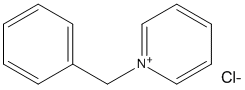
N-Benzylpyridinium
General
Type : Pyridine
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1-benzylpyridin-1-ium chloride
Canonical SMILES : C1=CC=C(C=C1)C[N+]2=CC=CC=C2.[Cl-]
InChI : InChI=1S\/C12H12N.ClH\/c1-3-7-12(8-4-1)11-13-9-5-2-6-10-13\;\/h1-10H,11H2\;1H\/q+1\;\/p-1
InChIKey : GNPSDJOWGWWXSS-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Other name(s) : 1-Benzylpyridinium chloride,Pyridinium, 1-(phenylmethyl)-, chloride,2876-13-3,1-benzylpyridin-1-ium chloride,Pyridinium, 1-(phenylmethyl)-, chloride (1:1),benzylpyridinium chloride
MW : 205.68
Formula : C12H12ClN
CAS_number : 2876-13-3
PubChem : 76135
UniChem : GNPSDJOWGWWXSS-UHFFFAOYSA-M
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (3)
| Title : Benzofuran-derived benzylpyridinium bromides as potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors - Baharloo_2015_Eur.J.Med.Chem_93C_196 |
| Author(s) : Baharloo F , Moslemin MH , Nadri H , Asadipour A , Mahdavi M , Emami S , Firoozpour L , Mohebat R , Shafiee A , Foroumadi A |
| Ref : Eur Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 93C :196 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Baharloo_2015_Eur.J.Med.Chem_93C_196 |
| ESTHER : Baharloo_2015_Eur.J.Med.Chem_93C_196 |
| PubMedSearch : Baharloo_2015_Eur.J.Med.Chem_93C_196 |
| PubMedID: 25681712 |
| Title : Indolinone-based acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis, biological activity and molecular modeling - Akrami_2014_Eur.J.Med.Chem_84C_375 |
| Author(s) : Akrami H , Mirjalili BF , Khoobi M , Nadri H , Moradi A , Sakhteman A , Emami S , Foroumadi A , Shafiee A |
| Ref : Eur Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 84C :375 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Akrami_2014_Eur.J.Med.Chem_84C_375 |
| ESTHER : Akrami_2014_Eur.J.Med.Chem_84C_375 |
| PubMedSearch : Akrami_2014_Eur.J.Med.Chem_84C_375 |
| PubMedID: 25036795 |
| Title : Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and docking study of 5-oxo-4,5-dihydropyrano[3,2-c]chromene derivatives as acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors - Khoobi_2013_Eur.J.Med.Chem_68C_260 |
| Author(s) : Khoobi M , Alipour M , Sakhteman A , Nadri H , Moradi A , Ghandi M , Emami S , Foroumadi A , Shafiee A |
| Ref : Eur Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 68C :260 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Khoobi_2013_Eur.J.Med.Chem_68C_260 |
| ESTHER : Khoobi_2013_Eur.J.Med.Chem_68C_260 |
| PubMedSearch : Khoobi_2013_Eur.J.Med.Chem_68C_260 |
| PubMedID: 23988409 |