EPN
EPN-oxon (Oxygen replaces the sulfur atom)
General
Type : Insecticide,Organophosphate,Sulfur Compound,Organothiophosphate,pNP
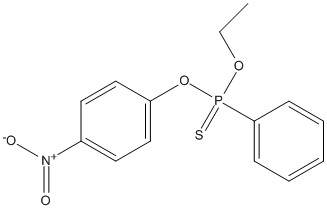
Chemical_Nomenclature : ethoxy-(4-nitrophenoxy)-phenyl-sulfanylidene-phosphorane
Canonical SMILES : CCOP(=S)(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC2=CC=C(C=C2)[N+](=O)[O-]
InChI : InChI=1S\/C14H14NO4PS\/c1-2-18-20(21,14-6-4-3-5-7-14)19-13-10-8-12(9-11-13)15(16)17\/h3-11H,2H2,1H3
InChIKey : AIGRXSNSLVJMEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Santox,Tsumaphos,Kasutop Dust,Meidon 15 Dust,MAPJ,Caswell No. 454,EPN 300,OMS 219,ENT 17,798,HSDB 4049,ethyl p-nitrophenol thio-benzene phosphonate,O'ethyl-O-p-nitrophenyl phenyl phosphonothioate
MW : 323.305
Formula : C14H14NO4PS
CAS_number : 2012-00-2
PubChem : 16421
UniChem : AIGRXSNSLVJMEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : EPN_(insecticide)
Target
References (10)
| Title : Variable response of cholinesterase activities following human exposure to different types of organophosphates - Moon_2015_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_34_698 |
| Author(s) : Moon J , Chun B , Lee S |
| Ref : Hum Exp Toxicol , 34 :698 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Moon_2015_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_34_698 |
| ESTHER : Moon_2015_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_34_698 |
| PubMedSearch : Moon_2015_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_34_698 |
| PubMedID: 25712411 |
| Title : Extremely sensitive biomarker of acute organophosphorus insecticide exposure - Fujikawa_2005_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_24_333 |
| Author(s) : Fujikawa Y , Satoh T , Suganuma A , Suzuki S , Niikura Y , Yui S , Yamaura Y |
| Ref : Hum Exp Toxicol , 24 :333 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Fujikawa_2005_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_24_333 |
| ESTHER : Fujikawa_2005_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_24_333 |
| PubMedSearch : Fujikawa_2005_Hum.Exp.Toxicol_24_333 |
| PubMedID: 16004201 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-CES1 , mouse-Ces1e , ratno-Ces1e |
| Title : Mutagenesis of organophosphorus hydrolase to enhance hydrolysis of the nerve agent VX - Gopal_2000_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_279_516 |
| Author(s) : Gopal S , Rastogi V , Ashman W , Mulbry W |
| Ref : Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications , 279 :516 , 2000 |
| Abstract : Gopal_2000_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_279_516 |
| ESTHER : Gopal_2000_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_279_516 |
| PubMedSearch : Gopal_2000_Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun_279_516 |
| PubMedID: 11118318 |
| Title : Degradation by rat tissues in vitro of organophosphorus esters which inhibit cholinesterase - Pla_1989_Biochem.Pharmacol_38_1527 |
| Author(s) : Pla A , Johnson MK |
| Ref : Biochemical Pharmacology , 38 :1527 , 1989 |
| Abstract : Pla_1989_Biochem.Pharmacol_38_1527 |
| ESTHER : Pla_1989_Biochem.Pharmacol_38_1527 |
| PubMedSearch : Pla_1989_Biochem.Pharmacol_38_1527 |
| PubMedID: 2719724 |
| Title : Enhancement of the binding of O-ethyl O-p-nitrophenyl phenylphosphonate (EPNoxon) to microsomal carboxylesterase by NAD in vitro - Sugiyama_1985_Jpn.J.Pharmacol_37_39 |
| Author(s) : Sugiyama S , Hosokawa M , Igarashi T , Ueno K , Satoh T , Kitagawa H |
| Ref : Japanese Journal of Pharmacology , 37 :39 , 1985 |
| Abstract : Sugiyama_1985_Jpn.J.Pharmacol_37_39 |
| ESTHER : Sugiyama_1985_Jpn.J.Pharmacol_37_39 |
| PubMedSearch : Sugiyama_1985_Jpn.J.Pharmacol_37_39 |
| PubMedID: 3990043 |
| Title : Effect of subchronic dermal application of O-ethyl O-4-nitrophenyl phenylphosphonothioate on producing delayed neurotoxicity in hens - Abou-Donia_1983_Neurotoxicol_4_247 |
| Author(s) : Abou-Donia MB , Graham DG , Makkawy HA , Abdo KM |
| Ref : Neurotoxicology , 4 :247 , 1983 |
| Abstract : Abou-Donia_1983_Neurotoxicol_4_247 |
| ESTHER : Abou-Donia_1983_Neurotoxicol_4_247 |
| PubMedSearch : Abou-Donia_1983_Neurotoxicol_4_247 |
| PubMedID: 6685263 |
| Title : Biochemical interaction of six OP delayed neurotoxicants with several neurotargets - El-Sebae_1981_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_16_465 |
| Author(s) : El-Sebae AH , Soliman SA , Ahmed NS , Curley A |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health B , 16 :465 , 1981 |
| Abstract : El-Sebae_1981_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_16_465 |
| ESTHER : El-Sebae_1981_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_16_465 |
| PubMedSearch : El-Sebae_1981_J.Environ.Sci.Health.B_16_465 |
| PubMedID: 6169754 |
| Title : Ecotoxicology of phenylphosphonothioates - Francis_1980_Environ.Health.Perspect_36_187 |
| Author(s) : Francis BM , Hansen LG , Fukuto TR , Lu PY , Metcalf RL |
| Ref : Environmental Health Perspectives , 36 :187 , 1980 |
| Abstract : Francis_1980_Environ.Health.Perspect_36_187 |
| ESTHER : Francis_1980_Environ.Health.Perspect_36_187 |
| PubMedSearch : Francis_1980_Environ.Health.Perspect_36_187 |
| PubMedID: 6159210 |
| Title : Dislodgable insecticide residues on cotton foliage: fenvalarate, permethrin, sulprofos, chlorpyrifos, methyl parathion, EPN, oxamyl, and profenofos - |
| Author(s) : Buck NA , Estesen BJ , Ware GW |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 24 :283 , 1980 |
| PubMedID: 6153915 |
| Title : Evaluation of cytotoxic responses caused by selected organophosphorus esters in chick sympathetic ganglia cultures - Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| Author(s) : Obersteiner EJ , Sharma RP |
| Ref : Can J Comp Med , 42 :80 , 1978 |
| Abstract : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| ESTHER : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| PubMedSearch : Obersteiner_1978_Can.J.Comp.Med_42_80 |
| PubMedID: 565668 |