Isofenphos-methyl
General
Type : Insecticide,Organophosphate,Benzoate,Sulfur Compound
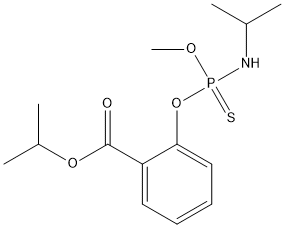
Chemical_Nomenclature : propan-2-yl 2-[methoxy-(propan-2-ylamino)phosphinothioyl]oxybenzoate
Canonical SMILES : CC(C)NP(=S)(OC)OC1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)OC(C)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C14H22NO4PS\/c1-10(2)15-20(21,17-5)19-13-9-7-6-8-12(13)14(16)18-11(3)4\/h6-11H,1-5H3,(H,15,21)
InChIKey : IXTOWLKEARFCCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Methyl-isp,Methyl Isofenphos,IFP
MW : 331.37
Formula : C14H22NO4PS
CAS_number : 99675-03-3
PubChem : 127394
UniChem : IXTOWLKEARFCCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families :
Stucture :
Protein :
References (2)
| Title : Toxic effects of isofenphos-methyl on zebrafish embryonic development - Wu_2023_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_254_114723 |
| Author(s) : Wu Y , Wang J , Xia Y , Tang K , Xu J , Wang A , Hu S , Wen L , Wang B , Yao W |
| Ref : Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety , 254 :114723 , 2023 |
| Abstract : Wu_2023_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_254_114723 |
| ESTHER : Wu_2023_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_254_114723 |
| PubMedSearch : Wu_2023_Ecotoxicol.Environ.Saf_254_114723 |
| PubMedID: 36871354 |
| Title : A potential biomarker of isofenphos-methyl in humans: A chiral view - Gao_2019_Environ.Int_127_694 |
| Author(s) : Gao B , Zhao S , Zhang Z , Li L , Hu K , Kaziem AE , He Z , Hua X , Shi H , Wang M |
| Ref : Environ Int , 127 :694 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Gao_2019_Environ.Int_127_694 |
| ESTHER : Gao_2019_Environ.Int_127_694 |
| PubMedSearch : Gao_2019_Environ.Int_127_694 |
| PubMedID: 30991225 |