Pipecuronium
neuromuscular non depolarising blocking drug long lasting similar in duration of action to pancuronium, aminosteroids related to pancuronium and vecuronium,. It is used as a muscle relaxant during anesthesia and surgical procedures
General
Type : Neuromuscular Nondepolarizing Agents,Nicotinic antagonist,Aminosteroid,Piperazine,Phenanthrene,Not A\/B H target
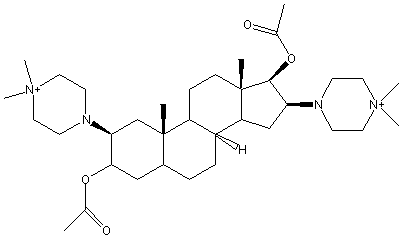
Chemical_Nomenclature : [(2R,3R,5R,8R,9R,10S,13S,14R,16R,17S) -17-acetyloxy-2,16-bis(4,4-dimethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydropyrazin-1-yl) -10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17 -tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] acetate
Canonical SMILES : CC(=O)OC1CC2CCC3C(C2(CC1N4CC[N+](CC4)(C)C)C)CCC5(C3CC(C5OC(=O)C)N6CC[N+](CC6)(C)C)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C35H62N4O4\/c1-24(40)42-32-21-26-9-10-27-28(35(26,4)23-31(32)37-15-19-39(7,8)20-16-37)11-12-34(3)29(27)22-30(33(34)43-25(2)41)36-13-17-38(5,6)18-14-36\/h26-33H,9-23H2,1-8H3\/q+2\/t26-,27+,28-,29-,30-,31-,32-,33-,34-,35-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : OWWLUIWOFHMHOQ-XGHATYIMSA-N
Other name(s) : C07554,Piperazinium
MW : 602.891
Formula : C35H62N4O4+2
CAS_number : 68399-58-6 || 52212-02-9 || 68399-57-5
PubChem : 50192
UniChem : OWWLUIWOFHMHOQ-XGHATYIMSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Pipecuronium_bromide
Target
References (7)
| Title : Inhibition of human plasma cholinesterase and erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase by nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents - Kato_2000_J.Anesth_14_30 |
| Author(s) : Kato M , Hashimoto Y , Horinouchi T , Ando T , Ito J , Yamanaka H |
| Ref : J Anesth , 14 :30 , 2000 |
| Abstract : Kato_2000_J.Anesth_14_30 |
| ESTHER : Kato_2000_J.Anesth_14_30 |
| PubMedSearch : Kato_2000_J.Anesth_14_30 |
| PubMedID: 14564607 |
| Title : Clinical pharmacokinetics of the newer neuromuscular blocking drugs - Atherton_1999_Clin.Pharmacokinet_36_169 |
| Author(s) : Atherton DP , Hunter JM |
| Ref : Clinical Pharmacokinetics , 36 :169 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Atherton_1999_Clin.Pharmacokinet_36_169 |
| ESTHER : Atherton_1999_Clin.Pharmacokinet_36_169 |
| PubMedSearch : Atherton_1999_Clin.Pharmacokinet_36_169 |
| PubMedID: 10223167 |
| Title : New neuromuscular blocking drugs [see comments] - Hunter_1995_N.Engl.J.Med_332_1691 |
| Author(s) : Hunter JM |
| Ref : N Engl J Med , 332 :1691 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Hunter_1995_N.Engl.J.Med_332_1691 |
| ESTHER : Hunter_1995_N.Engl.J.Med_332_1691 |
| PubMedSearch : Hunter_1995_N.Engl.J.Med_332_1691 |
| PubMedID: 7760871 |
| Title : Newer neuromuscular blocking agents - Bevan_1994_Pharmacol.Toxicol_74_3 |
| Author(s) : Bevan DR |
| Ref : Pharmacol Toxicol , 74 :3 , 1994 |
| Abstract : Bevan_1994_Pharmacol.Toxicol_74_3 |
| ESTHER : Bevan_1994_Pharmacol.Toxicol_74_3 |
| PubMedSearch : Bevan_1994_Pharmacol.Toxicol_74_3 |
| PubMedID: 8159634 |
| Title : Newer neuromuscular blocking drugs. An overview of their clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use - Mirakhur_1992_Drugs_44_182 |
| Author(s) : Mirakhur RK |
| Ref : Drugs , 44 :182 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Mirakhur_1992_Drugs_44_182 |
| ESTHER : Mirakhur_1992_Drugs_44_182 |
| PubMedSearch : Mirakhur_1992_Drugs_44_182 |
| PubMedID: 1382013 |
| Title : Characterization of somatodendritic neuronal nicotinic receptors located on the myenteric plexus - Torocsik_1991_Eur.J.Pharmacol_202_297 |
| Author(s) : Torocsik A , Oberfrank F , Sershen H , Lajtha A , Nemesy K , Vizi ES |
| Ref : European Journal of Pharmacology , 202 :297 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Torocsik_1991_Eur.J.Pharmacol_202_297 |
| ESTHER : Torocsik_1991_Eur.J.Pharmacol_202_297 |
| PubMedSearch : Torocsik_1991_Eur.J.Pharmacol_202_297 |
| PubMedID: 1748153 |
| Title : Prejunctional modulation of acetylcholine release from the skeletal neuromuscular junction: link between positive (nicotinic)- and negative (muscarinic)-feedback modulation - Vizi_1989_Br.J.Pharmacol_97_65 |
| Author(s) : Vizi ES , Somogyi GT |
| Ref : British Journal of Pharmacology , 97 :65 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Vizi_1989_Br.J.Pharmacol_97_65 |
| ESTHER : Vizi_1989_Br.J.Pharmacol_97_65 |
| PubMedSearch : Vizi_1989_Br.J.Pharmacol_97_65 |
| PubMedID: 2720313 |