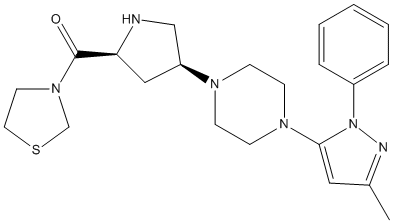
Teneligliptin
General
Type : Drug,Piperazine,Pyrrolidine,Gliptin,Thiazolidine,Sulfur Compound,Pyrazole
Chemical_Nomenclature : [(2S,4S)-4-[4-(5-methyl-2-phenylpyrazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-(1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl)methanone
Canonical SMILES : CC1=NN(C(=C1)N2CCN(CC2)C3CC(NC3)C(=O)N4CCSC4)C5=CC=CC=C5
InChI : InChI=1S\/C22H30N6OS\/c1-17-13-21(28(24-17)18-5-3-2-4-6-18)26-9-7-25(8-10-26)19-14-20(23-15-19)22(29)27-11-12-30-16-27\/h2-6,13,19-20,23H,7-12,14-16H2,1H3\/t19-,20-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : WGRQANOPCQRCME-PMACEKPBSA-N
Other name(s) : UNII-28ZHI4CF9C,CHEMBL2147777,Teneligliptin hydrobromide hydrate,M51,MP-513
MW : 426.58
Formula : C22H30N6OS
CAS_number : 760937-92-6
PubChem : 11949652
UniChem : WGRQANOPCQRCME-PMACEKPBSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : Teneligliptin ligand of proteins in family: DPP4N_Peptidase_S9
Stucture : 3VJK Crystal structure of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) in complex with MP-513
Protein : human-DPP4
References (10)
| Title : Evaluation of Teneligliptin a DPP4 Inhibitor in Terms of Efficacy and Safety with Respect to QT\/QTc Prolongation in Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) - Bhosle_2022_J.Assoc.Physicians.India_70_11 |
| Author(s) : Bhosle D , Chandekar B , Alimuddin S |
| Ref : J Assoc Physicians India , 70 :11 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Bhosle_2022_J.Assoc.Physicians.India_70_11 |
| ESTHER : Bhosle_2022_J.Assoc.Physicians.India_70_11 |
| PubMedSearch : Bhosle_2022_J.Assoc.Physicians.India_70_11 |
| PubMedID: 35598125 |
| Title : Teneligliptin, a DPP-4 Inhibitor, Decreases Plasma Levels of Inflammatory Chemokines During a Standard Meal Test in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes - Aso_2020_Am.J.Med.Sci_360_261 |
| Author(s) : Aso Y , Kase M , Sagara M , Sakurai S , Iijima T , Tomaru T , Jojima T , Usui I |
| Ref : American Journal of Medicine Sci , 360 :261 , 2020 |
| Abstract : Aso_2020_Am.J.Med.Sci_360_261 |
| ESTHER : Aso_2020_Am.J.Med.Sci_360_261 |
| PubMedSearch : Aso_2020_Am.J.Med.Sci_360_261 |
| PubMedID: 32540146 |
| Title : Teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, attenuated pro-inflammatory phenotype of perivascular adipose tissue and inhibited atherogenesis in normoglycemic apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice - Salim_2017_Vascul.Pharmacol_96-98_19 |
| Author(s) : Salim HM , Fukuda D , Higashikuni Y , Tanaka K , Hirata Y , Yagi S , Soeki T , Shimabukuro M , Sata M |
| Ref : Vascul Pharmacol , 96-98 :19 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Salim_2017_Vascul.Pharmacol_96-98_19 |
| ESTHER : Salim_2017_Vascul.Pharmacol_96-98_19 |
| PubMedSearch : Salim_2017_Vascul.Pharmacol_96-98_19 |
| PubMedID: 28347868 |
| Title : Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin add-on to insulin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 16-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with an open-label period - Kadowaki_2017_Expert.Opin.Pharmacother_18_1291 |
| Author(s) : Kadowaki T , Kondo K , Sasaki N , Miyayama K , Yokota S , Terata R , Gouda M |
| Ref : Expert Opin Pharmacother , 18 :1291 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Kadowaki_2017_Expert.Opin.Pharmacother_18_1291 |
| ESTHER : Kadowaki_2017_Expert.Opin.Pharmacother_18_1291 |
| PubMedSearch : Kadowaki_2017_Expert.Opin.Pharmacother_18_1291 |
| PubMedID: 28741385 |
| Title : A long-lasting dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, teneligliptin, as a preventive drug for the development of hepatic steatosis in high-fructose diet-fed ob\/ob mice - Nakamura_2017_Int.J.Mol.Med_39_969 |
| Author(s) : Nakamura K , Fukunishi S , Yokohama K , Ohama H , Tsuchimoto Y , Asai A , Tsuda Y , Higuchi K |
| Ref : Int J Mol Med , 39 :969 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Nakamura_2017_Int.J.Mol.Med_39_969 |
| ESTHER : Nakamura_2017_Int.J.Mol.Med_39_969 |
| PubMedSearch : Nakamura_2017_Int.J.Mol.Med_39_969 |
| PubMedID: 28260070 |
| Title : Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin in addition to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients on hemodialysis evaluated by continuous glucose monitoring - Yajima_2016_Diabetes.Res.Clin.Pract_122_78 |
| Author(s) : Yajima T , Yajima K , Hayashi M , Takahashi H , Yasuda K |
| Ref : Diabetes Res Clin Pract , 122 :78 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Yajima_2016_Diabetes.Res.Clin.Pract_122_78 |
| ESTHER : Yajima_2016_Diabetes.Res.Clin.Pract_122_78 |
| PubMedSearch : Yajima_2016_Diabetes.Res.Clin.Pract_122_78 |
| PubMedID: 27810689 |
| Title : Teneligliptin: a DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes - Kishimoto_2013_Diabetes.Metab.Syndr.Obes_6_187 |
| Author(s) : Kishimoto M |
| Ref : Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes , 6 :187 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Kishimoto_2013_Diabetes.Metab.Syndr.Obes_6_187 |
| ESTHER : Kishimoto_2013_Diabetes.Metab.Syndr.Obes_6_187 |
| PubMedSearch : Kishimoto_2013_Diabetes.Metab.Syndr.Obes_6_187 |
| PubMedID: 23671395 |
| Title : Discovery and preclinical profile of teneligliptin (3-[(2S,4S)-4-[4-(3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)piperazin-1-yl]pyrrolidin-2-y lcarbonyl]thiazolidine): a highly potent, selective, long-lasting and orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes - Yoshida_2012_Bioorg.Med.Chem_20_5705 |
| Author(s) : Yoshida T , Akahoshi F , Sakashita H , Kitajima H , Nakamura M , Sonda S , Takeuchi M , Tanaka Y , Ueda N , Sekiguchi S , Ishige T , Shima K , Nabeno M , Abe Y , Anabuki J , Soejima A , Yoshida K , Takashina Y , Ishii S , Kiuchi S , Fukuda S , Tsutsumiuchi R , Kosaka K , Murozono T , Nakamaru Y , Utsumi H , Masutomi N , Kishida H , Miyaguchi I , Hayashi Y |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry , 20 :5705 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Yoshida_2012_Bioorg.Med.Chem_20_5705 |
| ESTHER : Yoshida_2012_Bioorg.Med.Chem_20_5705 |
| PubMedSearch : Yoshida_2012_Bioorg.Med.Chem_20_5705 |
| PubMedID: 22959556 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-DPP4 |
| Title : [(S)-gamma-(4-Aryl-1-piperazinyl)-l-prolyl]thiazolidines as a novel series of highly potent and long-lasting DPP-IV inhibitors - Yoshida_2007_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_17_2618 |
| Author(s) : Yoshida T , Sakashita H , Akahoshi F , Hayashi Y |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Lett , 17 :2618 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Yoshida_2007_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_17_2618 |
| ESTHER : Yoshida_2007_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_17_2618 |
| PubMedSearch : Yoshida_2007_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_17_2618 |
| PubMedID: 17317162 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-DPP4 |
| Title : [(S)-gamma-(Arylamino)prolyl]thiazolidine compounds as a novel series of potent and stable DPP-IV inhibitors - Sakashita_2006_Bioorg.Med.Chem_14_3662 |
| Author(s) : Sakashita H , Akahoshi F , Kitajima H , Tsutsumiuchi R , Hayashi Y |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry , 14 :3662 , 2006 |
| Abstract : Sakashita_2006_Bioorg.Med.Chem_14_3662 |
| ESTHER : Sakashita_2006_Bioorg.Med.Chem_14_3662 |
| PubMedSearch : Sakashita_2006_Bioorg.Med.Chem_14_3662 |
| PubMedID: 16460948 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-DPP4 |