Methylchlorpyrifos
General
Type : Organophosphate,Sulfur Compound,Organothiophosphate,Insecticide
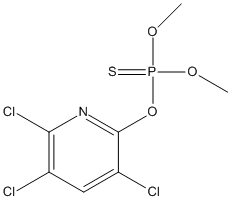
Chemical_Nomenclature : O,O-Dimethyl-O-(3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl)phosphorothioate
Canonical SMILES : COP(=S)(OC)OC1=NC(=C(C=C1Cl)Cl)Cl
InChI : InChI=1S\/C7H7Cl3NO3PS\/c1-12-15(16,13-2)14-7-5(9)3-4(8)6(10)11-7\/h3H,1-2H3
InChIKey : HRBKVYFZANMGRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : dimethoxy-sulfanylidene-(3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy-phosphorane,Noltran,Zertell,Reldan,Dursban methyl,Methyl dursban,Trichlormethylfos,Chlormethylfos,Fospirate,Cooper graincote,Chlorpyrifos-methyl,Dowco 214
MW : 322.53
Formula : C7H7Cl3NO3PS
CAS_number : 5598-13-0
PubChem : 21803
UniChem : HRBKVYFZANMGRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (3)
| Title : Organohalogen and organophosphorus pesticides in mixed feed rations: findings from FDA's domestic surveillance during fiscal years 1989-1994 - Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| Author(s) : Lovell RA , McChesney DG , Price WD |
| Ref : Journal of AOAC International , 79 :544 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| ESTHER : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| PubMedSearch : Lovell_1996_J.AOAC.Int_79_544 |
| PubMedID: 8920144 |
| Title : Acute toxicity of several organophosphorous insecticides and protection by cholinergic antagonists and 2-PAM on Artemia salina larvae - Sanchez-Fortun_1996_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_31_391 |
| Author(s) : Sanchez-Fortun S , Sanz F , Barahona MV |
| Ref : Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 31 :391 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Sanchez-Fortun_1996_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_31_391 |
| ESTHER : Sanchez-Fortun_1996_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_31_391 |
| PubMedSearch : Sanchez-Fortun_1996_Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_31_391 |
| PubMedID: 8854833 |
| Title : Resistance to organophosphorous insecticides in Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) from Martinique - Yebakima_1995_J.Med.Entomol_32_77 |
| Author(s) : Yebakima A , Raymond M , Marquine M , Pasteur N |
| Ref : Journal of Medical Entomology , 32 :77 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Yebakima_1995_J.Med.Entomol_32_77 |
| ESTHER : Yebakima_1995_J.Med.Entomol_32_77 |
| PubMedSearch : Yebakima_1995_J.Med.Entomol_32_77 |
| PubMedID: 7541837 |