ArisugacinB
Mycotoxin purified from culture of fungus Penicillium sp. FO-4259 growing on rice, related to Territeme B
General
Type : Natural,Meroterpenoid
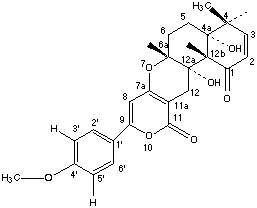
Chemical_Nomenclature : (4aR,6aR,12aS,12bS)-9-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-4a,12a-dihydroxy-4,4,6a,12b-tetramethyl-4a,6,6a,12,12a,12b-hexahydro-4H,11H-benzo[f]pyrano[4,3-b]chromene-1,11(5H)-dione
Canonical SMILES : CC1(C=CC(=O)C2(C1(CCC3(C2(CC4=C(O3)C=C(OC4=O)C5=CC=C(C=C5)OC)O)C)O)C)C
InChI : InChI=1S\/C27H30O7\/c1-23(2)11-10-21(28)25(4)26(23,30)13-12-24(3)27(25,31)15-18-20(34-24)14-19(33-22(18)29)16-6-8-17(32-5)9-7-16\/h6-11,14,30-31H,12-13,15H2,1-5H3\/t24-,25+,26-,27-\/m1\/s1
InChIKey : FNHNBWWIASUEQH-HVWQDESWSA-N
Other name(s) : CHEMBL278342,CHEBI:65436,Arisugacin B,BDBM50089621,(4aR,6aR,12aS,12bS)-4a,12a-dihydroxy-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4,4,6a,12b-tetramethyl-4a,6,6a,12,12a,12b-hexahydro-4H,11H-benzo[f]pyrano[4,3-b]chromene-1,11(5H)-dione,4a,12a-Dihydroxy-9-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-4,4,6a,12b-tetramethyl-4a,6,6a,12,12a,12b-hexahydro-4H,5H-7,10-dioxa-benzo[a]anthracene-1,11-dione
MW : 466.52
Formula : C27H30O7
CAS_number :
PubChem : 10050190
UniChem : FNHNBWWIASUEQH-HVWQDESWSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
References (5)
| Title : Synthesis of dihydroxanthone derivatives and evaluation of their inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase: unique structural analogs of tacrine based on the BCD-ring of arisugacin - Degen_1999_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_9_973 |
| Author(s) : Degen SJ , Mueller KL , Shen HC , Mulder JA , Golding GM , Wei LL , Zificsak CA , Neeno-Eckwall A , Hsung RP |
| Ref : Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Lett , 9 :973 , 1999 |
| Abstract : Degen_1999_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_9_973 |
| ESTHER : Degen_1999_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_9_973 |
| PubMedSearch : Degen_1999_Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett_9_973 |
| PubMedID: 10230623 |
| Title : Arisugacins, selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors of microbial origin - Otoguro_1997_Pharmacol.Ther_76_45 |
| Author(s) : Otoguro K , Kuno F , Omura S |
| Ref : Pharmacol Ther , 76 :45 , 1997 |
| Abstract : Otoguro_1997_Pharmacol.Ther_76_45 |
| ESTHER : Otoguro_1997_Pharmacol.Ther_76_45 |
| PubMedSearch : Otoguro_1997_Pharmacol.Ther_76_45 |
| PubMedID: 9535168 |
| Title : Arisugacins A and B, novel and selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Penicillium sp. FO-4259. I. Screening, taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological activity - Kuno_1996_J.Antibiotics_49_742 |
| Author(s) : Kuno F , Otoguro K , Shiomi K , Iwai Y , Omura S |
| Ref : Journal of Antibiotics , 49 :742 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Kuno_1996_J.Antibiotics_49_742 |
| ESTHER : Kuno_1996_J.Antibiotics_49_742 |
| PubMedSearch : Kuno_1996_J.Antibiotics_49_742 |
| PubMedID: 882350 |
| Title : Arisugacins A and B, novel and selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Penicillium sp. FO-4259. II. Structure elucidation - Kuno_1996_J.Antibiotics_49_748 |
| Author(s) : Kuno F , Shiomi K , Otoguro K , Sunazuka T , Omura S |
| Ref : Journal of Antibiotics , 49 :748 , 1996 |
| Abstract : Kuno_1996_J.Antibiotics_49_748 |
| ESTHER : Kuno_1996_J.Antibiotics_49_748 |
| PubMedSearch : Kuno_1996_J.Antibiotics_49_748 |
| PubMedID: 8823505 |