KT109
KT109 and KT172 are Specific DAGLB inhibitors. However inhibits also ABHD6 and CES1 (Iglesias 2016)
General
Type : Piperidine,Biphenyl,Triazol
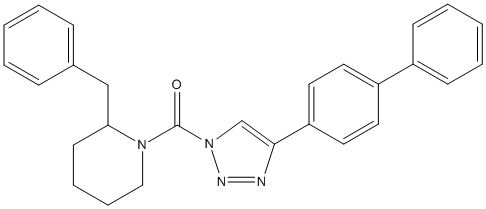
Chemical_Nomenclature : (2-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)-[4-(4-phenylphenyl)triazol-1-yl]methanone
Canonical SMILES : C1CCN(C(C1)CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)N3C=C(N=N3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C5=CC=CC=C5
InChI : InChI=1S\/C27H26N4O\/c32-27(30-18-8-7-13-25(30)19-21-9-3-1-4-10-21)31-20-26(28-29-31)24-16-14-23(15-17-24)22-11-5-2-6-12-22\/h1-6,9-12,14-17,20,25H,7-8,13,18-19H2
InChIKey : JKJMWHULJIOKPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : (4-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)(2-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)methanone,MLS004256813,CHEMBL2144065,SCHEMBL13192827,AOB3993
MW : 422.52
Formula : C27H26N4O
CAS_number : 1402612-55-8
PubChem : 53364540
UniChem : JKJMWHULJIOKPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : KT109 ligand of proteins in family: Lipase_3 || Carb_B_Chordata || ABHD6-Lip
Stucture :
Protein :
References (3)
| Title : Simplified assays of lipolysis enzymes for drug discovery and specificity assessment of known inhibitors - Iglesias_2016_J.Lipid.Res_57_131 |
| Author(s) : Iglesias J , Lamontagne J , Erb H , Gezzar S , Zhao S , Joly E , Truong VL , Skorey K , Crane S , Madiraju SR , Prentki M |
| Ref : J Lipid Res , 57 :131 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Iglesias_2016_J.Lipid.Res_57_131 |
| ESTHER : Iglesias_2016_J.Lipid.Res_57_131 |
| PubMedSearch : Iglesias_2016_J.Lipid.Res_57_131 |
| PubMedID: 26423520 |
| Title : Development and optimization of piperidyl-1,2,3-triazole ureas as selective chemical probes of endocannabinoid biosynthesis - Hsu_2013_J.Med.Chem_56_8257 |
| Author(s) : Hsu KL , Tsuboi K , Whitby LR , Speers AE , Pugh H , Inloes J , Cravatt BF |
| Ref : Journal of Medicinal Chemistry , 56 :8257 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Hsu_2013_J.Med.Chem_56_8257 |
| ESTHER : Hsu_2013_J.Med.Chem_56_8257 |
| PubMedSearch : Hsu_2013_J.Med.Chem_56_8257 |
| PubMedID: 24152245 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-DAGLB |
| Title : DAGLbeta inhibition perturbs a lipid network involved in macrophage inflammatory responses - Hsu_2012_Nat.Chem.Biol_8_999 |
| Author(s) : Hsu KL , Tsuboi K , Adibekian A , Pugh H , Masuda K , Cravatt BF |
| Ref : Nat Chemical Biology , 8 :999 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Hsu_2012_Nat.Chem.Biol_8_999 |
| ESTHER : Hsu_2012_Nat.Chem.Biol_8_999 |
| PubMedSearch : Hsu_2012_Nat.Chem.Biol_8_999 |
| PubMedID: 23103940 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-DAGLA , human-DAGLB |