Oxamyl
Some trade names include Vydate, DPX 1410, Oxamimidic Acid, dioxamyl
General
Type : Carbamate,Sulfur Compound
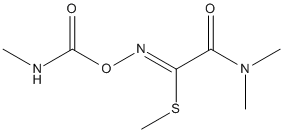
Chemical_Nomenclature : methyl (1Z)-2-(dimethylamino)-N-(methylcarbamoyloxy)-2-oxoethanimidothioate
Canonical SMILES : CNC(=O)ON=C(C(=O)N(C)C)SC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C7H13N3O3S\/c1-8-7(12)13-9-5(14-4)6(11)10(2)3\/h1-4H3,(H,8,12)\/b9-5-
InChIKey : KZAUOCCYDRDERY-UITAMQMPSA-N
Other name(s) : N,N-dimethyl-2-methylcarbamoyloxyimino-2-(methylthio)-acetamide2-(dimethylamino)-N-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]-2-oxoethanimidothioic acid methyl ester,N,N-dimethyl-2-methylcarbamoyloxyimino-2-(methylthio)acetamide,N,N-dimethyl-alpha-methylcarbamoxyloxyimino-alpha-(methylthio)acetamide,S-methyl N',N'-dimethyl-N-(methylcarbamoyloxy)-1-thio-oxamimidate(I),methyl 2-(dimethylamino)-N-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]-2-oxoethanimidothioate,Thioxamyl,Vydate L,DPX 1410,Thioxamyl and Oxamyl
MW : 219.36
Formula : C7H13N3O3S
CAS_number : 23135-22-0
PubChem : 9595287
UniChem : KZAUOCCYDRDERY-UITAMQMPSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Oxamyl
Target
References (23)
| Title : Microarray and Functional Pathway Analyses Revealed Significantly Elevated Gene Expressions Associated with Metabolic Resistance to Oxamyl (Vydate) in Lygus lineolaris - Zhu_2024_Toxics_12_ |
| Author(s) : Zhu YC , Du Y , Liu X , Portilla M , Chen J , Wang Y |
| Ref : Toxics , 12 : , 2024 |
| Abstract : Zhu_2024_Toxics_12_ |
| ESTHER : Zhu_2024_Toxics_12_ |
| PubMedSearch : Zhu_2024_Toxics_12_ |
| PubMedID: 38535921 |
| Title : Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Reversible Inhibitors: The Role of Oxamyl in the Production of Poisoned Baits - Biancardi_2022_Toxics_10_ |
| Author(s) : Biancardi A , Aimo C , Piazza P , Lo Chiano F , Rubini S , Baldini E , Vertuani S , Manfredini S |
| Ref : Toxics , 10 : , 2022 |
| Abstract : Biancardi_2022_Toxics_10_ |
| ESTHER : Biancardi_2022_Toxics_10_ |
| PubMedSearch : Biancardi_2022_Toxics_10_ |
| PubMedID: 36006110 |
| Title : Isolation of Oxamyl-degrading Bacteria and Identification of cehA as a Novel Oxamyl Hydrolase Gene - Rousidou_2016_Front.Microbiol_7_616 |
| Author(s) : Rousidou K , Chanika E , Georgiadou D , Soueref E , Katsarou D , Kolovos P , Ntougias S , Tourna M , Tzortzakakis EA , Karpouzas DG |
| Ref : Front Microbiol , 7 :616 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Rousidou_2016_Front.Microbiol_7_616 |
| ESTHER : Rousidou_2016_Front.Microbiol_7_616 |
| PubMedSearch : Rousidou_2016_Front.Microbiol_7_616 |
| PubMedID: 27199945 |
| Title : Potential enhancement of degradation of the nematicides aldicarb, oxamyl and fosthiazate in UK agricultural soils through repeated applications - Osborn_2010_Pest.Manag.Sci_66_253 |
| Author(s) : Osborn RK , Edwards SG , Wilcox A , Haydock PP |
| Ref : Pest Manag Sci , 66 :253 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Osborn_2010_Pest.Manag.Sci_66_253 |
| ESTHER : Osborn_2010_Pest.Manag.Sci_66_253 |
| PubMedSearch : Osborn_2010_Pest.Manag.Sci_66_253 |
| PubMedID: 19862790 |
| Title : Time course of cholinesterase inhibition in adult rats treated acutely with carbaryl, carbofuran, formetanate, methomyl, methiocarb, oxamyl or propoxur - Padilla_2007_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_219_202 |
| Author(s) : Padilla S , Marshall RS , Hunter DL , Lowit A |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 219 :202 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Padilla_2007_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_219_202 |
| ESTHER : Padilla_2007_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_219_202 |
| PubMedSearch : Padilla_2007_Toxicol.Appl.Pharmacol_219_202 |
| PubMedID: 17197007 |
| Title : Inhibition of 17 beta-estradiol and progesterone activity in human breast and endometrial cancer cells by carbamate insecticides - Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| Author(s) : Klotz DM , Arnold SF , McLachlan JA |
| Ref : Life Sciences , 60 :1467 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| ESTHER : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| PubMedSearch : Klotz_1997_Life.Sci_60_1467 |
| PubMedID: 9126867 |
| Title : Solid-phase extraction of polar pesticides from environmental water samples on graphitized carbon and Empore-activated carbon disks and on- line coupling to octadecyl-bonded silica analytical columns - Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| Author(s) : Slobodnik J , Oztezkizan O , Lingeman H , Brinkman UA |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 750 :227 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| ESTHER : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| PubMedSearch : Slobodnik_1996_J.Chromatogr.A_750_227 |
| PubMedID: 8938388 |
| Title : Acute toxic effects of oxamyl in the rat - Fayez_1992_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_18_155 |
| Author(s) : Fayez V , Kilgore WW |
| Ref : Fundamental & Applied Toxicology , 18 :155 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Fayez_1992_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_18_155 |
| ESTHER : Fayez_1992_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_18_155 |
| PubMedSearch : Fayez_1992_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_18_155 |
| PubMedID: 1318238 |
| Title : Relative inhibition of rat plasma and erythrocyte cholinesterases by pesticide combinations - Iyaniwura_1991_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_33_166 |
| Author(s) : Iyaniwura TT |
| Ref : Vet Hum Toxicol , 33 :166 , 1991 |
| Abstract : Iyaniwura_1991_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_33_166 |
| ESTHER : Iyaniwura_1991_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_33_166 |
| PubMedSearch : Iyaniwura_1991_Vet.Hum.Toxicol_33_166 |
| PubMedID: 2035247 |
| Title : Acute toxicity studies with oxamyl - Kennedy_1986_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_6_423 |
| Author(s) : Kennedy GL, Jr. |
| Ref : Fundamental & Applied Toxicology , 6 :423 , 1986 |
| Abstract : Kennedy_1986_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_6_423 |
| ESTHER : Kennedy_1986_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_6_423 |
| PubMedSearch : Kennedy_1986_Fundam.Appl.Toxicol_6_423 |
| PubMedID: 3699328 |
| Title : [Chromatographic methods of determining Vydate in the air] - Os'kina_1985_Gig.Sanit_8_49 |
| Author(s) : Os'kina VN |
| Ref : Gigiena i Sanitariia , 8 :49 , 1985 |
| Abstract : Os'kina_1985_Gig.Sanit_8_49 |
| ESTHER : Os'kina_1985_Gig.Sanit_8_49 |
| PubMedSearch : Os'kina_1985_Gig.Sanit_8_49 |
| PubMedID: 4065605 |
| Title : Observations on the influence of water and soil pH on the persistence of insecticides - Chapman_1982_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_17_487 |
| Author(s) : Chapman RA , Cole CM |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 17 :487 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Chapman_1982_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_17_487 |
| ESTHER : Chapman_1982_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_17_487 |
| PubMedSearch : Chapman_1982_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_17_487 |
| PubMedID: 7175098 |
| Title : Gas-liquid chromatographic method for determining oxamyl in peppers, tomatoes, and cucumbers - Greenberg_1981_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_64_1216 |
| Author(s) : Greenberg RS |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 64 :1216 , 1981 |
| Abstract : Greenberg_1981_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_64_1216 |
| ESTHER : Greenberg_1981_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_64_1216 |
| PubMedSearch : Greenberg_1981_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_64_1216 |
| PubMedID: 7287618 |
| Title : Dislodgable insecticide residues on cotton foliage: fenvalarate, permethrin, sulprofos, chlorpyrifos, methyl parathion, EPN, oxamyl, and profenofos - |
| Author(s) : Buck NA , Estesen BJ , Ware GW |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 24 :283 , 1980 |
| PubMedID: 6153915 |
| Title : In vitro rumen metabolism of 14C-labeled oxamyl and selected metabolites of oxamyl - |
| Author(s) : Belasco IJ , Harvey J, Jr. |
| Ref : Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry , 28 :689 , 1980 |
| PubMedID: 7462485 |
| Title : Determination of residues of methomyl and oxamyl and their oximes in crops by gas-liquid chromatography of oxime trimethylsilyl ethers - Chapman_1979_J.Chromatogr_171_249 |
| Author(s) : Chapman RA , Harris CR |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography , 171 :249 , 1979 |
| Abstract : Chapman_1979_J.Chromatogr_171_249 |
| ESTHER : Chapman_1979_J.Chromatogr_171_249 |
| PubMedSearch : Chapman_1979_J.Chromatogr_171_249 |
| PubMedID: 546852 |
| Title : Metabolism of oxamyl in mice and twospotted spider mites - |
| Author(s) : Chang KM , Knowles CO |
| Ref : Arch Environ Contam Toxicol , 8 :499 , 1979 |
| PubMedID: 485217 |
| Title : High pressure liquid chromatographic determination of methomyl and oxamyl on vegetable crops - Thean_1978_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_61_15 |
| Author(s) : Thean JE , Fong WG , Lorenz DR , Stephens TL |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 61 :15 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Thean_1978_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_61_15 |
| ESTHER : Thean_1978_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_61_15 |
| PubMedSearch : Thean_1978_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_61_15 |
| PubMedID: 621190 |
| Title : Metabolism of oxamyl and selected metabolites in the rat - |
| Author(s) : Harvey J, Jr. , Han JC |
| Ref : Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry , 26 :902 , 1978 |
| PubMedID: 670572 |
| Title : Titrimetric method for the determination of oxamyl residues in crops and soils - |
| Author(s) : Singhal JP , Khan S , Bansal OP |
| Ref : Analyst , 103 :872 , 1978 |
| PubMedID: 686387 |
| Title : Spectrophotometric determination of oxamyl as copper dithiocarbamate - |
| Author(s) : Singhal JP , Khan S , Bansal OP |
| Ref : Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry , 25 :377 , 1977 |
| PubMedID: 838976 |
| Title : Determination of residues of oxamyl in crops and soils by gas - liquid chromatography - |
| Author(s) : Bromilow RH |
| Ref : Analyst , 101 :982 , 1976 |
| PubMedID: 1015622 |