Ass-IN-10
eqBuChE (IC50 = 2.92 microM), hBuChE (IC50 = 5.74 microM), hBACE1 (IC50 = 41.60 microM), Abeta aggregation (IC50 = 3.09 microM) and tau aggregation (53.8% at 10 microM)
General
Type : Multitarget,BACE1-inhibitor,anti-Abeta-aggregation,anti-tau-aggregation,Alkyl linked bis-ligand,tert-Butyl
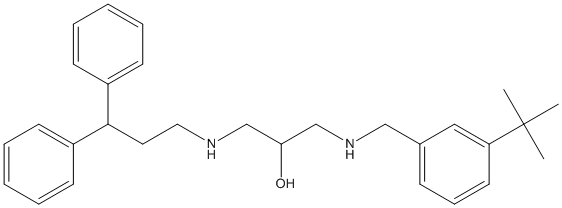
Chemical_Nomenclature : 1-[(3-tert-butylphenyl)methylamino]-3-(3,3-diphenylpropylamino)propan-2-ol
Canonical SMILES : CC(C)(C)C1=CC=CC(=C1)CNCC(CNCCC(C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C29H38N2O\/c1-29(2,3)26-16-10-11-23(19-26)20-31-22-27(32)21-30-18-17-28(24-12-6-4-7-13-24)25-14-8-5-9-15-25\/h4-16,19,27-28,30-32H,17-18,20-22H2,1-3H3
InChIKey : QEVPSMYJQDNACG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : 1-((3-(tert-Butyl)benzyl)amino)-3-((3,3-diphenylpropyl)amino)propan-2-ol
MW : 430.6
Formula : C29H38N2O
CAS_number : 2205015-77-4
PubChem : 154701599
UniChem : QEVPSMYJQDNACG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (1)
| Title : Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 1-Benzylamino-2-hydroxyalkyl Derivatives as New Potential Disease-Modifying Multifunctional Anti-Alzheimer's Agents - Panek_2018_ACS.Chem.Neurosci_9_1074 |
| Author(s) : Panek D , Wieckowska A , Jonczyk J , Godyn J , Bajda M , Wichur T , Pasieka A , Knez D , Pislar A , Korabecny J , Soukup O , Sepsova V , Sabate R , Kos J , Gobec S , Malawska B |
| Ref : ACS Chem Neurosci , 9 :1074 , 2018 |
| Abstract : Panek_2018_ACS.Chem.Neurosci_9_1074 |
| ESTHER : Panek_2018_ACS.Chem.Neurosci_9_1074 |
| PubMedSearch : Panek_2018_ACS.Chem.Neurosci_9_1074 |
| PubMedID: 29345897 |