EZ120P
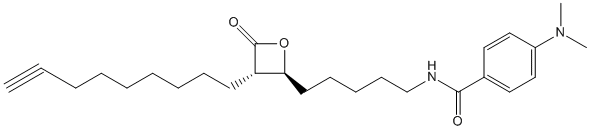
Modified version of Orlistat Tetrahydrolipstatin THL-alkyne EZ120 is selective for mycobacteria this is the alkyne of EZ120
General
Type : Oxooxetan,Lipase inhibitor,Alkyne
Chemical_Nomenclature :
Canonical SMILES : C1(=CC=C(C=C1)N(C)C)C(NCCCCCC2OC(C2CCCCCCCC#C)=O)=O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C26H38N2O3\/c1-4-5-6-7-8-9-11-14-23-24(31-26(23)30)15-12-10-13-20-27-25(29)21-16-18-22(19-17-21)28(2)3\/h1,16-19,23-24H,5-15,20H2,2-3H3,(H,27,29)
InChIKey : YFDWGEYULMRNNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) :
MW : 426.59
Formula : C26H38N2O3
CAS_number :
PubChem :
UniChem : YFDWGEYULMRNNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : EZ120P ligand of proteins in family: A85-Mycolyl-transferase
Stucture :
Protein : myctu-a85a || myctu-a85b || myctu-a85c
References (5)
| Title : Identification of cell wall synthesis inhibitors active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis by competitive activity-based protein profiling - Li_2022_Cell.Chem.Biol_29_883 |
| Author(s) : Li M , Patel HV , Cognetta AB, 3rd , Smith TC, 2nd , Mallick I , Cavalier JF , Previti ML , Canaan S , Aldridge BB , Cravatt BF , Seeliger JC |
| Ref : Cell Chemical Biology , 29 :883 , 2022 |
| Abstract : Li_2022_Cell.Chem.Biol_29_883 |
| ESTHER : Li_2022_Cell.Chem.Biol_29_883 |
| PubMedSearch : Li_2022_Cell.Chem.Biol_29_883 |
| PubMedID: 34599873 |
| Title : Cell Surface Biosynthesis and Remodeling Pathways in Mycobacteria Reveal New Drug Targets - Shaku_2020_Front.Cell.Infect.Microbiol_10_603382 |
| Author(s) : Shaku M , Ealand C , Kana BD |
| Ref : Front Cell Infect Microbiol , 10 :603382 , 2020 |
| Abstract : Shaku_2020_Front.Cell.Infect.Microbiol_10_603382 |
| ESTHER : Shaku_2020_Front.Cell.Infect.Microbiol_10_603382 |
| PubMedSearch : Shaku_2020_Front.Cell.Infect.Microbiol_10_603382 |
| PubMedID: 33282752 |
| Title : Microbial esterases and ester prodrugs: An unlikely marriage for combating antibiotic resistance - Larsen_2019_Drug.Dev.Res_80_33 |
| Author(s) : Larsen EM , Johnson RJ |
| Ref : Drug Dev Res , 80 :33 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Larsen_2019_Drug.Dev.Res_80_33 |
| ESTHER : Larsen_2019_Drug.Dev.Res_80_33 |
| PubMedSearch : Larsen_2019_Drug.Dev.Res_80_33 |
| PubMedID: 30302779 |
| Title : An Antibacterial beta-Lactone Kills Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Disrupting Mycolic Acid Biosynthesis - Lehmann_2018_Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl_57_348 |
| Author(s) : Lehmann J , Cheng TY , Aggarwal A , Park AS , Zeiler E , Raju RM , Akopian T , Kandror O , Sacchettini JC , Moody DB , Rubin EJ , Sieber SA |
| Ref : Angew Chem Int Ed Engl , 57 :348 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Lehmann_2018_Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl_57_348 |
| ESTHER : Lehmann_2018_Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl_57_348 |
| PubMedSearch : Lehmann_2018_Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl_57_348 |
| PubMedID: 29067779 |
| Title : Cyclipostins and cyclophostin analogs inhibit the antigen 85C from Mycobacterium tuberculosis both in vitro and in vivo - Viljoen_2018_J.Biol.Chem_293_2755 |
| Author(s) : Viljoen A , Richard M , Nguyen PC , Fourquet P , Camoin L , Paudal RR , Gnawali GR , Spilling CD , Cavalier JF , Canaan S , Blaise M , Kremer L |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 293 :2755 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Viljoen_2018_J.Biol.Chem_293_2755 |
| ESTHER : Viljoen_2018_J.Biol.Chem_293_2755 |
| PubMedSearch : Viljoen_2018_J.Biol.Chem_293_2755 |
| PubMedID: 29301937 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: myctu-a85c |