TerritremC
Mycotoxin purified from culture of fungus Aspergillus terreus 23-1 growing on rice
General
Type : Natural,Meroterpenoid
Chemical_Nomenclature : 4H,11H-Naphtho(2,1-b)pyrano(3,4-e)pyran-1,11(5H)-dione, 4a,6,6a,12,12a,12b-hexahydro-4a,12a-dihydroxy-9-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-4,4,6a,12b-tetramethyl-, (4aR-(4a-alpha,6a-beta,12a-alpha,12b-beta))-
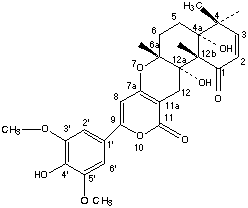
Canonical SMILES : CC1(C=CC(=O)C2(C1(CCC3(C2(CC4=C(O3)C=C(OC4=O)C5=CC(=C(C(=C5)OC)O)OC)O)C)O)C)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C28H32O9\/c1-24(2)8-7-21(29)26(4)27(24,32)10-9-25(3)28(26,33)14-16-18(37-25)13-17(36-23(16)31)15-11-19(34-5)22(30)20(12-15)35-6\/h7-8,11-13,30,32-33H,9-10,14H2,1-6H3\/t25-,26+,27-,28-\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : FTTNXWIFPFEOQT-JUDWXZBOSA-N
Other name(s) :
MW : 512.20
Formula : C28H32O9
CAS_number : 89020-33-7
PubChem : 160306
UniChem : FTTNXWIFPFEOQT-JUDWXZBOSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (4)
| Title : NMR assignments of territrems A, B, and C and the structure of MB2, the major metabolite of territrem B by rat liver microsomal fraction - Lee_1992_J.Nat.Prod_55_251 |
| Author(s) : Lee SS , Peng FC , Chiou CM , Ling KH |
| Ref : Journal of Natural Products , 55 :251 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Lee_1992_J.Nat.Prod_55_251 |
| ESTHER : Lee_1992_J.Nat.Prod_55_251 |
| PubMedSearch : Lee_1992_J.Nat.Prod_55_251 |
| PubMedID: 1624944 |
| Title : Biotransformation of territrems by S9 fraction from rat liver - Ling_1991_Drug.Metab.Dispos_19_587 |
| Author(s) : Ling KH , Chiou CM , Tseng YL |
| Ref : Drug Metabolism & Disposition: The Biological Fate of Chemicals , 19 :587 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Ling_1991_Drug.Metab.Dispos_19_587 |
| ESTHER : Ling_1991_Drug.Metab.Dispos_19_587 |
| PubMedSearch : Ling_1991_Drug.Metab.Dispos_19_587 |
| PubMedID: 1680623 |
| Title : Isolation, chemical structure, acute toxicity, and some physicochemical properties of territrem C from Aspergillus terreus - Ling_1984_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_47_98 |
| Author(s) : Ling KH , Liou HH , Yang CM , Yang CK |
| Ref : Applied Environmental Microbiology , 47 :98 , 1984 |
| Abstract : Ling_1984_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_47_98 |
| ESTHER : Ling_1984_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_47_98 |
| PubMedSearch : Ling_1984_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_47_98 |
| PubMedID: 6546485 |