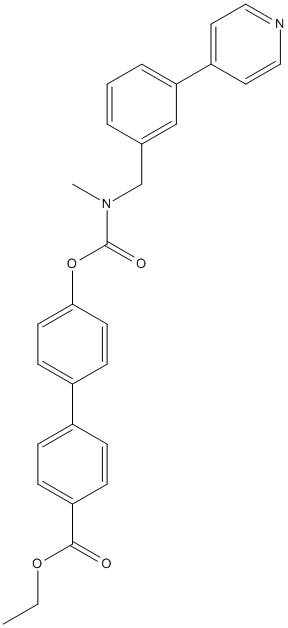
Canonical SMILES : CCOC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)OC(=O)N(C)CC3=CC=CC(=C3)C4=CC=NC=C4
InChI : InChI=1S\/C29H26N2O4\/c1-3-34-28(32)25-9-7-22(8-10-25)23-11-13-27(14-12-23)35-29(33)31(2)20-21-5-4-6-26(19-21)24-15-17-30-18-16-24\/h4-19H,3,20H2,1-2H3
InChIKey : AKIIPHDGVCFVCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Wwl113,AOB2409,SYN5248,WWL 113,WWL-113
MW : 466.52
Formula : C29H26N2O4
CAS_number : 947669-86-5
PubChem : 17759482
UniChem : AKIIPHDGVCFVCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : WWL113 ligand of proteins in family: ABHD6-Lip || Carb_B_Chordata
Stucture :
Protein : human-ABHD6 || human-CES3 || mouse-Ces1d
References (4)
| Title : Human leukocytes differentially express endocannabinoid-glycerol lipases and hydrolyze 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol and its metabolites from the 15-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase pathways - Turcotte_2019_J.Leukoc.Biol_106_1337 |
| Author(s) : Turcotte C , Dumais E , Archambault AS , Martin C , Blanchet MR , Bissonnette E , Boulet LP , Laviolette M , Di Marzo V , Flamand N |
| Ref : J Leukoc Biol , 106 :1337 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Turcotte_2019_J.Leukoc.Biol_106_1337 |
| ESTHER : Turcotte_2019_J.Leukoc.Biol_106_1337 |
| PubMedSearch : Turcotte_2019_J.Leukoc.Biol_106_1337 |
| PubMedID: 31556464 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-ABHD6 , human-ABHD12 , human-ABHD16A , human-CES1 , human-LYPLA2 , human-PPT1 |
| Title : A Unique Role of Carboxylesterase 3 (Ces3) in beta-Adrenergic Signaling-Stimulated Thermogenesis - Yang_2019_Diabetes_68_1178 |
| Author(s) : Yang L , Li X , Tang H , Gao Z , Zhang K , Sun K |
| Ref : Diabetes , 68 :1178 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Yang_2019_Diabetes_68_1178 |
| ESTHER : Yang_2019_Diabetes_68_1178 |
| PubMedSearch : Yang_2019_Diabetes_68_1178 |
| PubMedID: 30862682 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CES3 , mouse-Ces1d |
| Title : Integrated phenotypic and activity-based profiling links Ces3 to obesity and diabetes - Dominguez_2014_Nat.Chem.Biol_10_113 |
| Author(s) : Dominguez E , Galmozzi A , Chang JW , Hsu KL , Pawlak J , Li W , Godio C , Thomas J , Partida D , Niessen S , O'Brien PE , Russell AP , Watt MJ , Nomura DK , Cravatt BF , Saez E |
| Ref : Nat Chemical Biology , 10 :113 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Dominguez_2014_Nat.Chem.Biol_10_113 |
| ESTHER : Dominguez_2014_Nat.Chem.Biol_10_113 |
| PubMedSearch : Dominguez_2014_Nat.Chem.Biol_10_113 |
| PubMedID: 24362705 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CES3 , mouse-Ces1d |
| Title : ThermoMouse: an in vivo model to identify modulators of UCP1 expression in brown adipose tissue - Galmozzi_2014_Cell.Rep_9_1584 |
| Author(s) : Galmozzi A , Sonne SB , Altshuler-Keylin S , Hasegawa Y , Shinoda K , Luijten IH , Chang JW , Sharp LZ , Cravatt BF , Saez E , Kajimura S |
| Ref : Cell Rep , 9 :1584 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Galmozzi_2014_Cell.Rep_9_1584 |
| ESTHER : Galmozzi_2014_Cell.Rep_9_1584 |
| PubMedSearch : Galmozzi_2014_Cell.Rep_9_1584 |
| PubMedID: 25466254 |