MF217
General
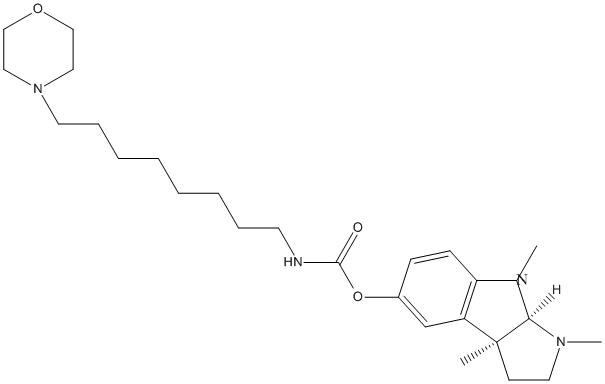
Type : Derivative of physostigmine-eserine,Carbamate,Morpholine,Indole
Chemical_Nomenclature : [(3aR,8bS)-3,4,8b-trimethyl-2,3a-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]indol-7-yl] N-(8-morpholin-4-yloctyl)carbamate
Canonical SMILES : CC12CCN(C1N(C3=C2C=C(C=C3)OC(=O)NCCCCCCCCN4CCOCC4)C)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C26H42N4O3\/c1-26-12-15-28(2)24(26)29(3)23-11-10-21(20-22(23)26)33-25(31)27-13-8-6-4-5-7-9-14-30-16-18-32-19-17-30\/h10-11,20,24H,4-9,12-19H2,1-3H3,(H,27,31)\/t24-,26+\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : PLDHPJSOABLSHM-RSXGOPAZSA-N
Other name(s) : MF 217,CHEMBL65018,Morphlinyloctylcarbamoyleseroline,Carbamic acid, (8-(4-morpholinyl)octyl)-, 1,2,3,3a,8,8a-hexahydro-1,3a,8-trimethylpyrrolo(2,3-b)indol-5-yl ester, (3aS-cis)-,AC1MINCM,8-Morpholinoctylphysostigmine,Morpholinoctylcarbamoyleseroline,MF-217
MW : 458.637
Formula : C26H42N4O3
CAS_number : 154619-56-4
PubChem : 3074014
UniChem : PLDHPJSOABLSHM-RSXGOPAZSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (1)
| Title : Long chain analogs of physostigmine as potential drugs for Alzheimer's disease: new insights into the mechanism of action in the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. - Perola_1997_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1343_41 |
| Author(s) : Perola E , Cellai L , Lamba D , Filocamo L , Brufani M |
| Ref : Biochimica & Biophysica Acta , 1343 :41 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Perola_1997_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1343_41 |
| ESTHER : Perola_1997_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1343_41 |
| PubMedSearch : Perola_1997_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1343_41 |
| PubMedID: 9428657 |