JJKK-048
JJKK-048 (IC50 363 pM) and KML29 (IC50 3.6 nM) both were reported to be highly selective MAGL inhibitors, and their selectivity is more than 10,000-fold over FAAH
General
Type : Benzodioxo,Piperidine,Triazol
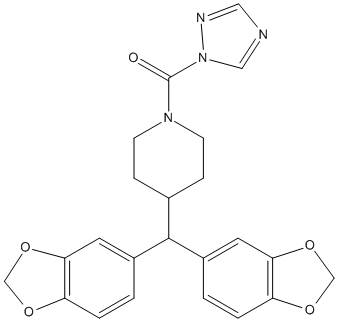
Chemical_Nomenclature : [4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]piperidin-1-yl]-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methanone
Canonical SMILES : C1CN(CCC1C(C2=CC3=C(C=C2)OCO3)C4=CC5=C(C=C4)OCO5)C(=O)N6C=NC=N6
InChI : InChI=1S\/C23H22N4O5\/c28-23(27-12-24-11-25-27)26-7-5-15(6-8-26)22(16-1-3-18-20(9-16)31-13-29-18)17-2-4-19-21(10-17)32-14-30-19\/h1-4,9-12,15,22H,5-8,13-14H2
InChIKey : CLSNATLUIXZPMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : JJKK 048,JJKK048,CHEMBL3087181,1515855-97-6,GTPL9481,MolPort-035-941-193
MW : 434.45
Formula : C23H22N4O5
CAS_number :
PubChem : 76313567
UniChem : CLSNATLUIXZPMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : JJKK-048 ligand of proteins in family: Monoglyceridelipase_lysophospholip
Stucture :
Protein : human-MGLL
References (4)
| Title : Monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor JJKK048 ameliorates ABCG2 transporter-mediated regorafenib resistance induced by hypoxia in triple negative breast cancer cells - Puris_2023_J.Pharm.Sci__ |
| Author(s) : Puris E , Petralla S , Auriola S , Kidron H , Fricker G , Gynther M |
| Ref : J Pharm Sci , : , 2023 |
| Abstract : Puris_2023_J.Pharm.Sci__ |
| ESTHER : Puris_2023_J.Pharm.Sci__ |
| PubMedSearch : Puris_2023_J.Pharm.Sci__ |
| PubMedID: 37220829 |
| Title : Anticonvulsive effects of endocannabinoids\; an investigation to determine the role of regulatory components of endocannabinoid metabolism in the Pentylenetetrazol induced tonic- clonic seizures - Zareie_2018_Metab.Brain.Dis_33_939 |
| Author(s) : Zareie P , Sadegh M , Palizvan MR , Moradi-Chameh H |
| Ref : Metabolic Brain Disease , 33 :939 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Zareie_2018_Metab.Brain.Dis_33_939 |
| ESTHER : Zareie_2018_Metab.Brain.Dis_33_939 |
| PubMedSearch : Zareie_2018_Metab.Brain.Dis_33_939 |
| PubMedID: 29504066 |
| Title : In Vivo Characterization of the Ultrapotent Monoacylglycerol Lipase Inhibitor {4-[bis-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)methyl]-piperidin-1-yl}(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)m ethanone (JJKK-048) - Aaltonen_2016_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_359_62 |
| Author(s) : Aaltonen N , Kedzierska E , Orzelska-Gorka J , Lehtonen M , Navia-Paldanius D , Jakupovic H , Savinainen JR , Nevalainen T , Laitinen JT , Parkkari T , Gynther M |
| Ref : Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics , 359 :62 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Aaltonen_2016_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_359_62 |
| ESTHER : Aaltonen_2016_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_359_62 |
| PubMedSearch : Aaltonen_2016_J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther_359_62 |
| PubMedID: 27451409 |
| Title : Piperazine and piperidine triazole ureas as ultrapotent and highly selective inhibitors of monoacylglycerol lipase - Aaltonen_2013_Chem.Biol_20_379 |
| Author(s) : Aaltonen N , Savinainen JR , Ribas CR , Ronkko J , Kuusisto A , Korhonen J , Navia-Paldanius D , Hayrinen J , Takabe P , Kasnanen H , Pantsar T , Laitinen T , Lehtonen M , Pasonen-Seppanen S , Poso A , Nevalainen T , Laitinen JT |
| Ref : Chemical Biology , 20 :379 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Aaltonen_2013_Chem.Biol_20_379 |
| ESTHER : Aaltonen_2013_Chem.Biol_20_379 |
| PubMedSearch : Aaltonen_2013_Chem.Biol_20_379 |
| PubMedID: 23521796 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-MGLL |