DL0410
IC50 against BChE 3.57 uM
General
Type : Piperidine,Biphenyl
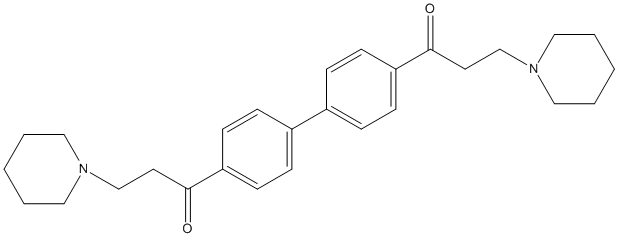
Chemical_Nomenclature : 3-piperidin-1-yl-1-[4-[4-(3-piperidin-1-ylpropanoyl)phenyl]phenyl]propan-1-one
Canonical SMILES : C1CCN(CC1)CCC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C(=O)CCN4CCCCC4
InChI : InChI=1S\/C28H36N2O2\/c31-27(15-21-29-17-3-1-4-18-29)25-11-7-23(8-12-25)24-9-13-26(14-10-24)28(32)16-22-30-19-5-2-6-20-30\/h7-14H,1-6,15-22H2
InChIKey : OEJCMWCXCHXDOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : J6487,1,1'-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4, 4'-diyl)bis(3-(piperidin-1-yl) propan-1-one)dihydrochloride
MW : 432.60
Formula : C28H36N2O2
CAS_number :
PubChem : 42602188
UniChem : OEJCMWCXCHXDOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : DL0410 ligand of proteins in family: ACHE || BCHE
Stucture :
Protein : human-BCHE || human-ACHE
References (8)
| Title : Pharmacokinetics, excretion and metabolites analysis of DL0410, a dualacting cholinesterase inhibitor and histamine3 receptor antagonist - Pang_2019_Mol.Med.Rep_20_1103 |
| Author(s) : Pang X , Zhao Y , Song J , Kang , Wu S , Wang L , Liu A , Du G |
| Ref : Mol Med Rep , 20 :1103 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Pang_2019_Mol.Med.Rep_20_1103 |
| ESTHER : Pang_2019_Mol.Med.Rep_20_1103 |
| PubMedSearch : Pang_2019_Mol.Med.Rep_20_1103 |
| PubMedID: 31173186 |
| Title : DL0410 Ameliorates Memory and Cognitive Impairments Induced by Scopolamine via Increasing Cholinergic Neurotransmission in Mice - Lian_2017_Molecules_22_ |
| Author(s) : Lian W , Fang J , Xu L , Zhou W , Kang , Xiong W , Jia H , Liu AL , Du GH |
| Ref : Molecules , 22 : , 2017 |
| Abstract : Lian_2017_Molecules_22_ |
| ESTHER : Lian_2017_Molecules_22_ |
| PubMedSearch : Lian_2017_Molecules_22_ |
| PubMedID: 28272324 |
| Title : Multi-Protection of DL0410 in Ameliorating Cognitive Defects in D-Galactose Induced Aging Mice - Lian_2017_Front.Aging.Neurosci_9_409 |
| Author(s) : Lian W , Jia H , Xu L , Zhou W , Kang , Liu A , Du G |
| Ref : Front Aging Neurosci , 9 :409 , 2017 |
| Abstract : Lian_2017_Front.Aging.Neurosci_9_409 |
| ESTHER : Lian_2017_Front.Aging.Neurosci_9_409 |
| PubMedSearch : Lian_2017_Front.Aging.Neurosci_9_409 |
| PubMedID: 29276489 |
| Title : Effects of P-Glycoprotein on the Transport of DL0410, a Potential Multifunctional Anti-Alzheimer Agent - Pang_2017_Molecules_22_2 |
| Author(s) : Pang X , Wang L , Kang , Zhao Y , Wu S , Liu AL , Du GH |
| Ref : Molecules , 22 : , 2017 |
| Abstract : Pang_2017_Molecules_22_2 |
| ESTHER : Pang_2017_Molecules_22_2 |
| PubMedSearch : Pang_2017_Molecules_22_2 |
| PubMedID: 28757552 |
| Title : DL0410, a novel dual cholinesterase inhibitor, protects mouse brains against Abeta-induced neuronal damage via the Akt\/JNK signaling pathway - Zhou_2016_Acta.Pharmacol.Sin_37_1401 |
| Author(s) : Zhou D , Zhou W , Song JK , Feng ZY , Yang RY , Wu S , Wang L , Liu AL , Du GH |
| Ref : Acta Pharmacol Sin , 37 :1401 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Zhou_2016_Acta.Pharmacol.Sin_37_1401 |
| ESTHER : Zhou_2016_Acta.Pharmacol.Sin_37_1401 |
| PubMedSearch : Zhou_2016_Acta.Pharmacol.Sin_37_1401 |
| PubMedID: 27498773 |
| Title : DL0410 can reverse cognitive impairment, synaptic loss and reduce plaque load in APP\/PS1 transgenic mice - Yang_2015_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_139_15 |
| Author(s) : Yang RY , Zhao G , Wang DM , Pang XC , Wang SB , Fang JS , Li C , Liu AL , Wu S , Du GH |
| Ref : Pharmacol Biochem Behav , 139 :15 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Yang_2015_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_139_15 |
| ESTHER : Yang_2015_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_139_15 |
| PubMedSearch : Yang_2015_Pharmacol.Biochem.Behav_139_15 |
| PubMedID: 26476132 |
| Title : Discovery of Multitarget-Directed Ligands against Alzheimer's Disease through Systematic Prediction of Chemical-Protein Interactions - Fang_2015_J.Chem.Inf.Model_55_149 |
| Author(s) : Fang J , Li Y , Liu R , Pang X , Li C , Yang R , He Y , Lian W , Liu AL , Du GH |
| Ref : J Chem Inf Model , 55 :149 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Fang_2015_J.Chem.Inf.Model_55_149 |
| ESTHER : Fang_2015_J.Chem.Inf.Model_55_149 |
| PubMedSearch : Fang_2015_J.Chem.Inf.Model_55_149 |
| PubMedID: 25531792 |
| Title : Predictions of BCHE Inhibitors Using Support Vector Machine and Naive Bayesian Classification Techniques in Drug Discovery - Fang_2013_J.Chem.Inf.Model_53_3009 |
| Author(s) : Fang J , Yang R , Gao L , Zhou D , Yang S , Liu AL , Du GH |
| Ref : J Chem Inf Model , 53 :3009 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Fang_2013_J.Chem.Inf.Model_53_3009 |
| ESTHER : Fang_2013_J.Chem.Inf.Model_53_3009 |
| PubMedSearch : Fang_2013_J.Chem.Inf.Model_53_3009 |
| PubMedID: 24144102 |