ML348
Quite specific for LYPLA1: APT1 (LYPLA1) Ki= 300 nM; APT2 (LYPLA2) Ki> 10microM
General
Type : Trifluoro,Piperazine
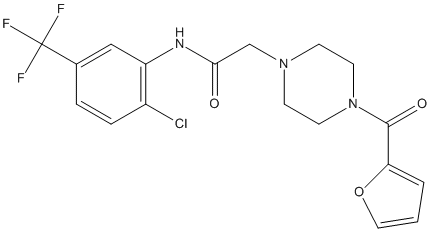
Chemical_Nomenclature : N-[2-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-[4-(furan-2-carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]acetamide
Canonical SMILES : C1CN(CCN1CC(=O)NC2=C(C=CC(=C2)C(F)(F)F)Cl)C(=O)C3=CC=CO3
InChI : InChI=1S\/C18H17ClF3N3O3\/c19-13-4-3-12(18(20,21)22)10-14(13)23-16(26)11-24-5-7-25(8-6-24)17(27)15-2-1-9-28-15\/h1-4,9-10H,5-8,11H2,(H,23,26)
InChIKey : OXKNHBBDOIMFFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 71Q,ML 348,ML-348,GNF-Pf-1127,SMR000033454,ST082657
MW : 415.79
Formula : C18H17ClF3N3O3
CAS_number : 899713-86-1
PubChem : 3238952
UniChem : OXKNHBBDOIMFFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : ML348 ligand of proteins in family: LYsophospholipase_carboxylesterase
Stucture : 5SYM Cocrystal structure of the human acyl protein thioesterase 1 with an isoform-selective inhibitor, ML348
Protein : human-LYPLA1
References (6)
| Title : Increasing brain palmitoylation rescues behavior and neuropathology in Huntington disease mice - Virlogeux_2021_Sci.Adv_7_eabb0799 |
| Author(s) : Virlogeux A , Scaramuzzino C , Lenoir S , Carpentier R , Louessard M , Genoux A , Lino P , Hinckelmann MV , Perrier AL , Humbert S , Saudou F |
| Ref : Sci Adv , 7 : , 2021 |
| Abstract : Virlogeux_2021_Sci.Adv_7_eabb0799 |
| ESTHER : Virlogeux_2021_Sci.Adv_7_eabb0799 |
| PubMedSearch : Virlogeux_2021_Sci.Adv_7_eabb0799 |
| PubMedID: 33789888 |
| Title : Molecular Mechanism for Isoform-Selective Inhibition of Acyl Protein Thioesterases 1 and 2 (APT1 and APT2) - Won_2016_ACS.Chem.Biol_11_3374 |
| Author(s) : Won SJ , Davda D , Labby KJ , Hwang SY , Pricer R , Majmudar JD , Armacost KA , Rodriguez LA , Rodriguez CL , Chong FS , Torossian KA , Palakurthi J , Hur ES , Meagher JL , Brooks CL, 3rd , Stuckey JA , Martin BR |
| Ref : ACS Chemical Biology , 11 :3374 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Won_2016_ACS.Chem.Biol_11_3374 |
| ESTHER : Won_2016_ACS.Chem.Biol_11_3374 |
| PubMedSearch : Won_2016_ACS.Chem.Biol_11_3374 |
| PubMedID: 27748579 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-LYPLA2 |
| Title : Acyl protein thioesterase 1 and 2 (APT-1, APT-2) inhibitors palmostatin B, ML348 and ML349 have different effects on NRAS mutant melanoma cells - Vujic_2016_Oncotarget_7_7297 |
| Author(s) : Vujic I , Sanlorenzo M , Esteve-Puig R , Vujic M , Kwong A , Tsumura A , Murphy R , Moy A , Posch C , Monshi B , Rappersberger K , Ortiz-Urda S |
| Ref : Oncotarget , 7 :7297 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Vujic_2016_Oncotarget_7_7297 |
| ESTHER : Vujic_2016_Oncotarget_7_7297 |
| PubMedSearch : Vujic_2016_Oncotarget_7_7297 |
| PubMedID: 26771141 |
| Title : Acyl protein thioesterase inhibitors as probes of dynamic S-palmitoylation - Davda_2014_Medchemcomm_5_268 |
| Author(s) : Davda D , Martin BR |
| Ref : Medchemcomm , 5 :268 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Davda_2014_Medchemcomm_5_268 |
| ESTHER : Davda_2014_Medchemcomm_5_268 |
| PubMedSearch : Davda_2014_Medchemcomm_5_268 |
| PubMedID: 25558349 |
| Title : Characterization of a Selective, Reversible Inhibitor of Lysophospholipase 1 (LYPLA1) - Adibekian_2013_Probe.Report__3 |
| Author(s) : Adibekian A , Martin BR , Chang JW , Hsu KL , Tsuboi K , Bachovchin DA , Speers AE , Brown SJ , Spicer T , Fernandez-Vega V , Ferguson J , Cravatt BF , Hodder P , Rosen H |
| Ref : Probe Report , : , 2013 |
| Abstract : Adibekian_2013_Probe.Report__3 |
| ESTHER : Adibekian_2013_Probe.Report__3 |
| PubMedSearch : Adibekian_2013_Probe.Report__3 |
| PubMedID: 24624465 |
| Title : Confirming target engagement for reversible inhibitors in vivo by kinetically tuned activity-based probes - Adibekian_2012_J.Am.Chem.Soc_134_10345 |
| Author(s) : Adibekian A , Martin BR , Chang JW , Hsu KL , Tsuboi K , Bachovchin DA , Speers AE , Brown SJ , Spicer T , Fernandez-Vega V , Ferguson J , Hodder PS , Rosen H , Cravatt BF |
| Ref : J Am Chem Soc , 134 :10345 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Adibekian_2012_J.Am.Chem.Soc_134_10345 |
| ESTHER : Adibekian_2012_J.Am.Chem.Soc_134_10345 |
| PubMedSearch : Adibekian_2012_J.Am.Chem.Soc_134_10345 |
| PubMedID: 22690931 |