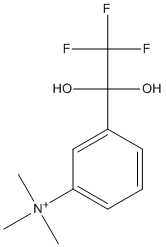
NAF
Transition state analogue TMTFA is an equilibrium mixture of the free ketone and ketone hydrate NAF in aqueous solution, with a hydration equilibrium constant of 60 000
General
Type : Trifluoro,Quaternary compound,Transition state analogue
Chemical_Nomenclature : trimethyl-[3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1,1-dihydroxyethyl)phenyl]azanium
Canonical SMILES : C[N+](C)(C)C1=CC=CC(=C1)C(C(F)(F)F)(O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C11H15F3NO2\/c1-15(2,3)9-6-4-5-8(7-9)10(16,17)11(12,13)14\/h4-7,16-17H,1-3H3\/q+1
InChIKey : KGVDBJQLTHWAJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : N,N,N-trimethyl-3-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1,1-dihydroxyethyl)anilinium,M-(n,n,n-trimethylammonio)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1,1-dihydroxyethylbenzene,AC1L1H65,SCHEMBL4311749,CHEBI:44394
MW : 250.23
Formula : C11H15F3NO2+
CAS_number :
PubChem : 3991
UniChem : KGVDBJQLTHWAJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Target
Families : NAF ligand of proteins in family
ACHE
Protein :
mouse-ACHE
torca-ACHE
References (3)
| Title : Substrate and product trafficking through the active center gorge of acetylcholinesterase analyzed by crystallography and equilibrium binding - Bourne_2006_J.Biol.Chem_281_29256 |
| Author(s) : Bourne Y , Radic Z , Sulzenbacher G , Kim E , Taylor P , Marchot P |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 281 :29256 , 2006 |
| Abstract : Bourne_2006_J.Biol.Chem_281_29256 |
| ESTHER : Bourne_2006_J.Biol.Chem_281_29256 |
| PubMedSearch : Bourne_2006_J.Biol.Chem_281_29256 |
| PubMedID: 16837465 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: mouse-ACHE |
| Title : A preliminary comparison of structural models for catalytic intermediates of acetylcholinesterase - Silman_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_43 |
| Author(s) : Silman I , Millard CB , Ordentlich A , Greenblatt HM , Harel M , Barak D , Shafferman A , Sussman JL |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 119-120 :43 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Silman_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_43 |
| ESTHER : Silman_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_43 |
| PubMedSearch : Silman_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_43 |
| PubMedID: 10421437 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: torca-ACHE |
| Title : The X-ray structure of a transition state analog complex reveals the molecular origins of the catalytic power and substrate specificity of acetylcholinesterase. - |
| Author(s) : Harel M , Quinn DM , Nair HK , Silman I , Sussman JL |
| Ref : Journal of the American Chemical Society , 118 :2340 , 1996 |
| PubMedID: |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: torca-ACHE |