Mevinphos
General
Type : Organophosphate
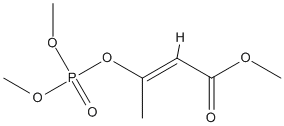
Chemical_Nomenclature : methyl (E)-3-dimethoxyphosphoryloxybut-2-enoate
Canonical SMILES : CC(=CC(=O)OC)OP(=O)(OC)OC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C7H13O6P\/c1-6(5-7(8)10-2)13-14(9,11-3)12-4\/h5H,1-4H3\/b6-5+
InChIKey : GEPDYQSQVLXLEU-AATRIKPKSA-N
Other name(s) : 3-[(Dimethoxyphosphinyl)oxy]-2-butenoic acid methyl ester,2-methoxycarbonyl-1-methylvinyl dimethyl phosphate,methyl 3-(dimethoxyphosphinoyloxy)but-2-enoate,methyl 3-[(dimethoxyphosphinyl)oxy]-2-butenoate,Apavinphos,CMDP,ENT 22374,Fosdrin,Gesfid,Meniphos,Menite,Mevinox,OS-2046,PD5,Mevinphos,Phosfene Duraphos and Phosdrin
MW : 224.15
Formula : C7H13O6P
CAS_number : 7786-34-7 || 26718-65-0
PubChem : 5355863
UniChem : GEPDYQSQVLXLEU-AATRIKPKSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Mevinphos
Target
References (35)
| Title : Muscarinic receptor-independent activation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in rostral ventrolateral medulla underlies the sympathoexcitatory phase of cardiovascular responses during mevinphos intoxication in the rat - Tsai_2007_Shock_27_559 |
| Author(s) : Tsai CY , Wu CH , Chan SH , Chang AY |
| Ref : Shock , 27 :559 , 2007 |
| Abstract : Tsai_2007_Shock_27_559 |
| ESTHER : Tsai_2007_Shock_27_559 |
| PubMedSearch : Tsai_2007_Shock_27_559 |
| PubMedID: 17438462 |
| Title : [The effect of parasympatholytics on the therapeutic effectiveness of the oxime HI-6 against organophosphorus compounds (Soman, substance VX, Fosdrin) in mice] - Kassa_1997_Cas.Lek.Cesk_136_124 |
| Author(s) : Kassa J , Vachek J |
| Ref : Casopis Lekaru Ceskych , 136 :124 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Kassa_1997_Cas.Lek.Cesk_136_124 |
| ESTHER : Kassa_1997_Cas.Lek.Cesk_136_124 |
| PubMedSearch : Kassa_1997_Cas.Lek.Cesk_136_124 |
| PubMedID: 9221183 |
| Title : The efficacy of monopyridinium (2-PAAM, 2-PAEM) and bispyridinium (obidoxime, HI-6) oximes against mevinphos in mice - Kassa_1997_Pharmacol.Toxicol_81_144 |
| Author(s) : Kassa J , Bielavsky J |
| Ref : Pharmacol Toxicol , 81 :144 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Kassa_1997_Pharmacol.Toxicol_81_144 |
| ESTHER : Kassa_1997_Pharmacol.Toxicol_81_144 |
| PubMedSearch : Kassa_1997_Pharmacol.Toxicol_81_144 |
| PubMedID: 9335072 |
| Title : Risk factors for systemic illnesses following agricultural exposures to restricted organophosphates in California, 1984-1988 - Weinbaum_1997_Am.J.Ind.Med_31_572 |
| Author(s) : Weinbaum Z , Schenker MB , Gold EB , Samuels SJ , O'Malley MA |
| Ref : American Journal of Industrial Medicine , 31 :572 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Weinbaum_1997_Am.J.Ind.Med_31_572 |
| ESTHER : Weinbaum_1997_Am.J.Ind.Med_31_572 |
| PubMedSearch : Weinbaum_1997_Am.J.Ind.Med_31_572 |
| PubMedID: 9099360 |
| Title : Aphicide persistence on spinach and mustard greens - Sweeden_1997_J.Econ.Entomol_90_195 |
| Author(s) : Sweeden MB , McLeod PJ |
| Ref : J Econ Entomol , 90 :195 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Sweeden_1997_J.Econ.Entomol_90_195 |
| ESTHER : Sweeden_1997_J.Econ.Entomol_90_195 |
| PubMedSearch : Sweeden_1997_J.Econ.Entomol_90_195 |
| PubMedID: 9071890 |
| Title : [Comparison of the therapeutic effectiveness of selected cholinesterase reactivators with atropine in acute fosdrine poisoning in mice] - Kassa_1996_Ceska.Slov.Farm_45_31 |
| Author(s) : Kassa J , Bajgar J |
| Ref : Ceska a Slovenska Farmacie , 45 :31 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Kassa_1996_Ceska.Slov.Farm_45_31 |
| ESTHER : Kassa_1996_Ceska.Slov.Farm_45_31 |
| PubMedSearch : Kassa_1996_Ceska.Slov.Farm_45_31 |
| PubMedID: 8620316 |
| Title : Acute pancreatitis following organophosphate intoxication - Hsiao_1996_J.Toxicol.Clin.Toxicol_34_343 |
| Author(s) : Hsiao CT , Yang CC , Deng JF , Bullard MJ , Liaw SJ |
| Ref : Journal of Toxicology Clinical Toxicology , 34 :343 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Hsiao_1996_J.Toxicol.Clin.Toxicol_34_343 |
| ESTHER : Hsiao_1996_J.Toxicol.Clin.Toxicol_34_343 |
| PubMedSearch : Hsiao_1996_J.Toxicol.Clin.Toxicol_34_343 |
| PubMedID: 8667474 |
| Title : Risks from occupational and dietary exposure to mevinphos - Cochran_1996_Rev.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_146_1 |
| Author(s) : Cochran RC , Formoli TA , Silva MH , Kellner TP , Lewis CM , Pfeifer KF |
| Ref : Rev Environ Contam Toxicol , 146 :1 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Cochran_1996_Rev.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_146_1 |
| ESTHER : Cochran_1996_Rev.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_146_1 |
| PubMedSearch : Cochran_1996_Rev.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_146_1 |
| PubMedID: 8714219 |
| Title : [Comparison of the effect of selected cholinesterase reactivators combined with atropine on soman and fosdrin toxicity in mice] - Kassa_1995_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove.Suppl_38_63 |
| Author(s) : Kassa J |
| Ref : Sb Ved Pr Lek Fak Karlovy Univerzity Hradci Kralove Suppl , 38 :63 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Kassa_1995_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove.Suppl_38_63 |
| ESTHER : Kassa_1995_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove.Suppl_38_63 |
| PubMedSearch : Kassa_1995_Sb.Ved.Pr.Lek.Fak.Karlovy.Univerzity.Hradci.Kralove.Suppl_38_63 |
| PubMedID: 9441373 |
| Title : Exposure of sprayers and plant handlers to mevinphos in Finnish greenhouses - Kangas_1993_Am.Ind.Hyg.Assoc.J_54_150 |
| Author(s) : Kangas J , Laitinen S , Jauhiainen A , Savolainen K |
| Ref : American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal , 54 :150 , 1993 |
| Abstract : Kangas_1993_Am.Ind.Hyg.Assoc.J_54_150 |
| ESTHER : Kangas_1993_Am.Ind.Hyg.Assoc.J_54_150 |
| PubMedSearch : Kangas_1993_Am.Ind.Hyg.Assoc.J_54_150 |
| PubMedID: 8480630 |
| Title : Biological monitoring of workers exposed to mevinphos in greenhouses - |
| Author(s) : Jauhiainen A , Kangas J , Laitinen S , Savolainen K |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 49 :37 , 1992 |
| PubMedID: 1392293 |
| Title : Chromatographic analysis of cis- and trans-mevinphos in poisoned wildlife - Allender_1992_J.Chromatogr_609_315 |
| Author(s) : Allender WJ , Keegan J |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography , 609 :315 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Allender_1992_J.Chromatogr_609_315 |
| ESTHER : Allender_1992_J.Chromatogr_609_315 |
| PubMedSearch : Allender_1992_J.Chromatogr_609_315 |
| PubMedID: 1430046 |
| Title : Effect of colloidal soil components on the adsorption of mevinphos - |
| Author(s) : Sanchez-Camazano M , Sanchez-Martin MJ |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 44 :106 , 1990 |
| PubMedID: 2306526 |
| Title : Electroretinographic study of the white mouse intoxicated by organo- phosphorus: mevinphos and malathion - Carricaburu_1981_Toxicol.Eur.Res_3_87 |
| Author(s) : Carricaburu P , Lacroix R , Lacroix J |
| Ref : Toxicol Eur Res , 3 :87 , 1981 |
| Abstract : Carricaburu_1981_Toxicol.Eur.Res_3_87 |
| ESTHER : Carricaburu_1981_Toxicol.Eur.Res_3_87 |
| PubMedSearch : Carricaburu_1981_Toxicol.Eur.Res_3_87 |
| PubMedID: 7245190 |
| Title : Evaluation of Bravo, Phosdrin and Telvar as possible environmental mutagens - |
| Author(s) : Kahlon PS , Banerjee MR |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 22 :365 , 1979 |
| PubMedID: 465804 |
| Title : Neurological effects and cholinesterase inhibition in man by subacute administration of mevinphos - |
| Author(s) : Verberk MM , Salle HJ |
| Ref : Activitas Nervosa Superior (Praha) , 2 :333 , 1979 |
| PubMedID: 233186 |
| Title : A note on dermal poisoning from mevinphos and parathion - |
| Author(s) : Reichert ER , Klemmer HW , Haley TJ |
| Ref : Clinical Toxicology , 12 :33 , 1978 |
| PubMedID: 630818 |
| Title : [Changes in the electromyographic potentials in cats poisoned with superlethal doses of phosdrin and treated with doline] - Mashkova_1978_Eksp.Med.Morfol_17_32 |
| Author(s) : Mashkova D , Kotev G , Kolchev K |
| Ref : Eksperimentalna Meditsina i Morfologii , 17 :32 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Mashkova_1978_Eksp.Med.Morfol_17_32 |
| ESTHER : Mashkova_1978_Eksp.Med.Morfol_17_32 |
| PubMedSearch : Mashkova_1978_Eksp.Med.Morfol_17_32 |
| PubMedID: 639745 |
| Title : Evaluation of cytotoxic responses caused by selected organophosphorus esters in chick sympathetic ganglia cultures - Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| Author(s) : Obersteiner EJ , Sharma RP |
| Ref : Can J Comp Med , 42 :80 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| ESTHER : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| PubMedSearch : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| PubMedID: 565668 |
| Title : [Electrophysiologic shifts in the functional antagonism between phosphororganic pesticides and their antidotes] - Mashkova_1977_Eksp.Med.Morfol_16_216 |
| Author(s) : Mashkova D , Kolchev K , Kotev G |
| Ref : Eksperimentalna Meditsina i Morfologii , 16 :216 , 1977 |
| Abstract : Mashkova_1977_Eksp.Med.Morfol_16_216 |
| ESTHER : Mashkova_1977_Eksp.Med.Morfol_16_216 |
| PubMedSearch : Mashkova_1977_Eksp.Med.Morfol_16_216 |
| PubMedID: 590179 |
| Title : Incipient cholinesterase inhibition in volunteers ingesting monocrotophos or mevinphos for one month - |
| Author(s) : Verberk MM |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 42 :345 , 1977 |
| PubMedID: 595013 |
| Title : Some behavioral effects of pesticides: The interaction of mevinphos and atropine in pigeons - Mertens_1976_Aviat.Space.Environ.Med_47_137 |
| Author(s) : Mertens HW , Steen JA , Lewis MF |
| Ref : Aviat Space Environ Med , 47 :137 , 1976 |
| Abstract : Mertens_1976_Aviat.Space.Environ.Med_47_137 |
| ESTHER : Mertens_1976_Aviat.Space.Environ.Med_47_137 |
| PubMedSearch : Mertens_1976_Aviat.Space.Environ.Med_47_137 |
| PubMedID: 1252204 |
| Title : Acute toxicity of mevinphos to gerbils - |
| Author(s) : Steen JA , Hanneman GD , Nelson PL , Folk ED |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 36 :195 , 1976 |
| PubMedID: 1273839 |
| Title : Effects of mevinphos (Phosdrin) on unit discharge patterns in avian hippocampus - Revzin_1976_Aviat.Space.Environ.Med_47_608 |
| Author(s) : Revzin AM |
| Ref : Aviat Space Environ Med , 47 :608 , 1976 |
| Abstract : Revzin_1976_Aviat.Space.Environ.Med_47_608 |
| ESTHER : Revzin_1976_Aviat.Space.Environ.Med_47_608 |
| PubMedSearch : Revzin_1976_Aviat.Space.Environ.Med_47_608 |
| PubMedID: 938396 |
| Title : [Effect of arpenal on the EMG-potentials of the anterior tibial muscle in cats during acute phosdrine poisoning] - Mashkova_1976_Eksp.Med.Morfol_15_237 |
| Author(s) : Mashkova D |
| Ref : Eksperimentalna Meditsina i Morfologii , 15 :237 , 1976 |
| Abstract : Mashkova_1976_Eksp.Med.Morfol_15_237 |
| ESTHER : Mashkova_1976_Eksp.Med.Morfol_15_237 |
| PubMedSearch : Mashkova_1976_Eksp.Med.Morfol_15_237 |
| PubMedID: 1017412 |
| Title : The effects of mevinphos on appetitive operant behavior in the gerbil - Mertens_1975_Psychopharmacologia_41_47 |
| Author(s) : Mertens HW , Steen JO , Lewis MF |
| Ref : Psychopharmacologia , 41 :47 , 1975 |
| Abstract : Mertens_1975_Psychopharmacologia_41_47 |
| ESTHER : Mertens_1975_Psychopharmacologia_41_47 |
| PubMedSearch : Mertens_1975_Psychopharmacologia_41_47 |
| PubMedID: 1124269 |
| Title : The minimal oral toxicity level for mevinphos in man - |
| Author(s) : Rider JA , Puletti EJ , Swader JI |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 32 :97 , 1975 |
| PubMedID: 1135882 |
| Title : Short-term toxicity of mevinphos in man - |
| Author(s) : Holmes JH , Starr HG, Jr. , Kaulla KNv , Hanisch RC |
| Ref : Archives of Environmental Health , 29 :84 , 1974 |
| PubMedID: 4835176 |
| Title : Some behavioral effects of pesticides: phosdrin and free-operant escape- avoidance behavior in gerbils - |
| Author(s) : Mertens HW , Lewis MF , Steen JA |
| Ref : Aerospace Medicine , 45 :1171 , 1974 |
| PubMedID: 4429058 |
| Title : [Changes in the spontaneous and evoked EEG activity of the cat's brain following administration of a lethal dose of phosdrin and treatment with antidote AV-72] - |
| Author(s) : Kotev G , Atsev E , Dishovski K , Kolchev K |
| Ref : Eksperimentalna Meditsina i Morfologii , 13 :153 , 1974 |
| PubMedID: 4466638 |
| Title : Behavioral changes from chronic exposure to pesticides used in aerial application: effects of phosdrin on the performance of monkeys and pigeons on variable interval reinforcement schedules - |
| Author(s) : Lewis MF , Mertens HW , Steen JA |
| Ref : Aerospace Medicine , 44 :290 , 1973 |
| PubMedID: 4632217 |