EMPA
VX hydrolysis product, ethylmethylphosphonate (EMPA), non toxic
General
Type : Organophosphate
Chemical_Nomenclature : ethoxy(methyl)phosphinic acid
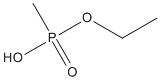
Canonical SMILES : CCOP(=O)(C)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C3H9O3P\/c1-3-6-7(2,4)5\/h3H2,1-2H3,(H,4,5)
InChIKey : UFZOPKFMKMAWLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Ethyl methylphosphonate,UNII-921S33S5Y5,Phosphonic acid, methyl-, monoethyl ester,Phosphonic acid, methyl-, ethyl ester,AC1L9MPF
MW : 124.07
Formula : C3H9O3P
CAS_number : 1832-53-7
PubChem : 449085
UniChem : UFZOPKFMKMAWLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : EMPA ligand of proteins in family: ACHE
Stucture : 6CQY Crystal Structure of Recombinant Human Acetylcholinesterase in Complex with EMPA and HI-6
Protein : human-ACHE
References (8)
| Title : Lewis acid-assisted detection of nerve agents in water - Butala_2015_Chem.Commun.(Camb)_51_9269 |
| Author(s) : Butala RR , Creasy WR , Fry RA , McKee ML , Atwood DA |
| Ref : Chem Commun (Camb) , 51 :9269 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Butala_2015_Chem.Commun.(Camb)_51_9269 |
| ESTHER : Butala_2015_Chem.Commun.(Camb)_51_9269 |
| PubMedSearch : Butala_2015_Chem.Commun.(Camb)_51_9269 |
| PubMedID: 25820753 |
| Title : Fate of malathion and a phosphonic acid in activated sludge with varying solids retention times - Janeczko_2014_Water.Res_57_127 |
| Author(s) : Janeczko AK , Walters EB , Schuldt SJ , Magnuson ML , Willison SA , Brown LM , Ruiz ON , Felker DL , Racz L |
| Ref : Water Res , 57 :127 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Janeczko_2014_Water.Res_57_127 |
| ESTHER : Janeczko_2014_Water.Res_57_127 |
| PubMedSearch : Janeczko_2014_Water.Res_57_127 |
| PubMedID: 24709533 |
| Title : Polysaccharide-thickened aqueous fluoride solutions for rapid destruction of the nerve agent VX. Introducing the opportunity for extensive decontamination scenarios - Elias_2014_Environ.Sci.Technol_48_2893 |
| Author(s) : Elias S , Saphier S , Columbus I , Zafrani Y |
| Ref : Environ Sci Technol , 48 :2893 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Elias_2014_Environ.Sci.Technol_48_2893 |
| ESTHER : Elias_2014_Environ.Sci.Technol_48_2893 |
| PubMedSearch : Elias_2014_Environ.Sci.Technol_48_2893 |
| PubMedID: 24517492 |
| Title : Catalytic degradation of the nerve agent VX by water-swelled polystyrene-supported ammonium fluorides - Marciano_2011_J.Org.Chem_76_8549 |
| Author(s) : Marciano D , Goldvaser M , Columbus I , Zafrani Y |
| Ref : J Org Chem , 76 :8549 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Marciano_2011_J.Org.Chem_76_8549 |
| ESTHER : Marciano_2011_J.Org.Chem_76_8549 |
| PubMedSearch : Marciano_2011_J.Org.Chem_76_8549 |
| PubMedID: 21905719 |
| Title : Decomposition of adsorbed VX on activated carbons studied by 31P MAS NMR - Columbus_2006_Environ.Sci.Technol_40_3952 |
| Author(s) : Columbus I , Waysbort D , Shmueli L , Nir I , Kaplan D |
| Ref : Environ Sci Technol , 40 :3952 , 2006 |
| Abstract : Columbus_2006_Environ.Sci.Technol_40_3952 |
| ESTHER : Columbus_2006_Environ.Sci.Technol_40_3952 |
| PubMedSearch : Columbus_2006_Environ.Sci.Technol_40_3952 |
| PubMedID: 16830567 |
| Title : Characterization of VX on concrete using ion trap secondary ionization mass spectrometry - Groenewold_2000_J.Am.Soc.Mass.Spectrom_11_69 |
| Author(s) : Groenewold GS , Appelhans AD , Gresham GL , Olson JE , Jeffery M , Weibel M |
| Ref : J Am Soc Mass Spectrom , 11 :69 , 2000 |
| Abstract : Groenewold_2000_J.Am.Soc.Mass.Spectrom_11_69 |
| ESTHER : Groenewold_2000_J.Am.Soc.Mass.Spectrom_11_69 |
| PubMedSearch : Groenewold_2000_J.Am.Soc.Mass.Spectrom_11_69 |
| PubMedID: 10631666 |
| Title : Capillary ion electrophoresis screening of nerve agent degradation products in environmental samples using conductivity detection - Rosso_1998_J.Chromatogr.A_824_125 |
| Author(s) : Rosso TE , Bossle PC |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography A , 824 :125 , 1998 |
| Abstract : Rosso_1998_J.Chromatogr.A_824_125 |
| ESTHER : Rosso_1998_J.Chromatogr.A_824_125 |
| PubMedSearch : Rosso_1998_J.Chromatogr.A_824_125 |
| PubMedID: 9818432 |
| Title : Determination of the main hydrolysis product of O-ethyl S-2- diisopropylaminoethyl methylphosphonothiolate, ethyl methylphosphonic acid, in human serum - Katagi_1997_J.Chromatogr.B.Biomed.Sci.Appl_689_327 |
| Author(s) : Katagi M , Nishikawa M , Tatsuno M , Tsuchihashi H |
| Ref : Journal of Chromatography B Biomed Sci Appl , 689 :327 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Katagi_1997_J.Chromatogr.B.Biomed.Sci.Appl_689_327 |
| ESTHER : Katagi_1997_J.Chromatogr.B.Biomed.Sci.Appl_689_327 |
| PubMedSearch : Katagi_1997_J.Chromatogr.B.Biomed.Sci.Appl_689_327 |
| PubMedID: 9080318 |