NEDPA
tabun analogue. Less toxic but giving the same adduct. Not to be confonded with Ephenidine (NEDPA or EPE)
General
Type : Organophosphate,Surrogate OP,Nerve Agent G-series,pNP
Chemical_Nomenclature : N-[ethoxy-(4-nitrophenoxy)phosphoryl]-N-methylmethanamine
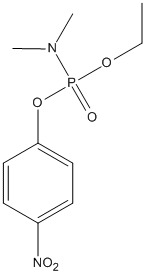
Canonical SMILES : CCOP(=O)(N(C)C)OC1=CC=C(C=C1)[N+](=O)[O-]
InChI : InChI=1S\/C10H15N2O5P\/c1-4-16-18(15,11(2)3)17-10-7-5-9(6-8-10)12(13)14\/h5-8H,4H2,1-3H3
InChIKey : VLJXABBXKHWHBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 4-Nitrophenyl ethyl dimethylphosphoramidate
MW : 274.21
Formula : C10H15N2O5P
CAS_number :
PubChem : 123172233
UniChem : VLJXABBXKHWHBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : NEDPA ligand of proteins in family: ACHE || Cholesterol_esterase
Stucture :
Protein : torca-ACHE || human-CEL
References (2)
| Title : X-ray structures of human bile-salt activated lipase conjugated to nerve agents surrogates - Touvrey_2019_Toxicology_411_15 |
| Author(s) : Touvrey C , Courageux C , Guillon V , Terreux R , Nachon F , Brazzolotto X |
| Ref : Toxicology , 411 :15 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Touvrey_2019_Toxicology_411_15 |
| ESTHER : Touvrey_2019_Toxicology_411_15 |
| PubMedSearch : Touvrey_2019_Toxicology_411_15 |
| PubMedID: 30359675 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CEL |
| Title : Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo inhibition potencies of highly relevant nerve agent surrogates - Meek_2012_Toxicol.Sci_126_525 |
| Author(s) : Meek EC , Chambers HW , Coban A , Funck KE , Pringle RB , Ross MK , Chambers JE |
| Ref : Toxicol Sci , 126 :525 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Meek_2012_Toxicol.Sci_126_525 |
| ESTHER : Meek_2012_Toxicol.Sci_126_525 |
| PubMedSearch : Meek_2012_Toxicol.Sci_126_525 |
| PubMedID: 22247004 |