Cruformate
General
Type : Insecticide,Organophosphate,tert-Butyl
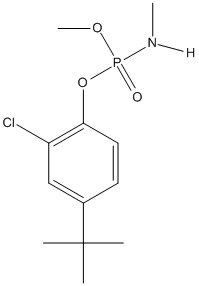
Chemical_Nomenclature : N-[(4-tert-butyl-2-chlorophenoxy)-methoxyphosphoryl]methanamine
Canonical SMILES : CC(C)(C)C1=CC(=C(C=C1)OP(=O)(NC)OC)Cl
InChI : InChI=1S\/C12H19ClNO3P\/c1-12(2,3)9-6-7-11(10(13)8-9)17-18(15,14-4)16-5\/h6-8H,1-5H3,(H,14,15)
InChIKey : BOFHKBLZOYVHSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 4-tert-butyl-2-chlorophenyl methyl methylphosphoramidate,2-chloro-4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl methyl methylphosphoramidate,Butyl-2-chlorophenyl methyl methylphosphoramidate,Chloro-4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl methyl ester methylphosphoramidic acid,Phosphoramidic acid, methyl-, 4-tert-butyl-2-chlorophenyl methyl ester,Ruelene,Amidofos,Amidophos,Montrel,Rulene,Ruelene drench,Dowco 132
MW : 291.71
Formula : C12H19ClNO3P
CAS_number : 299-86-5
PubChem : 9300
UniChem : BOFHKBLZOYVHSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (9)
| Title : Systemic activity of coumaphos, famphur, crufomate, ronnel, and phosmet given orally to hens for control of the northern fowl mite, Ornitbonyssus sulviarum (Canestrini and Fanzago) - DeVaney_1980_Poult.Sci_59_1208 |
| Author(s) : DeVaney JA , Ivie GW |
| Ref : Poult Sci , 59 :1208 , 1980 |
| Abstract : DeVaney_1980_Poult.Sci_59_1208 |
| ESTHER : DeVaney_1980_Poult.Sci_59_1208 |
| PubMedSearch : DeVaney_1980_Poult.Sci_59_1208 |
| PubMedID: 6157151 |
| Title : Economic value and course of infection after treatment of cattle having a low level of nematode parasitism - Leland_1980_Am.J.Vet.Res_41_623 |
| Author(s) : Leland SE, Jr. , Davis GV , Caley HK , Arnett DW , Ridley RK |
| Ref : American Journal of Veterinary Research , 41 :623 , 1980 |
| Abstract : Leland_1980_Am.J.Vet.Res_41_623 |
| ESTHER : Leland_1980_Am.J.Vet.Res_41_623 |
| PubMedSearch : Leland_1980_Am.J.Vet.Res_41_623 |
| PubMedID: 6447467 |
| Title : Isolation and concentration of organophosphorus pesticides from drinking water at the ng\/L level, using macroreticular resin - LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| Author(s) : LeBel GL , Williams DT , Griffith G , Benoit FM |
| Ref : J Assoc Off Analytical Chemistry , 62 :241 , 1979 |
| Abstract : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| ESTHER : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| PubMedSearch : LeBel_1979_J.Assoc.Off.Anal.Chem_62_241 |
| PubMedID: 447594 |
| Title : Teratogenicity to 35-day fetuses, excretion patterns and placental transfer in beef heifers administered 4-tert-butyl-2-chlorophenyl methyl methyl-phosphoramidate (Ruelene) - |
| Author(s) : Rumsey TS , Samuelson G , Bond J , Daniels FL |
| Ref : J Anim Sci , 39 :386 , 1974 |
| PubMedID: 4858630 |
| Title : GLC determination of crufomate (Ruelene) in bovine blood and the use of UV irradiation as a conformatory test - Greenhalgh_1972_Bull.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_7_237 |
| Author(s) : Greenhalgh R , Dokladalova J , Haufe WO |
| Ref : Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology , 7 :237 , 1972 |
| Abstract : Greenhalgh_1972_Bull.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_7_237 |
| ESTHER : Greenhalgh_1972_Bull.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_7_237 |
| PubMedSearch : Greenhalgh_1972_Bull.Environ.Contam.Toxicol_7_237 |
| PubMedID: 4669489 |
| Title : Some effects of orally administered ruelene on host sheep and two ectoparasites: the yellow-fever mosquito and the rocky mountain wood tick - Smith_1968_J.Econ.Entomol_61_292 |
| Author(s) : Smith HG, Jr. , Goulding RL |
| Ref : J Econ Entomol , 61 :292 , 1968 |
| Abstract : Smith_1968_J.Econ.Entomol_61_292 |
| ESTHER : Smith_1968_J.Econ.Entomol_61_292 |
| PubMedSearch : Smith_1968_J.Econ.Entomol_61_292 |
| PubMedID: 5636843 |
| Title : Toxicology of 4-tert-butyl-2-chlorophenyl methyl methylphosphoramidate (Ruelene) in laboratory animals - |
| Author(s) : McCollister DD , Olson KJ , Rowe VK , Paynter OE , Weir RJ , Dieterick WH |
| Ref : Food Cosmet Toxicol , 6 :185 , 1968 |
| PubMedID: 5671150 |
| Title : [Ruelene--an effective agent in controlling subcutaneous gadfly] - |
| Author(s) : Metelitsa VK , Nepoklonov AA |
| Ref : Veterinariia , 43 :47 , 1966 |
| PubMedID: 6012098 |