HT-01
General
Type : Fluorescent Probe,BODIPY-derivative,Carboxamide,Triazol,Trifluoro,Boron compound
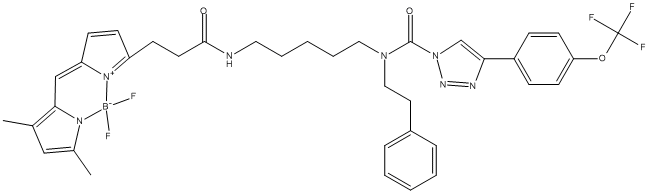
Chemical_Nomenclature : N-[5-[3-[(5Z)-5-[(1-difluoroboranyl-3,5-dimethylpyrrol-2-yl)methylidene]pyrrol-2-yl]propanoylamino]pentyl]-N-(2-phenylethyl)-4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]triazole-1-carboxamide
Canonical SMILES : B(N1C(=CC(=C1C=C2C=CC(=N2)CCC(=O)NCCCCCN(CCC3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)N4C=C(N=N4)C5=CC=C(C=C5)OC(F)(F)F)C)C)(F)F
InChI : InChI=1S\/C37H39BF5N7O3\/c1-26-23-27(2)50(38(42)43)34(26)24-31-14-13-30(45-31)15-18-35(51)44-20-7-4-8-21-48(22-19-28-9-5-3-6-10-28)36(52)49-25-33(46-47-49)29-11-16-32(17-12-29)53-37(39,40)41\/h3,5-6,9-14,16-17,23-25H,4,7-8,15,18-22H2,1-2H3,(H,44,51)\/b31-24-
InChIKey : UNTGPHFCORHEAQ-QLTSDVKISA-N
Other name(s) : HT01,ZINC169839040
MW : 735.6
Formula : C37H39BF5N7O3
CAS_number :
PubChem : 99773041
UniChem : UNTGPHFCORHEAQ-QLTSDVKISA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : HT-01 ligand of proteins in family: Lipase_3 || ABHD6-Lip
Stucture :
References (2)
| Title : An in vivo multiplexed small-molecule screening platform - Gruner_2016_Nat.Methods_13_883 |
| Author(s) : Gruner BM , Schulze CJ , Yang D , Ogasawara D , Dix MM , Rogers ZN , Chuang CH , McFarland CD , Chiou SH , Brown JM , Cravatt BF , Bogyo M , Winslow MM |
| Ref : Nat Methods , 13 :883 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Gruner_2016_Nat.Methods_13_883 |
| ESTHER : Gruner_2016_Nat.Methods_13_883 |
| PubMedSearch : Gruner_2016_Nat.Methods_13_883 |
| PubMedID: 27617390 |
| Title : DAGLbeta inhibition perturbs a lipid network involved in macrophage inflammatory responses - Hsu_2012_Nat.Chem.Biol_8_999 |
| Author(s) : Hsu KL , Tsuboi K , Adibekian A , Pugh H , Masuda K , Cravatt BF |
| Ref : Nat Chemical Biology , 8 :999 , 2012 |
| Abstract : Hsu_2012_Nat.Chem.Biol_8_999 |
| ESTHER : Hsu_2012_Nat.Chem.Biol_8_999 |
| PubMedSearch : Hsu_2012_Nat.Chem.Biol_8_999 |
| PubMedID: 23103940 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-DAGLA , human-DAGLB |