Betulinic-acid
Betulinic Acid is a pentacyclic lupane-type triterpene derivative of betulin (isolated from the bark of Betula alba, the common white birch) with antiinflammatory, anti-HIV and antineoplastic activities. Betulinic acid (BA) inhibitor of CES1 (IC50, 15 nM) high selectivity over CES2 (> 2400-fold). Epibetulinic acid CID 485711 QGJZLNKBHJESQX-ULZDWRHHSA-N 38736-77-5. || Epibetulinic acid inhibition of human-CES1 IC50 0.041+/-0.006 microM; Ki 0.059 microM mixed (DME D-luciferin-methyl-ester) substrate. Betulinic acid inhibition of human-CES1 IC50 0.048+/-0.005 microM; Ki 0.066 microM mixed (DME D-luciferin-methyl-ester) substrate
General
Type : Natural,Terpenoid
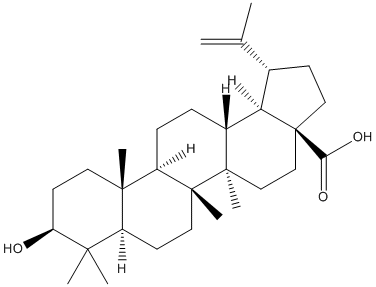
Chemical_Nomenclature : (1R,3aS,5aR,5bR,7aR,9S,11aR,11bR,13aR,13bR)-9-hydroxy-5a,5b,8,8,11a-pentamethyl-1-prop-1-en-2-yl-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,7a,9,10,11,11b,12,13,13a,13b-hexadecahydrocyclopenta[a]chrysene-3a-carboxylic acid
Canonical SMILES : CC(=C)C1CCC2(C1C3CCC4C5(CCC(C(C5CCC4(C3(CC2)C)C)(C)C)O)C)C(=O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C30H48O3\/c1-18(2)19-10-15-30(25(32)33)17-16-28(6)20(24(19)30)8-9-22-27(5)13-12-23(31)26(3,4)21(27)11-14-29(22,28)7\/h19-24,31H,1,8-17H2,2-7H3,(H,32,33)\/t19-,20+,21-,22+,23-,24+,27-,28+,29+,30-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : QGJZLNKBHJESQX-FZFNOLFKSA-N
Other name(s) : betulinic acid,Betulic acid,Mairin,Lupatic Acid,NSC 113090,CCRIS 6748,3-Hydroxylup-20(29)-en-28-oic acid,UNII-4G6A18707N,3beta-Hydroxy-20(29)-lupaene-28-oic acid,EINECS 207-448-8,NSC677578,NSC 677578,CHEBI:3087,CHEMBL269277,Epibetulinic acid
MW : 456.71
Formula : C30H48O3
CAS_number : 472-15-1
PubChem : 64971
UniChem : QGJZLNKBHJESQX-FZFNOLFKSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Betulinic_acid
Target
Families : Betulinic-acid ligand of proteins in family: Carb_B_Chordata || ABHD12-PHARC
Stucture :
Protein : human-CES1 || human-ABHD12
References (3)
| Title : Pentacyclic triterpenoid acids in Styrax as potent and highly specific inhibitors against human carboxylesterase 1A - Wang_2020_Food.Funct_11_8680 |
| Author(s) : Wang L , Guan XQ , He RJ , Qin WW , Xiong Y , Zhang F , Song YQ , Huo PC , Song PF , Tang H , Ge GB |
| Ref : Food Funct , 11 :8680 , 2020 |
| Abstract : Wang_2020_Food.Funct_11_8680 |
| ESTHER : Wang_2020_Food.Funct_11_8680 |
| PubMedSearch : Wang_2020_Food.Funct_11_8680 |
| PubMedID: 32940318 |
| Title : Discovery of natural pentacyclic triterpenoids as potent and selective inhibitors against human carboxylesterase 1 - Song_2019_Fitoterapia_137_104199 |
| Author(s) : Song PF , Zhu YD , Ma HY , Wang YN , Wang DD , Zou LW , Ge GB , Yang L |
| Ref : Fitoterapia , 137 :104199 , 2019 |
| Abstract : Song_2019_Fitoterapia_137_104199 |
| ESTHER : Song_2019_Fitoterapia_137_104199 |
| PubMedSearch : Song_2019_Fitoterapia_137_104199 |
| PubMedID: 31175950 |
| Title : Discovery of Triterpenoids as Reversible Inhibitors of alpha\/beta-hydrolase Domain Containing 12 (ABHD12) - Parkkari_2014_PLoS.One_9_e98286 |
| Author(s) : Parkkari T , Haavikko R , Laitinen T , Navia-Paldanius D , Rytilahti R , Vaara M , Lehtonen M , Alakurtti S , Yli-Kauhaluoma J , Nevalainen T , Savinainen JR , Laitinen JT |
| Ref : PLoS ONE , 9 :e98286 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Parkkari_2014_PLoS.One_9_e98286 |
| ESTHER : Parkkari_2014_PLoS.One_9_e98286 |
| PubMedSearch : Parkkari_2014_PLoS.One_9_e98286 |
| PubMedID: 24879289 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: human-ABHD12 |