Triethylene-glycol
General
Type : Polymer,Poly-ethylene-glycol
Chemical_Nomenclature : 2-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethoxy]ethanol
Canonical SMILES : C(COCCOCCO)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C6H14O4\/c7-1-3-9-5-6-10-4-2-8\/h7-8H,1-6H2
InChIKey : ZIBGPFATKBEMQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Triglycol,2,2'-(Ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))diethanol,Trigen,Triethylenglykol,PGE,Triethylene glycol
MW : 150.17
Formula : C6H14O4
CAS_number : 112-27-6
PubChem : 8172
UniChem : ZIBGPFATKBEMQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
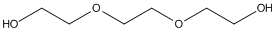
Target
Families : Triethylene-glycol ligand of proteins in family
ACHE
Acetyl_esterase
Protein :
torca-ACHE
ecoli-Aes
References (2)
| Title : The Impact of Crystallization Conditions on Structure-Based Drug Design: A Case Study on the Methylene Blue\/Acetylcholinesterase Complex - Dym_2016_Protein.Sci_25_1096 |
| Author(s) : Dym O , Song W , Felder CE , Roth E , Shnyrov V , Ashani Y , Xu Y , Joosten RP , Weiner L , Sussman JL , Silman I |
| Ref : Protein Science , 25 :1096 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Dym_2016_Protein.Sci_25_1096 |
| ESTHER : Dym_2016_Protein.Sci_25_1096 |
| PubMedSearch : Dym_2016_Protein.Sci_25_1096 |
| PubMedID: 26990888 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: torca-ACHE |
| Title : Structural and mutational analyses of Aes, an inhibitor of MalT in Escherichia coli - Schiefner_2014_Proteins_82_268 |
| Author(s) : Schiefner A , Gerber K , Brosig A , Boos W |
| Ref : Proteins , 82 :268 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Schiefner_2014_Proteins_82_268 |
| ESTHER : Schiefner_2014_Proteins_82_268 |
| PubMedSearch : Schiefner_2014_Proteins_82_268 |
| PubMedID: 23934774 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: ecoli-Aes |