TK90
Eutomer of Dual sEH/PPARgamma Modulator TK70 is found also in complex with PPARgamma pdb:7A7H
General
Type : Butyrate,Carboxamide,Trifluoro,Multitarget,PPARgamma ligand
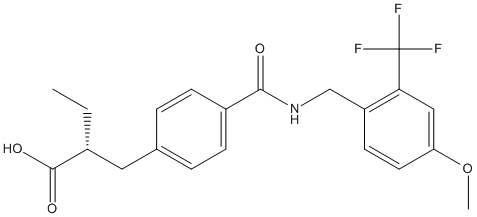
Chemical_Nomenclature : (2R)-2-[[4-[[4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylcarbamoyl]phenyl]methyl]butanoic acid
Canonical SMILES : CCC(CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)NCC2=C(C=C(C=C2)OC)C(F)(F)F)C(=O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C21H22F3NO4\/c1-3-14(20(27)28)10-13-4-6-15(7-5-13)19(26)25-12-16-8-9-17(29-2)11-18(16)21(22,23)24\/h4-9,11,14H,3,10,12H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26)(H,27,28)\/t14-\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : VPAHYLNIDWFBPW-CQSZACIVSA-N
Other name(s) : TK9
MW : 409.4
Formula : C21H22F3NO4
CAS_number :
PubChem : 129520967
UniChem : VPAHYLNIDWFBPW-CQSZACIVSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : TK90 ligand of proteins in family: Epoxide_hydrolase
Stucture : 7A7G Soluble epoxide hydrolase in complex with TK90
Protein : human-EPHX2
References (1)
| Title : Combined Cardioprotective and Adipocyte Browning Effects Promoted by the Eutomer of Dual sEH\/PPARgamma Modulator - Hartmann_2021_J.Med.Chem_64_2815 |
| Author(s) : Hartmann M , Bibli SI , Tews D , Ni X , Kircher T , Kramer JS , Kilu W , Heering J , Hernandez-Olmos V , Weizel L , Scriba GKE , Krait S , Knapp S , Chaikuad A , Merk D , Fleming I , Fischer-Posovszky P , Proschak E |
| Ref : Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 64 :2815 , 2021 |
| Abstract : Hartmann_2021_J.Med.Chem_64_2815 |
| ESTHER : Hartmann_2021_J.Med.Chem_64_2815 |
| PubMedSearch : Hartmann_2021_J.Med.Chem_64_2815 |
| PubMedID: 33620196 |