5-hydroxy-tryptamine
Serotonin. Not really related to cholinesterase but acts on AAA activity of cholinesterases. (see results of Balasubramanian and Layer 's groups).Biochemical messenger and regulator, synthesized from the essential amino acid L-tryptophan. In humans it is found primarily in the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and blood platelets. Serotonin mediates several important physiological functions including neurotransmission, gastrointestinal motility, hemostasis, and cardiovascular integrity. Multiple receptor families explain the broad physiological actions and distribution of this biochemical mediator
General
Type : Derivative of Tryptamine,Indole,Not A\/B H target,Natural,5-HT-receptor-ligand
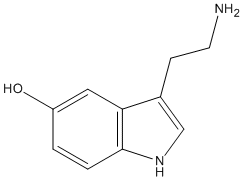
Chemical_Nomenclature : 3-(2-aminoethyl) indol-5-ol
Canonical SMILES : C1=CC2=C(C=C1O)C(=CN2)CCN
InChI : InChI=1S\/C10H12N2O\/c11-4-3-7-6-12-10-2-1-8(13)5-9(7)10\/h1-2,5-6,12-13H,3-4,11H2
InChIKey : QZAYGJVTTNCVMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Serotonin,Enteramine,Thrombocytin,Thrombotonin,Hippophain,Serotonine,Antemoqua,Antemovis,5-HT
MW : 176.2
Formula : C10H12N2O
CAS_number : 50-67-9
PubChem : 5202
UniChem : QZAYGJVTTNCVMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Serotonin
Target
References (5)
| Title : Cholinesterases exhibiting aryl acylamidase activity in human amniotic fluid - Jayanthi_1992_Clin.Chim.Acta_205_157 |
| Author(s) : Jayanthi LD , Balasubramanian N , Balasubramanian AS |
| Ref : Clinica Chimica Acta , 205 :157 , 1992 |
| Abstract : Jayanthi_1992_Clin.Chim.Acta_205_157 |
| ESTHER : Jayanthi_1992_Clin.Chim.Acta_205_157 |
| PubMedSearch : Jayanthi_1992_Clin.Chim.Acta_205_157 |
| PubMedID: 1349516 |
| Title : Inhibition of erythrocyte and plasma cholinesterase by 5-hydroxytryptamine - Osman_1982_Arzneimittelforschung_32_1120 |
| Author(s) : Osman MY , Mahfouz MM , El-Habet AE , El-Sherbini H |
| Ref : Arzneimittelforschung , 32 :1120 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Osman_1982_Arzneimittelforschung_32_1120 |
| ESTHER : Osman_1982_Arzneimittelforschung_32_1120 |
| PubMedSearch : Osman_1982_Arzneimittelforschung_32_1120 |
| PubMedID: 6890835 |
| Title : Serotonin-sensitive aryl acylamidase activity of platelet acetylcholinesterase - Majumdar_1982_Biochem.Pharmacol_31_2319 |
| Author(s) : Majumdar R , George ST , Balasubramanian AS |
| Ref : Biochemical Pharmacology , 31 :2319 , 1982 |
| Abstract : Majumdar_1982_Biochem.Pharmacol_31_2319 |
| ESTHER : Majumdar_1982_Biochem.Pharmacol_31_2319 |
| PubMedSearch : Majumdar_1982_Biochem.Pharmacol_31_2319 |
| PubMedID: 7126246 |
| Title : The identity of the serotonin-sensitive aryl acylamidase with acetylcholinesterase from human erythrocytes, sheep basal ganglia and electric eel - George_1980_Eur.J.Biochem_111_511 |
| Author(s) : George ST , Balasubramanian AS |
| Ref : European Journal of Biochemistry , 111 :511 , 1980 |
| Abstract : George_1980_Eur.J.Biochem_111_511 |
| ESTHER : George_1980_Eur.J.Biochem_111_511 |
| PubMedSearch : George_1980_Eur.J.Biochem_111_511 |
| PubMedID: 7460914 |
| Title : Aryl acylamidase of monkey brain and liver: response to inhibitors and relationship to acetylcholinesterase - |
| Author(s) : Oommen A , Balasubramanian AS |
| Ref : Biochemical Pharmacology , 27 :891 , 1978 |
| PubMedID: 418784 |