DEPQ
fluorescent leaving group is 7HMC (7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin)
General
Type : Organophosphate,Quinoline
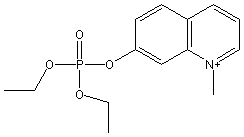
Chemical_Nomenclature : diethyl (1-methylquinolin-1-ium-7-yl) phosphate
Canonical SMILES : CCOP(=O)(OCC)OC1=CC2=C(C=CC=[N+]2C)C=C1
InChI : InChI=1S\/C14H19NO4P\/c1-4-17-20(16,18-5-2)19-13-9-8-12-7-6-10-15(3)14(12)11-13\/h6-11H,4-5H2,1-3H3\/q+1
InChIKey : CVKRJKJYOIKAHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 7-[(diethoxyphosphoryl)oxy]-1-methylquinolinium iodide
MW : 296.28
Formula : C14H19NO4P+
CAS_number :
PubChem : 10402289
UniChem : CVKRJKJYOIKAHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (2)
| Title : Role of edrophonium in prevention of the re-inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by phosphorylated oxime - Luo_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_129 |
| Author(s) : Luo C , Saxena A , Ashani Y , Leader H , Radic Z , Taylor P , Doctor BP |
| Ref : Chemico-Biological Interactions , 119-120 :129 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Luo_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_129 |
| ESTHER : Luo_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_129 |
| PubMedSearch : Luo_1999_Chem.Biol.Interact_119-120_129 |
| PubMedID: 10421446 |
| Title : Organophosphorylation of acetylcholinesterase in the presence of peripheral site ligands. Distinct effects of propidium and fasciculin - Mallender_1999_J.Biol.Chem_274_8491 |
| Author(s) : Mallender WD , Szegletes T , Rosenberry TL |
| Ref : Journal of Biological Chemistry , 274 :8491 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Mallender_1999_J.Biol.Chem_274_8491 |
| ESTHER : Mallender_1999_J.Biol.Chem_274_8491 |
| PubMedSearch : Mallender_1999_J.Biol.Chem_274_8491 |
| PubMedID: 10085081 |