URB602
General
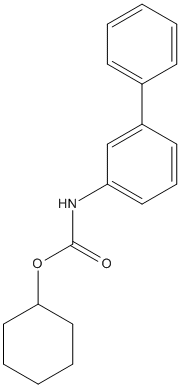
Type : Biphenyl,Carbamate
Chemical_Nomenclature : cyclohexyl N-(3-phenylphenyl)carbamate
Canonical SMILES : C1CCC(CC1)OC(=O)NC2=CC=CC(=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3
InChI : InChI=1S\/C19H21NO2\/c21-19(22-18-12-5-2-6-13-18)20-17-11-7-10-16(14-17)15-8-3-1-4-9-15\/h1,3-4,7-11,14,18H,2,5-6,12-13H2,(H,20,21)
InChIKey : HHVUFQYJOSFTEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Cyclohexyl [1,1'-biphenyl]-3-ylcarbamate,565460-15-3,Cyclohexyl biphenyl-3-ylcarbamate,CHEMBL77767
MW : 295.37
Formula : C19H21NO2
CAS_number :
PubChem : 10979337
UniChem : HHVUFQYJOSFTEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : URB602
Target
Families : URB602 ligand of proteins in family: Monoglyceridelipase_lysophospholip
Stucture :
Protein : human-MGLL
References (24)
| Title : Stress Promotes Drug Seeking Through Glucocorticoid-Dependent Endocannabinoid Mobilization in the Prelimbic Cortex - McReynolds_2018_Biol.Psychiatry_84_85 |
| Author(s) : McReynolds JR , Doncheck EM , Li Y , Vranjkovic O , Graf EN , Ogasawara D , Cravatt BF , Baker DA , Liu QS , Hillard CJ , Mantsch JR |
| Ref : Biological Psychiatry , 84 :85 , 2018 |
| Abstract : McReynolds_2018_Biol.Psychiatry_84_85 |
| ESTHER : McReynolds_2018_Biol.Psychiatry_84_85 |
| PubMedSearch : McReynolds_2018_Biol.Psychiatry_84_85 |
| PubMedID: 29100630 |
| Title : Design, synthesis, molecular modelling and in vitro cytotoxicity analysis of novel carbamate derivatives as inhibitors of Monoacylglycerol lipase - Lauria_2018_Bioorg.Med.Chem_26_2561 |
| Author(s) : Lauria S , Perrotta C , Casati S , Di Renzo I , Ottria R , Eberini I , Palazzolo L , Parravicini C , Ciuffreda P |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry , 26 :2561 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Lauria_2018_Bioorg.Med.Chem_26_2561 |
| ESTHER : Lauria_2018_Bioorg.Med.Chem_26_2561 |
| PubMedSearch : Lauria_2018_Bioorg.Med.Chem_26_2561 |
| PubMedID: 29678535 |
| Title : 2-Arachidonoylglycerol endocannabinoid signaling coupled to metabotropic glutamate receptor type-5 modulates anxiety-like behavior in the rat ventromedial prefrontal cortex - Almeida-Santos_2017_J.Psychopharmacol__269881117704986 |
| Author(s) : Almeida-Santos AF , Moreira FA , Guimaraes FS , Aguiar DC |
| Ref : J Psychopharmacol , :269881117704986 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Almeida-Santos_2017_J.Psychopharmacol__269881117704986 |
| ESTHER : Almeida-Santos_2017_J.Psychopharmacol__269881117704986 |
| PubMedSearch : Almeida-Santos_2017_J.Psychopharmacol__269881117704986 |
| PubMedID: 28440729 |
| Title : Pharmacological inhibition of MAGL attenuates experimental colon carcinogenesis - Pagano_2017_Pharmacol.Res_119_227 |
| Author(s) : Pagano E , Borrelli F , Orlando P , Romano B , Monti M , Morbidelli L , Aviello G , Imperatore R , Capasso R , Piscitelli F , Buono L , Di Marzo V , Izzo AA |
| Ref : Pharmacol Res , 119 :227 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Pagano_2017_Pharmacol.Res_119_227 |
| ESTHER : Pagano_2017_Pharmacol.Res_119_227 |
| PubMedSearch : Pagano_2017_Pharmacol.Res_119_227 |
| PubMedID: 28193521 |
| Title : Inhibition of monoacylglycerol lipase: Another signalling pathway for potential therapeutic targets in migraine? - Greco_2017_Cephalalgia__333102417727537 |
| Author(s) : Greco R , Demartini C , Zanaboni AM , Berliocchi L , Piomelli D , Tassorelli C |
| Ref : Cephalalgia , :333102417727537 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Greco_2017_Cephalalgia__333102417727537 |
| ESTHER : Greco_2017_Cephalalgia__333102417727537 |
| PubMedSearch : Greco_2017_Cephalalgia__333102417727537 |
| PubMedID: 28816506 |
| Title : Inhibition of Monoacylglycerol Lipase Activity Decreases Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in INS-1 (832\/13) Cells and Rat Islets - Berdan_2016_PLoS.One_11_e0149008 |
| Author(s) : Berdan CA , Erion KA , Burritt NE , Corkey BE , Deeney JT |
| Ref : PLoS ONE , 11 :e0149008 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Berdan_2016_PLoS.One_11_e0149008 |
| ESTHER : Berdan_2016_PLoS.One_11_e0149008 |
| PubMedSearch : Berdan_2016_PLoS.One_11_e0149008 |
| PubMedID: 26867016 |
| Title : Monoglyceride lipase: Structure and inhibitors - Scalvini_2016_Chem.Phys.Lipids_197_13 |
| Author(s) : Scalvini L , Piomelli D , Mor M |
| Ref : Chemistry & Physic of Lipids , 197 :13 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Scalvini_2016_Chem.Phys.Lipids_197_13 |
| ESTHER : Scalvini_2016_Chem.Phys.Lipids_197_13 |
| PubMedSearch : Scalvini_2016_Chem.Phys.Lipids_197_13 |
| PubMedID: 26216043 |
| Title : Synthesis and characterization of a new fluorogenic substrate for monoacylglycerol lipase and application to inhibition studies - Lauria_2015_Anal.Bioanal.Chem_407_8163 |
| Author(s) : Lauria S , Casati S , Ciuffreda P |
| Ref : Anal Bioanal Chem , 407 :8163 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Lauria_2015_Anal.Bioanal.Chem_407_8163 |
| ESTHER : Lauria_2015_Anal.Bioanal.Chem_407_8163 |
| PubMedSearch : Lauria_2015_Anal.Bioanal.Chem_407_8163 |
| PubMedID: 26329281 |
| Title : Monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor protects primary cultured neurons against homocysteine-induced impairments in rat caudate nucleus through COX-2 signaling - Dong_2015_Life.Sci_138_64 |
| Author(s) : Dong M , Lu Y , Zou Z , Yang H |
| Ref : Life Sciences , 138 :64 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Dong_2015_Life.Sci_138_64 |
| ESTHER : Dong_2015_Life.Sci_138_64 |
| PubMedSearch : Dong_2015_Life.Sci_138_64 |
| PubMedID: 25818189 |
| Title : Pretreatment with the monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor URB602 protects from the long-term consequences of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats - Carloni_2012_Pediatr.Res_72_400 |
| Author(s) : Carloni S , Alonso-Alconada D , Girelli S , Duranti A , Tontini A , Piomelli D , Hilario E , Alvarez A , Balduini W |
| Ref : Pediatr Res , 72 :400 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Carloni_2012_Pediatr.Res_72_400 |
| ESTHER : Carloni_2012_Pediatr.Res_72_400 |
| PubMedSearch : Carloni_2012_Pediatr.Res_72_400 |
| PubMedID: 22821058 |
| Title : Characterization of the effects of reuptake and hydrolysis inhibition on interstitial endocannabinoid levels in the brain: an in vivo microdialysis study - Wiskerke_2012_ACS.Chem.Neurosci_3_407 |
| Author(s) : Wiskerke J , Irimia C , Cravatt BF , De Vries TJ , Schoffelmeer AN , Pattij T , Parsons LH |
| Ref : ACS Chem Neurosci , 3 :407 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Wiskerke_2012_ACS.Chem.Neurosci_3_407 |
| ESTHER : Wiskerke_2012_ACS.Chem.Neurosci_3_407 |
| PubMedSearch : Wiskerke_2012_ACS.Chem.Neurosci_3_407 |
| PubMedID: 22860210 |
| Title : Cytoplasmic fungal lipases release fungicides from ultra-deformable vesicular drug carriers - Steinberg_2012_PLoS.One_7_e38181 |
| Author(s) : Steinberg G |
| Ref : PLoS ONE , 7 :e38181 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Steinberg_2012_PLoS.One_7_e38181 |
| ESTHER : Steinberg_2012_PLoS.One_7_e38181 |
| PubMedSearch : Steinberg_2012_PLoS.One_7_e38181 |
| PubMedID: 22666476 |
| Title : The design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel URB602 analogues as potential monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitors - Szabo_2011_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_21_6782 |
| Author(s) : Szabo M , Agostino M , Malone DT , Yuriev E , Capuano B |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Lett , 21 :6782 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Szabo_2011_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_21_6782 |
| ESTHER : Szabo_2011_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_21_6782 |
| PubMedSearch : Szabo_2011_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_21_6782 |
| PubMedID: 21982493 |
| Title : Endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol protects neurons against beta-amyloid insults - Chen_2011_Neurosci_178_159 |
| Author(s) : Chen X , Zhang J , Chen C |
| Ref : Neuroscience , 178 :159 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Chen_2011_Neurosci_178_159 |
| ESTHER : Chen_2011_Neurosci_178_159 |
| PubMedSearch : Chen_2011_Neurosci_178_159 |
| PubMedID: 21256197 |
| Title : Peripheral antinociceptive effects of inhibitors of monoacylglycerol lipase in a rat model of inflammatory pain - Guindon_2011_Br.J.Pharmacol_163_1464 |
| Author(s) : Guindon J , Guijarro A , Piomelli D , Hohmann AG |
| Ref : British Journal of Pharmacology , 163 :1464 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Guindon_2011_Br.J.Pharmacol_163_1464 |
| ESTHER : Guindon_2011_Br.J.Pharmacol_163_1464 |
| PubMedSearch : Guindon_2011_Br.J.Pharmacol_163_1464 |
| PubMedID: 21198549 |
| Title : Behavioral sequelae following acute diisopropylfluorophosphate intoxication in rats: comparative effects of atropine and cannabinomimetics - Wright_2010_Neurotoxicol.Teratol_32_329 |
| Author(s) : Wright LK , Liu J , Nallapaneni A , Pope CN |
| Ref : Neurotoxicology & Teratology , 32 :329 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Wright_2010_Neurotoxicol.Teratol_32_329 |
| ESTHER : Wright_2010_Neurotoxicol.Teratol_32_329 |
| PubMedSearch : Wright_2010_Neurotoxicol.Teratol_32_329 |
| PubMedID: 20034559 |
| Title : A fluorescence-based assay for monoacylglycerol lipase compatible with inhibitor screening - Wang_2008_Assay.Drug.Dev.Technol_6_387 |
| Author(s) : Wang Y , Chanda P , Jones PG , Kennedy JD |
| Ref : Assay Drug Dev Technol , 6 :387 , 2008 |
| Abstract : Wang_2008_Assay.Drug.Dev.Technol_6_387 |
| ESTHER : Wang_2008_Assay.Drug.Dev.Technol_6_387 |
| PubMedSearch : Wang_2008_Assay.Drug.Dev.Technol_6_387 |
| PubMedID: 18452392 |
| Title : Pharmacological enhancement of endocannabinoid signaling reduces the cholinergic toxicity of diisopropylfluorophosphate - Nallapaneni_2008_Neurotoxicol_29_1037 |
| Author(s) : Nallapaneni A , Liu J , Karanth S , Pope C |
| Ref : Neurotoxicology , 29 :1037 , 2008 |
| Abstract : Nallapaneni_2008_Neurotoxicol_29_1037 |
| ESTHER : Nallapaneni_2008_Neurotoxicol_29_1037 |
| PubMedSearch : Nallapaneni_2008_Neurotoxicol_29_1037 |
| PubMedID: 18765251 |
| Title : Distribution and function of monoacylglycerol lipase in the gastrointestinal tract - Duncan_2008_Am.J.Physiol.Gastrointest.Liver.Physiol_295_G1255 |
| Author(s) : Duncan M , Thomas AD , Cluny NL , Patel A , Patel KD , Lutz B , Piomelli D , Alexander SP , Sharkey KA |
| Ref : American Journal of Physiology Gastrointest Liver Physiol , 295 :G1255 , 2008 |
| Abstract : Duncan_2008_Am.J.Physiol.Gastrointest.Liver.Physiol_295_G1255 |
| ESTHER : Duncan_2008_Am.J.Physiol.Gastrointest.Liver.Physiol_295_G1255 |
| PubMedSearch : Duncan_2008_Am.J.Physiol.Gastrointest.Liver.Physiol_295_G1255 |
| PubMedID: 18948437 |
| Title : Inhibitors of monoacylglycerol lipase as novel analgesics - Hohmann_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_150_673 |
| Author(s) : Hohmann AG |
| Ref : British Journal of Pharmacology , 150 :673 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Hohmann_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_150_673 |
| ESTHER : Hohmann_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_150_673 |
| PubMedSearch : Hohmann_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_150_673 |
| PubMedID: 17293886 |
| Title : The inhibition of monoacylglycerol lipase by URB602 showed an anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effect in a murine model of acute inflammation - Comelli_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_152_787 |
| Author(s) : Comelli F , Giagnoni G , Bettoni I , Colleoni M , Costa B |
| Ref : British Journal of Pharmacology , 152 :787 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Comelli_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_152_787 |
| ESTHER : Comelli_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_152_787 |
| PubMedSearch : Comelli_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_152_787 |
| PubMedID: 17700715 |
| Title : Lack of selectivity of URB602 for 2-oleoylglycerol compared to anandamide hydrolysis in vitro - Vandevoorde_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_150_186 |
| Author(s) : Vandevoorde S , Jonsson KO , Labar G , Persson E , Lambert DM , Fowler CJ |
| Ref : British Journal of Pharmacology , 150 :186 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Vandevoorde_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_150_186 |
| ESTHER : Vandevoorde_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_150_186 |
| PubMedSearch : Vandevoorde_2007_Br.J.Pharmacol_150_186 |
| PubMedID: 17143303 |
| Title : Identification of a novel endocannabinoid-hydrolyzing enzyme expressed by microglial cells - Muccioli_2007_J.Neurosci_27_2883 |
| Author(s) : Muccioli GG , Xu C , Odah E , Cudaback E , Cisneros JA , Lambert DM , Lopez Rodriguez ML , Bajjalieh S , Stella N |
| Ref : Journal of Neuroscience , 27 :2883 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Muccioli_2007_J.Neurosci_27_2883 |
| ESTHER : Muccioli_2007_J.Neurosci_27_2883 |
| PubMedSearch : Muccioli_2007_J.Neurosci_27_2883 |
| PubMedID: 17360910 |
| Title : URB602 inhibits monoacylglycerol lipase and selectively blocks 2-arachidonoylglycerol degradation in intact brain slices - King_2007_Chem.Biol_14_1357 |
| Author(s) : King AR , Duranti A , Tontini A , Rivara S , Rosengarth A , Clapper JR , Astarita G , Geaga JA , Luecke H , Mor M , Tarzia G , Piomelli D |
| Ref : Chemical Biology , 14 :1357 , 2007 |
| Abstract : King_2007_Chem.Biol_14_1357 |
| ESTHER : King_2007_Chem.Biol_14_1357 |
| PubMedSearch : King_2007_Chem.Biol_14_1357 |
| PubMedID: 18096504 |